1 . “Assume you are wrong.” The advice came from Brian Nosek, a psychology professor, who was offering a strategy for pursuing better science.
To understand the context for Nosek’s advice, we need to take a step back to the nature of science itself. You see despite what many of us learned in elementary school, there is no single scientific method. Just as scientific theories become elaborated and change, so do scientific methods.
But methodological reform hasn’t come without some fretting and friction. Nasty things have been said by and about methodological reformers. Few people like having the value of their life’s work called into question. On the other side, few people are good at voicing criticisms in kind and constructive ways. So, part of the challenge is figuring out how to bake critical self-reflection into the culture of science itself, so it unfolds as a welcome and integrated part of the process, and not an embarrassing sideshow.
What Nosek recommended was a strategy for changing the way we offer and respond to critique. Assuming you are right might be a motivating force, sustaining the enormous effort that conducting scientific work requires. But it also makes it easy to interpret criticisms as personal attacks. Beginning, instead, from the assumption you are wrong, a criticism is easier to interpret as a constructive suggestion for how to be less wrong — a goal that your critic presumably shares.
One worry about this approach is that it could be demoralizing for scientists. Striving to be less wrong might be a less effective motivation than the promise of being right. Another concern is that a strategy that works well within science could backfire when it comes to communicating science with the public. Without an appreciation for how science works, it’s easy to take uncertainty or disagreements as marks against science, when in fact they reflect some of the very features of science that make it our best approach to reaching reliable conclusions about the world. Science is reliable because it responds to evidence: as the quantity and quality of our evidence improves, our theories can and should change, too.
Despite these worries, I like Nosek’s suggestion because it builds in cognitive humility along with a sense that we can do better. It also builds in a sense of community — we’re all in the same boat when it comes to falling short of getting things right.
Unfortunately, this still leaves us with an untested hypothesis (假说): that assuming one is wrong can change community norms for the better, and ultimately support better science and even, perhaps, better decisions in life. I don’t know if that’s true. In fact, I should probably assume that it’s wrong. But with the benefit of the scientific community and our best methodological tools, I hope we can get it less wrong, together.
1. What can we learn from Paragraph 3?| A.Reformers tend to devalue researchers’ work. |
| B.Scientists are unwilling to express kind criticisms. |
| C.People hold wrong assumptions about the culture of science. |
| D.The scientific community should practice critical self-reflection. |
| A.the enormous efforts of scientists at work | B.the reliability of potential research results |
| C.the public’s passion for scientific findings | D.the improvement in the quality of evidence |
| A.discouraging | B.ineffective | C.unfair | D.misleading |
| A.doubtful but sincere | B.disapproving but soft |
| C.authoritative and direct | D.reflective and humorous |
2 . Art Builds Understanding
Despite the long history of scholarship on experiences of art, researchers have yet to capture and understand the most meaningful aspects of such experiences, including the thoughts and insights we gain when we visit a museum, the sense of encounter after seeing a meaningful work of art, or the changed thinking after experiences with art. These powerful encounters can be inspiring, uplifting, and contribute to well-being and flourishing.
According to the mirror model of art developed by Pablo P. L. Tinio, aesthetic reception corresponds to artistic creation in a mirror-reversed fashion. Artists aim to express ideas and messages about the human condition or the world at large.
In addition, art making and art viewing are connected by creative thinking. Research in a lab at Yale University shows that an educational program that uses art appreciation activities builds creative thinking skills. It showed that the more time visitors spent engaging with art and the more they reflected on it, the greater the correspondence with the artists’ intentions and ideas.
Correspondence in feeling and thinking suggests a transfer — between creator and viewer — of ideas, concepts, and emotions contained in the works of art. Art has the potential to communicate across space and time.
| A.The viewers gain a new perspective on the story. |
| B.The theory of aesthetic cognitivism describes the value of art. |
| C.This helps to create connections and insights that otherwise would not happen. |
| D.To do so, they explore key ideas and continually expand them as they develop their work. |
| E.After spending more time with the work, the viewer begins to access the ideas of the artist. |
| F.For example, in one activity, people are asked to view a work of art from different perspectives. |
| G.Participants were more original in their thinking when compared to those who did not take part in the program. |
3 . Debate about artificial intelligence (AI) tends to focus on its potential dangers: algorithmic bias (算法偏见) and discrimination, the mass destruction of jobs and even, some say, the extinction of humanity. However, others are focusing on the potential rewards. Luminaries in the field such as Demis Hassabis and Yann LeCun believe that AI can turbocharge scientific progress and lead to a golden age of discovery. Could they be right?
Such claims are worth examining, and may provide a useful counterbalance to fears about large-scale unemployment and killer robots. Many previous technologies have, of course, been falsely hailed as panaceas (万灵药). But the mechanism by which AI will supposedly solve the world’s problems has a stronger historical basis.
In the 17th century microscopes and telescopes opened up new vistas of discovery and encouraged researchers to favor their own observations over the received wisdom of antiquity (古代), while the introduction of scientific journals gave them new ways to share and publicize their findings. Then, starting in the late 19th century, the establishment of research laboratories, which brought together ideas, people and materials on an industrial scale, gave rise to further innovations. From the mid-20th century, computers in turn enabled new forms of science based on simulation and modelling.
All this is to be welcomed. But the journal and the laboratory went further still: they altered scientific practice itself and unlocked more powerful means of making discoveries, by allowing people and ideas to mingle in new ways and on a larger scale. AI, too, has the potential to set off such a transformation.
Two areas in particular look promising. The first is “literature-based discovery” (LBD), which involves analyzing existing scientific literature, using ChatGPT-style language analysis, to look for new hypotheses, connections or ideas that humans may have missed. The second area is “robot scientists”. These are robotic systems that use AI to form new hypotheses, based on analysis of existing data and literature, and then test those hypotheses by performing hundreds or thousands of experiments, in fields including systems biology and materials science. Unlike human scientists, robots are less attached to previous results, less driven by bias—and, crucially, easy to replicate. They could scale up experimental research, develop unexpected theories and explore avenues that human investigators might not have considered.
The idea is therefore feasible. But the main barrier is sociological: it can happen only if human scientists are willing and able to use such tools. Governments could help by pressing for greater use of common standards to allow AI systems to exchange and interpret laboratory results and other data. They could also fun d more research into the integration of AI smarts with laboratory robotics, and into forms of AI beyond those being pursued in the private sector. Less fashionable forms of AI, such as model-based machine learning, may be better suited to scientific tasks such as forming hypotheses.
1. Regarding Demis and Yann’s viewpoint, the author is likely to be ______.| A.supportive | B.puzzled | C.unconcerned | D.doubtful |
| A.LBD focuses on testing the reliability of ever-made hypotheses. |
| B.Resistance to AI prevents the transformation of scientific practice. |
| C.Robot scientists form hypotheses without considering previous studies. |
| D.Both journals and labs need adjustments in promoting scientific findings. |
| A.Official standards have facilitated the exchange of data. |
| B.Performing scientific tasks relies on government funding. |
| C.Less popular AI forms might be worth paying attention to. |
| D.The application of AI in public sector hasn’t been launched. |
| A.Transforming Science. How Can AI Help? |
| B.Making Breakthroughs. What Is AI’s Strength? |
| C.Reshaping History. How May AI Develop Further? |
| D.Redefining Discovery. How Can AI Overcome Its Weakness? |
4 . It seems rather obvious that facial characteristics are determined by our genes. But until recently geneticists(遗传学家) had very little understanding of which parts of our DNA were linked to our facial appearance.
An international team of researchers identified more than 130 chromosomal(染色体的) regions associated with specific aspects of facial shape. This is a critical first step toward understanding how genetics impact our faces, Live Science noted.
Researchers scanned the DNA of more than 8,000 people and analyzed dozens of shape measurements from their 3D facial images to look at the statistical relationships between about 7 million genetic markers—known locations in the genetic code where humans vary—and the facial features.
“When we find a statistical relation between a facial feature and one or more genetic markers, it points us to a very precise region of DNA on a chromosome. The genes located around that region then become our prime candidates for facial features like nose or lip shape,” Seth Weinberg, co-author of the study, wrote on Live Science.
Researchers discovered some interesting patterns after looking at the implicated(牵涉其中) genes at these DNA regions. Your nose is the part that is most influenced by your genes. Areas like the cheeks, which are highly influenced by lifestyle factors like diet, showed the fewest genetic associations.
There is also a high degree of overlap(重合) between the genes involved in facial and limb development. This provides an important clue as to why many genetic syndromes(综合症) are characterized by both hand and facial malformations(畸形). Some genes involved in facial shape may be involved in cancer, too. It explains why people treated for pediatric(小儿科的) cancer show some distinctive facial features.
So, can someone take your DNA and construct an accurate image of your face? It’s unlikely. The 130-plus genetic regions that were identified explain less than 10 percent of the variation in facial shape. But even if we understood all of the genes impacting facial appearance, prediction would still be a big challenge. That’s because facial features are affected by other factors as well, such as age, diet, climate and sun exposure.
Still, the knowledge of patients’ genetic information can be an invaluable tool in creating personalized treatment plans in fields like orthodontics(畸齿矫正学) or reconstructive surgery. For example, if someday doctors can use genetics to predict when a child’s jaw will hit its growth peak, it will help them decide the best time to intervene.
1. What’s the main purpose of the research?| A.To explain why humans vary based on statistics. |
| B.To identify the factors impacting facial appearance. |
| C.To discover the link between genes and facial features. |
| D.To study the relationship between facial features and genetic markers. |
| A.The nose is most influenced by genes. |
| B.Facial malformations affect limb development. |
| C.The cheeks are most closely associated with age. |
| D.Facial shape and cancer are impacted by exactly the same genes. |
| A.It could improve orthodontic treatments. |
| B.It could be useful for changing facial shapes. |
| C.It could help recreate one’s jaw at an early age. |
| D.It could help predict facial appearance with ease. |

What may well be the oldest metal coins in the world have been identified at an ancient abandoned city known as Guanzhuang in China. Like many Bronze Age (青铜时代) coins from the region, they were cast in the shape of spades with finely carved handles. These ancient coins existed during an in-between period between barter (以物易物) and money, when coins were a novel concept, but everybody knew that agricultural tools were valuable.
Reading about this incredible discovery, I kept thinking about the way modern people represent computer networks by describing machines as having “addresses”, like a house. We also talk about one computer using a “port” to send information to another computer, as if the data were a floating boat with destination. It’s as if we are in the Bronze Age of information technology, grasping desperately for real-world reference to transform our civilization.
Now consider what happened to spade coins. Over centuries, metalworkers made these coins into more abstract shapes. Some became almost human figures. Others’ handles were reduced to small half-circles. As spade coins grew more abstract, people carved them with number values and the locations where they were made. They became more like modern coins, flat and covered in writing. Looking at one of these later pieces, you would have no idea that they were once intended to look like a spade.
This makes me wonder if we will develop an entirely new set of symbols that allow us to interact with our digital information more smoothly.
Taking spade coins as our guide, we can guess that far-future computer networks will no longer contain any recognizable references to houses. But they still might bring some of the ideas we associate with home to our mind. In fact, computer networks — if they still exist at all — are likely to be almost the indispensable part of our houses and cities, their sensors inset with walls and roads. Our network addresses might actually be the same as our street addresses. If climate change leads to floods, our mobile devices might look more like boats than phones, assisting us to land.
My point is that the metaphors of the information age aren’t random. Mobile devices do offer us comfort after a long day at work. In some sense, our desire to settle on the shores of data lakes could change the way we understand home, as well as how we build computers. So as we cast our minds forward, we have to think about what new abstractions will go along with our information technology. Perhaps the one thing we count on is that humans will still appreciate the comforts of home.
1. Many Bronze Age coins were made into the shape of a spade because ___________.| A.a lot of emphasis was put on agriculture |
| B.this stylish design made the coins valuable |
| C.these coins also served as agricultural tools |
| D.the handles made the coins easily exchanged |
| A.To show they both used to be new concepts when first invented. |
| B.To explain abstract digital worlds are different from concrete coins. |
| C.To suggest computers will experience dramatic changes as coins did. |
| D.To highlight their same importance in our civilizational transformation. |
| A.Flexible. | B.Essential. | C.Wasteful. | D.Alternative. |
| A.What Coins and Computers Bring Us |
| B.How Agriculture Loses to Digital Industry |
| C.How Bronze Age Develops to Information Age |
| D.What Ancient Money Tells Us About the Future |
Some of the world’s most important scientists think the idea of people living on Mars will come true one day. Stephen Hawking believed humans must move into space to survive. “Once we spread out into space and establish independent colonies, our future should be safe.” he said. Robert Zubrin, a rocket scientist, agrees and thinks starting with Mars makes the most sense. He thinks sending people to Mars will allow us to learn a lot — for example, about the ability of humans to live in a very different environment.
However, scientists will need to terraform Mars for people to be able to live. Terraforming means changing the environment on a planet so that it is similar to Earth’s. One of the main goals of terraforming Mars is to warm it up because the average temperature there is about -60℃. One idea for warming Mars is to build factories there that produce greenhouse gases. This could take many centuries. However, it should lead to rainfall and the growth of plants, resulting in more air that people can breathe.
Another big concern for scientists is whether humans can move to Mars and still stay healthy in mind and body. As a test, six people lived in a Mars-like environment in Hawaii for a year before “returning to Earth” recently. It was a 1,200-square-foot room that was on the side of a volcano and used the sun for energy. Christiane Heinicke, one of the people who lived there, said that one of the biggest issues was feeling bored. So humans on Mars would always need to keep themselves busy with various activities.
One particular organisation based in Europe is planning to send the first humans to Mars before 2030. The organisation believes that its project is giving people worldwide the chance to be part of the first human crew ever to live on Mars for good. However, many experts think the project’s cost of USS6 billion is too low for it to be successful. The American space agency NASA believes that sending people to Mars would cost about USS100 billion, although this estimate is based on bringing them back to Earth, too. Regardless, it seems that humans living on Mars may well happen a lot sooner than most people believe.
1. What can we learn if we send humans to Mars according to Robert Zubrin?2. What does “terraforming” mean?
3. Please decide which part is false in the following statement, then underline it and explain why.
According to the test, in order to stay healthy in mind and body on Mars, it is necessary for humans on Mars to stay away from various activities.
4. What should we do now before humans can live on Mars? (In about 40 words)
7 . If you’ re reaching for the last piece of pizza at a party, and meanwhile see another hand going for it, your next move probably depends on how you feel and whom the hand belongs to. Your little sister — you might just grab the pizza. Your boss — you probably will give up. But if you’re hungry and feeling particularly confident, you might go for it.
Now researchers have made progress in understanding how mammals’ brain encodes social rank and uses this information to shape behaviours — such as whether to fight for that last pizza slice. They discovered that an area of the brain called the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) was responsible for representing social rank in mammals; changes to a mouse’s mPFC affect its dominance (支配) behaviour. But it was unknown how the mPFC represented this information and which neurons (神经元) were involved in changing dominance behaviour.
In the new study, Professor Kay Tye let groups of four mice share a cage, allowing a social hierarchy (等级) to naturally develop — some mice became more dominant and others more subordinate. As soon as the mice were paired up, he discovered, the activity of their mPFC neurons could predict — with 90 percent certainty — the rank of their opponent.
“We expected animals might only signal rank when they are in a competition,” says co-researcher Nancy. “But it turns out animals walk around with this representation of social rank all the time.”
When the researchers next asked whether the activity of the mPFC neurons was associated with behaviour, they found something surprising. The brain activity patterns were linked with slight changes in behaviour, such as how fast a mouse moved, and they also could predict — a full 30 seconds before the competition started — which mouse would win the food reward.
The winner was not always the more dominant, but the one engaged in a “winning mindset”. Just as you might sometimes be in a more competitive mood and be more likely to snatch that pizza slice before your boss, a subordinate mouse might be in a more “winning mindset” than a more dominant mouse and end up winning.
The areas of the mPFC associated with social rank and “winning mindset” are next to one another and highly connected. Signals on social rank impact the state of the brain involved in “winning mindset”. In other words, a subordinate mouse’s confidence and “winning mindset” may partially decrease when faced with a dominant one.
“This is further evidence to suggest that we are in different brain states when we are with others compared to when we’re alone,” says Tye. “Regardless of who you’re with, if you’re aware of other people around you, your brain is using different neurons.”
1. The author writes Paragraph 1 in order to ________.| A.tell an interesting story | B.present a typical example |
| C.introduce a major topic | D.provide a convincing proof |
| A.The mPFC neurons. | B.The researchers. |
| C.The brain activity patterns. | D.The changes in behaviour. |
| A.mPFC neurons change dominance behaviour. |
| B.Brain activities can influence social hierarchy. |
| C.Dominant opponents boost “winning mindset”. |
| D.Social rank and “winning mindset” affect behaviour. |
| A.Those eager to win may succeed. | B.When alone, we are more confident. |
| C.Social rank guides competitive behaviour. | D.“Winning mindset” establishes dominance. |
8 . Both misinformation, which includes honest mistakes, and disinformation, which involves an intention to mislead, have had a growing impact on teenage students over the past 20 years. One tool that schools can use to deal with this problem is called media literacy education. The idea is to teach teenage students how to evaluate and think critically about the messages they receive. Yet there is profound disagreement about what to teach.
Some approaches teach students to distinguish the quality of the information in part by learning how responsible journalism works. Yet some scholars argue that these methods overstate journalism and do little to cultivate critical thinking skills. Other approaches teach students methods for evaluating the credibility of news and information sources, in part by determining the incentive of those sources. They teach students to ask: What encouraged them to create it and why? But even if these approaches teach students specific skills well, some experts argue that determining credibility of the news is just the first step. Once students figure out if it’s true or false, what is the other assessment and the other analysis they need to do?
Worse still, some approaches to media literacy education not only don’t work but might actually backfire by increasing students’ skepticism about the way the media work. Students may begin to read all kinds of immoral motives into everything. It is good to educate students to challenge their assumptions, but it’s very easy for students to go from healthy critical thinking to unhealthy skepticism and the idea that everyone is lying all the time.
To avoid these potential problems, broad approaches that help students develop mindsets in which they become comfortable with uncertainty are in need. According to educational psychologist William Perry of Harvard University, students go through various stages of learning. First, children are black-and-white thinkers—they think there are right answers and wrong answers. Then they develop into relativists, realizing that knowledge can be contextual. This stage is the one where people can come to believe there is no truth. With media literacy education, the aim is to get students to the next level—that place where they can start to see and appreciate the fact that the world is messy, and that’s okay. They have these fundamental approaches to gathering knowledge that they can accept, but they still value uncertainty.
Schools still have a long way to go before they get there, though. Many more studies will be needed for researchers to reach a comprehensive understanding of what works and what doesn’t over the long term. “Education scholars need to take an ambitious step forward,” says Howard Schneider, director of the Center for News Literacy at Stony Brook University.
1. As for media literacy education, what is the author’s major concern?| A.How to achieve its goal. | B.How to measure its progress. |
| C.How to avoid its side effects. | D.How to promote its importance. |
| A.Importance. | B.Variety. | C.Motivation. | D.Benefit. |
| A.compare different types of thinking |
| B.evaluate students’ mind development |
| C.explain a theory of educational psychology |
| D.stress the need to raise students’ thinking levels |
| A.Media Literacy Education: Much Still Remains |
| B.Media Literacy Education: Schools Are to Blame |
| C.Media Literacy Education: A Way to Identify False Information |
| D.Media Literacy Education: A Tool for Testing Critical Thinking |
9 . In 1953, when visiting his daughter’s maths class, the Harvard psychologist B.F. Skinner found every pupil learning the same topic in the same way at the same speed. Later, he built his first “teaching machine”, which let children tackle questions at their own pace. Since then, education technology (edtech) has repeated the cycle of hype and flop (炒作和失败), even as computers have reshaped almost every other part of life.
Softwares to “personalize” learning can help hundreds of millions of children stuck in miserable classes—but only if edtech supporters can resist the temptation to revive harmful ideas about how children learn. Alternatives have so far failed to teach so many children as efficiently as the conventional model of schooling, where classrooms, hierarchical year-groups, standardized curriculums and fixed timetables are still the typical pattern for most of the world’s nearly 1.5 billion schoolchildren. Under this pattern, too many do not reach their potential. That condition remained almost unchanged over the past 15 years, though billions have been spent on IT in schools during that period.
What really matters then? The answer is how edtech is used. One way it can help is through tailor-made instruction. Reformers think edtech can put individual attention within reach of all pupils. The other way edtech can aid learning is by making schools more productive. In California schools, instead of textbooks, pupils have “playlists”, which they use to access online lessons and take tests. The software assesses children’s progress, lightening teachers’ marking load and allowing them to focus on other tasks. A study suggested that children in early adopters of this model score better in tests than their peers at other schools.
Such innovation is welcome. But making the best of edtech means getting several things right. First, “personalized learning” must follow the evidence on how children learn. It must not be an excuse to revive pseudoscientific ideas such as “learning styles”: the theory that each child has a particular way of taking in information. This theory gave rise to government-sponsored schemes like Brain Gym, which claimed that some pupils should stretch or bend while doing sums. A less consequential falsehood is that technology means children do not need to learn facts or learn from a teacher—instead they can just use Google. Some educationalists go further, arguing that facts get in the way of skills such as creativity. Actually, the opposite is true. According to studies, most effective ways of boosting learning nearly all relied on the craft of a teacher.
Second, edtech must narrow, rather than widen, inequalities in education. Here there are grounds for optimism. Some of the pioneering schools are private ones in Silicon Valley. But many more are run by charter-school groups teaching mostly poor pupils, where laggards (成绩落后者) make the most progress relative to their peers in normal classes. A similar pattern can be observed outside America.
Third, the potential for edtech will be realized only if teachers embrace it. They are right to ask for evidence that products work. But skepticism should not turn into irrational opposition. Given what edtech promises today, closed-mindedness has no place in the classroom.
1. According to the passage, education technology can ________.| A.decrease teachers’ working load |
| B.facilitate personalized learning |
| C.help standardize curriculums |
| D.be loved by schoolchildren |
| A.The students who are better at memorization tend to be less creative. |
| B.Schools with bans on phones have better results than high-tech ones. |
| C.Shakespeare was trained in grammar but he penned many great plays. |
| D.Lu Xun’s creativity was unlocked after he gave up studying medicine. |
| A.at the service of teaching |
| B.limited in use among pupils |
| C.aimed at narrowing the wealth gap |
| D.in line with students’ learning styles |
| A.To stress the importance of edtech. |
| B.To introduce the application of edtech. |
| C.To discuss how to get the best out of edtech. |
| D.To appeal for more open-mindedness to edtech. |
10 . A medical capsule robot is a small, often pill-sized device that can do planned movement inside the body after being swallowed or surgically inserted. Most models use wireless electronics or magnets or a combination of the two to control the movement of the capsule. Such devices have been equipped with cameras to allow observation and diagnosis, with sensors that “feel,” and even with mechanical needles that administer drugs.
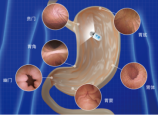
But in practice, Biomechatronics engineer Pietro Valdastri has found that developing capsule models from scratch (从头开始) is costly, time-consuming and requires advanced skills. “The problem was we had to do them from scratch every time,” said Valdastri in an interview. “And other research groups were redeveloping those same modules from scratch, which didn’t make sense.”
Since most of the capsules have the same parts of components: a microprocessor, communication submodules, an energy source, sensors, and actuators (致动器), Valdastri and his team made the modular platform in which the pieces work in concert and can be interchanged with ease. They also developed a flexible board on which the component parts are snapped in like Legos. The board can be folded to fit the body of the capsule, down to about 14 mm. Additionally, they compiled (编译) a library of components that designers could choose from, enabling hundreds of different combinations. They arranged it all in a free online system. Designers can take the available designs or adapt them to their specific needs.
“Instead of redeveloping all the modules from scratch, people with limited technological experience can use our modules to build their own capsule robots in clinical use and focus on their innovation,” Valdastri said.
Now, the team has designed a capsule equipped with a surgical clip to stop internal bleeding. Researchers at Scotland’s Royal Infirmary of Edinburg have also expressed interest in using the system to make a crawling capsule that takes images of the colon(结肠). One research group, led by professors at the Institute of Digestive Disease of the Chinese University of HongKong, is making a swimming capsule equipped with a camera that pushes itself through the stomach.
One limitation of Valdastri’s system is that it’s only for designing models. Researchers can confirm their hypotheses (假设) and do first design using the platform, but will need to move to a custom approach to develop their capsules further and make them practical for clinical use.
1. According to the passage, Valdastri and his team created the platform to ________.| A.adopt the latest technologies |
| B.make their robots dream come true |
| C.help build specialized capsule robots |
| D.do preciser observation and diagnosis |
| A.Perform live. | B.Run independently. |
| C.Act in a cooperative way. | D.Carry on step by step. |
| A.Valdastri’s system can’t provide a complete capsule creation. |
| B.The modular platform is more useful than a custom approach. |
| C.The capsules can move in human’s body automatically. |
| D.It costs more to module the capsules on the board. |



