要求:1.题目自拟;
2.简述图片中的现象;
3.发表自己的看法。

________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
2 . Google’s £ 400m acquisition of the UK artificial intelligence research company DeepMind in 20l4 was testimony to the quality of British scientific research. Furthermore, the insistence of the three UK co-founders that their company would not move to California was seen as evidence of London’s potential to become a successful centre for technology innovation. Four years later, the future of the UK capital’s tech aspirations and of DeepMind’s centre of gravity look a lot less certain.
DeepMind’s announcement last week that it would transfer control of its health unit to a new Google Health division in California has raised questions about data privacy. The health unit has access to the records of 1. 6m patients of Britain’s National Health Service. After four years of relative operating freedom, the company is confronting the hard reality of being owned by Google. For Google, however, which has been patient so far about its return on investment, the time for DeepMind’s work to be commercialised-specifically a patient management App called Streams-appears to have arrived.
The UK Company founded by Demis Hassabis, Shane Legg and Mustafa Suleyman has repeatedly vindicated Google’s assessment of its world class artificial intelligence research. In2016, its AlphaGo programme beat the world’s best player of the fiendishly complex board game “Go” after thousands of practice games. In2017 its progeny, AlphaGo Zero, did it again---without any expert human input.
When algorithms beat humans at their own games it is impressive; when they start beating them at their work it becomes unsettling. This year, another DeepMind algorithm proved better than retinal specialists at London’s Moorfields Eye Hospital at making referrals when tested on patient scans.
This was clear progress. DeepMind’s health work is what is most immediately relevant to Britons since, through a partnership with the Royal Free Hospital, it has access to the data of so many patients. The move to California has understandably raised privacy concerns at a time when big tech companies, including Facebook, are coming under growing scrutiny for the careless way they have exploited private data for commercial gain. Moreover, the transfer appears to contravene promises by DeepMind that “at no stage will patient data ever be linked or associated with Google accounts, products or services”. It is worrying that at the same time DeepMind’s independent review panel-set up to scrutinize its sensitive relationship with the NHS-is also being wound up.
DeepMind, which sees the move as a way of ensuring millions benefit from its work, claims that its contracts with the NHS are sufficient to protect patients’ data, which will remain under the strict control of Britain’s health service. Google has said nothing. There is a clear need for both companies to offer much greater assurances.
Last year, DeepMind set up an ethics and society department, whose independent advisers were selected for their integrity. They had a reputation for asking tough questions which set the company apart in the tech sector. If indeed the founders believed this culture would be unaffected by the gravitational pull of a buyer as powerful as Google, they were naive. WhatsApp and Instagram made the same mistake.
But for the sake of the NHS patients whose data are at issue, it is to be hoped that the same culture and integrity survives in California. The Silicon Valley mantra of “move fast and break things” might work for companies developing software. It has no place governing healthcare and technology.
1. The first paragraph is used to_________.| A.take about the future of DeepMind |
| B.remind readers of the cost of Google’s acquisition of DeepMind |
| C.leading to the problems that DeepMind will face |
| D.highlighting the quality of British scientific research |
| A.DeepMind has no relative operating freedom. |
| B.Google Health division is allowed to retrieve the records of 1. 6m patients. |
| C.Britain’s National Health Service leaks the private data of their patients. |
| D.Some companies have collected private data for commercial gain carelessly. |
| A.Both Google and DeepMind should offer the public much greater assurances. |
| B.WhatsApp and Instagram are likely to leak information of their clients. |
| C.People feel nervous about algorithms employed by high-tech. |
| D.The ethics and society department set up by DeepMind may work. |
| A.Critical | B.Positive |
| C.Negative | D.Ambiguous |
3 . Gone are the days when a mother’s place was in the home: in Britain women with children are now as likely to be in paid work as their unburdened sisters. Many put their little darlings in day care long before they start school. Mindful that a poor start can spoil a person’s chances of success later in life, the state has intervened ever more closely in how babies and toddlers are looked after. Inspectors call not only at nurseries but also at homes where youngsters are minded; three-year-olds follow the national curriculum. Child care has increasingly become a profession.
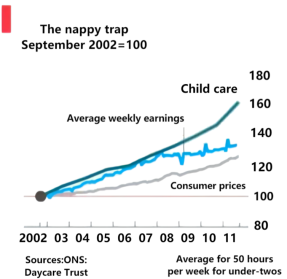
For years after the government first began in 2001 to twist the arms of anyone who looked after an unrelated child to register with the schools, the numbers so doing fell. Kind but clueless neighbours stopped looking after little ones, who were instead herded into formal nurseries or handed over to one of the ever-fewer registered child-minders. The decline in the number of people taking in children now appears to have halted. According to data released by the Office for Standards in Education on October 27th, the number of registered child-minders reached its lowest point in September 2010 and has since recovered slightly.
The new lot are certainly better qualified. In 2010 fully 82% of nursery workers held diplomas notionally equivalent to A-levels, the university-entrance exams taken mostly by 18-year-olds, up from 56% seven years earlier, says Anand Shukla of the Daycare Trust, a charity. Nurseries staffed by university graduates tend to be rated highest by inspectors, increasing their appeal to the pickiest parents. As a result, more graduates are being recruited.
But professionalization has also pushed up the price of child care, defying even the economic depression. A survey by the Daycare Trust finds that a full-time nursery place in England for a child aged under two, who must be intensively supervised, costs £194 ($310) per week, on average. Prices in London and the south-east are far higher. Parents in Britain spend more on child care than anywhere else in the world, according to the OECD, a think-tank. Some 68% of a typical second earner's net income is spent on freeing her to work, compared with an OECD average of 52%.
The price of child care is not only eye-watering, but has also become a barrier to work. Soon after it took power the coalition government pledged to ensure that people are better off in work than on benefits, but a recent survey by Save the Children, a charity, found that the high cost of day care prevented a quarter of low-paid workers from returning to their jobs once they had started a family. The government pays for free part-time nursery places for three-and four-year-olds, and contributes towards day-care costs for younger children from poor areas. Alas, extending such an aid during stressful economic times would appear to be anything but child’s play.
1. Which of the following is true according to the first paragraph?| A.Nursery education plays a leading role in one’s personal growth. |
| B.Pregnant women have to work to lighten families’ economic burden. |
| C.Children in nursery have to take uniform nation courses. |
| D.The supervision of the state makes child care professional. |
| A.the registered child-minders are required to take the university-entrance exams |
| B.the number of registered child-minders has been declining since 2001 |
| C.anyone who looks after children at home must register with the schools |
| D.the growing recognition encourages more graduates to work as child-minders |
| A.prevents mothers from getting employed |
| B.may further depress the national economy |
| C.makes many families live on benefits |
| D.is far more than parents can afford |
| A.Objective. | B.Skeptical. | C.Supportive. | D.Biased. |
| A.The professionalization of child care has pushed up its price. |
| B.The high cost of child nursing makes many mothers give up their jobs. |
| C.The employment of more graduates makes nurseries more popular. |
| D.Parents in Britain pay most for child nursing throughout the world. |
4 . “NON-FUNGIBLE TOKENS” (NFTs) leapt from the more obscure corners of the internet into the mainstream in March 2021 when Christies, a British auction house, sold a digital work of art for $69m. What it actually flogged was an NFT, a cryptocurrency chit that proves a buyer owns an intangible marker connected to a unique piece of digital art, music or other item. Much like René Magritte’s painting of a pipe that proclaims “this is not a pipe” an NFT is not the thing it represents. Tweets, videos of basketball dunks and even the source code to the world wide web have been sold as NFTs in recent months. From June to September they generated almost $11bn in sales, an eight-fold increase on the previous four months, according to DappRadar, a market tracker. What exactly is an NFT? And why are people spending tens of millions of dollars on them?
An NFT is a record on a cryptocurrency’s blockchain (an immutable ledger(不可篡改的账本) that can record more than just virtual coins) that represents pieces of digital media. Invented a few years ago, it can link not only to art but also to text, videos or bits of code. Promoters of NFTs claim that they solve a thorny(棘手的) problem with digital art: how to own an original. For creators who freely upload their work or sell it as identical copies, the concept of an original is difficult to pin down(确定). Exclusivity is impossible to enforce when digital files can be shared freely on the internet. But collectors want the cachet that comes with having an exclusive claim on an artwork. This is where NFTs fit in.
To mint(铸币,造币) an NFT, the creator establishes a unique record of the artwork, generally on a website. Then the creator places the record on a blockchain, usually Ethereum’s, which requires a transaction fee known as gas. Possession of a private encryption key associated with the transaction proves ownership. This gives an artist or collector something to sell. An NFT may link to a version of the work, but rarely includes the rights to reproduce or distribute it. That differentiates it from a commercial licensing arrangement, too.
NFTs have myriad(众多的) problems. They often change hands using cryptocurrencies, many of which currently have sky-high valuations, leading to fears of a bubble. Anyone can mint an NFT, since the systems involved are decentralised(去中心化的), although doing so with someone else’s work could be infringe their copyright. Some artists have already claimed misappropriation of their work.Most NFTs are simply links to images. Unless they have been issued in a certain way to ensure they are tamper-proof(防更改的) these can in theory be meddled with after the sale. The high electricity usage of blockchains—Bitcoin’s is greater than that of Chile—has prompted arguments over whether artists are contributing to climate change by embracing NFTs. And ownership may be difficult to prove in the long term, as web-based records may not last for ever.
Yet NFTs have some value beyond the cryptocurrency hype (加密货币炒作): artists struggle to make a living when their works can be easily replicated and pirated. NFTs will create new problems in an attempt to solve old ones, but for now many creators and collectors are too busy cashing in to care.
1. What can we learn from the first paragraph?| A.What is the core concept of NFTs. | B.Where NFTs can fit in. |
| C.How to make NFTs. | D.What’s the disadvantages of NFTs. |
| A.It seldom change hands using cryptocurrencies. |
| B.The systems involved are centralized. |
| C.The high electricity usage of blockchains possibly contribute to climate change by embracing NFTs. |
| D.It is a record on a cryptocurrency’s blockchain. |
| A.Quote. | B.Analogy. | C.Comparison. | D.Personification |
| A.What is an NFT? |
| B.How to make NFTs? |
| C.NFTs have some value beyond the cryptocurrency hype. |
| D.NFTs have myriad problems. |
5 . As far as we know batteries are playing an important role in our life.We couldn’t live without batteries.Why so? Batteries provide power for anything from small sensors to large systems. While scientists are finding ways to make them smaller but even more powerful, problems can arise when these batteries are much larger and heavier than the devices themselves. University of Missouri(MU) researchers are developing a nuclear energy source that is smaller, lighter and more efficient.
“To provide enough power, we need certain methods with high energy density(密度)”,said Jae Kwon, assistant professor of electrical and computer engineering at MU. “The radioisotope(放射性同位素) battery can provide power density that is much higher than chemical batteries.”
Kwon and his research team have been working on building a small nuclear battery, presently the size and thickness of a penny, intended to power various micro / nanoelectromechanreal systems (M/NEMS). Although nuclear batteries can cause concerns, Kwon said they are safe.
“People hear the word ‘nuclear’ and think of something very dangerous,” he said, “However, nuclear power sources have already been safely powering a variety of devices, such as pace-makers, space satellites and underwater systems.”
His new idea is not only in the battery’s size, but also in its semiconductor(半导体). Kwon’s battery uses a liquid semiconductor rather than a solid semiconductor.
“The key part of using a radioactive battery is that when you harvest the energy, part of the radiation energy can damage the lattice structure(晶体结构) of the solid semiconductor,”Kwon said,“By using a liquid semiconductor, we believe we can minimize that problem.”
Together with J. David Robertson, chemistry professor and associate director of the MU Research Reactor, Kwon is working to build and test the battery. In the future, they hope to increase the battery’s power, shrink its size and try with various other materials. Kwon said that battery could be thinner than the thickness of human hair.
1. According to paragraph 1 and 2,we can learn that________.| A.Batteries can only power small sensors . |
| B.The larger batteries are,the more power they can provide. |
| C.Certain methods with high energy density can provide power abundantly . |
| D.Jae Kwon is a professor of electrical and computer engineering at MU. |
| A.He teaches chemistry at MU. |
| B.He developed a chemical battery. |
| C.He is working on a nuclear energy source. |
| D.He made a breakthrough in computer engineering. |
| A.to show chemical batteries are widely applied. |
| B.to introduce nuclear batteries can be safely used. |
| C.to describe a nuclear-powered system. |
| D.to introduce various energy sources. |
| A.get rid of the radioactive waste |
| B.test the power of nuclear batteries. |
| C.decrease the size of nuclear batteries |
| D.decline the damage to lattice structure. |
| A.uses a solid semiconductor |
| B.will soon replace the present ones. |
| C.could be extremely thin. |
| D.has passed the final test. |
| A.science news report | B.book review |
| C.newspaper advertisement | D.science fiction story |
1.网络对教育的影响(利与弊);
2.你的建议。
注意:
1.写作词数应为80左右;
2.请按如下格式在答题卡的相应位置作答。
| A. cultivate B. reassuring C. opposing D. objective E. confidence F. evidence G. perceived H. functioning I. estimate J. existing K. scientism |
Why Doubt Is Essential To Science
The confidence people place in science is frequently based not on what it really is, but on what people would like it to be. When I asked students at the beginning of the year how they would define science, many of them replied that it is a(n)
But doubt in science is a feature, not a bug. Indeed, science, when properly
As a historian of science, I would argue that it's the responsibility of scientists and historians of science to show that the real power of science lies precisely in what is often
Scientists understand this, but in the
8 . If the
To create the Wigner crystals, Wang’s team built a device
In ordinary materials, electrons zoom around too quickly to be
A mismatch
| A.conditions | B.situations | C.environments | D.circumstances |
| A.item | B.thing | C.material | D.article |
| A.cube | B.solid | C.structure | D.dimension |
| A.occasionally | B.surprisingly | C.indirectly | D.directly |
| A.scientist | B.theorist | C.predictr | D.fantasist |
| A.potently | B.absolutely | C.definitely | D.convincingly |
| A.observing | B.containing | C.watching | D.undertaking |
| A.significantly | B.obviously | C.tiny | D.inconspicuously |
| A.magnetic field | B.force | C.attraction | D.repulsion |
| A.interrelations | B.arrangements | C.requirements | D.pairs |
| A.sphere pattern | B.cylinder pattern | C.honeycomb pattern | D.corn pattern |
| A.heating | B.cooling | C.speeding | D.slowing |
| A.within | B.between | C.among | D.through |
| A.speed up | B.stop | C.settle down | D.calm down |
| A.light | B.voltage | C.energy | D.ion |
9 . Revealing the source of Jupiter’s x-ray auroral flares

Abstract
Jupiter’s rapidly rotating, strong magnetic field provides a natural laboratory that is key to understanding the dynamics (动力学) of high-energy plasmas (等离子体). Spectacular auroral (极光的) X-ray flares (耀斑) are diagnostic of the most energetic processes governing magnetospheres but seemingly unique to Jupiter. Since their discovery 40 years ago, the processes that produce Jupiter’s X-ray flares have remained unknown. Here, we report simultaneous (同时的) in situ satellite and space-based telescope observations that reveal the processes that produce Jupiter’s X-ray flares, showing surprising similarities to terrestrial ion aurora. Planetary-scale electromagnetic waves are observed to modulate (调节) electromagnetic ion cyclotron waves, periodically causing heavy ions to precipitate and produce Jupiter’s X-ray pulses. Our findings show that ion aurorae share common mechanisms across planetary systems, despite temporal, spatial, and energetic scales varying by orders of magnitude.
INTRODUCTION
Aurorae, observed from planetary polar regions across the solar system, are displays of light that are produced when energetic particles precipitate along magnetic field lines and transfer their energy to the atmosphere. Jupiter’s soft x-ray aurorae are produced by energetic [~ (MeV) (电子伏)] heavy ions (S and O), originally from the moon Io’s (木卫一的) volcanic activities. The dynamic X-ray emissions often pulse with a regular beat of a few tens of minutes. The spectacular quasi-periodic (准周期性的) auroral pulsations at Jupiter have also been observed in ultraviolet (UV), infrared, and radio emissions. The X-ray aurorae are predominately confined (主要局限于) to the region poleward of Jupiter’s main aurora, connecting to Jupiter’s outer magnetosphere via magnetic field lines. The mapping of the emissions leads to the suggestion that the particle precipitations were driven by magnetic reconnection. However, observations show that the x-ray pulsations last for several Jupiter days or longer, evidencing that the driver may not be a transient process like magnetic reconnection.
To date, 40 years after their discovery, the mechanisms that cause these X-ray aurorae remain unknown. Simultaneous measurements of the magnetospheric environment and the auroral emissions are critical to revealing their driving mechanisms. Here, we present observations of Jupiter’s unique x-ray aurorae with simultaneous in situ measurements from the magnetosphere. In this study, we reveal the physical driver for Jupiter’s pulsating x-ray emissions by analyzing simultaneous in situ measurements from Juno and remote spectroscopic imaging by XMM-Newton telescope (XMM,牛顿卫星) during 16 and 17 July 2017. XMM’s European Photon Imaging Camera (EPIC-pn and MOS) instruments provided spatial, spectral, and timing data of Jupiter for a continuous 26-hour (~2.6 Jupiter rotations) observation from 18:26 UT on 16 July to 22:13 UT on 17 July, which was shifted to account for the ~46-min light travel time between Jupiter and Earth. This XMM observation was planned to coincide with the time when NASA’s Juno spacecraft was moving from 62 to 68 RJ (1 RJ = 71 492 km) radially away from the planet in the Southern Hemisphere in the predawn sector between ~0400 and 0430 magnetospheric local time (MLT).
Ionosphere-magnetosphere (电离层) mapping from previous observations suggested that the origins of Jupiter’s X-ray auroral pulsations occurred at these distances from the planet. Juno provided contemporaneous (同时发生的) in situ measurements from the plasma sheet only when Jupiter’s north magnetic pole tilted to Earth. Therefore, we focus on the northern aurora, for which Juno’s in situ measurements detail what was happening in the plasma sheet during the X-ray pulses. At Jupiter, the analysis of these comparisons between in situ and remote sensing observations is more complex than at Earth. At Earth, during the time scale of an auroral event, typically tens of minutes, a spacecraft in the terrestrial magnetosphere usually travels little (e.g., hundreds of kilometers) in comparison to the spatial scale of a magnetospheric event (e.g., several Earth radii) that would cause a large auroral brightening so that this in situ spacecraft could be magnetically connected to the aurora region over the full auroral lifetime. This is not true for Jupiter, because the footprint of the aurora (which is rotating with Jupiter) with respect to Juno’s location changes substantially during an observation. There are also substantial travel times (a few tens of minutes) along the magnetic field expected from the outer magnetosphere to the Jovian aurora. Therefore, the correlation between a single outer magnetosphere event in Jupiter’s in situ measurements and a single auroral pulse cannot be expected on a one-to-one level basis. Instead, a series of successive events are required to draw reliable careful correlations, with the regular periodicity of the x-ray flares, providing an invaluable diagnostic signature of the source process.
(Adapted from an essay on Science.)
1. What does the essay focus on?| A.The X-ray pulses happening on Jupiter. |
| B.The formation of the aurora in the pole of Jupiter. |
| C.The ways to teach people how to appreciate auroras. |
| D.The process of detecting the X-ray pulses on Jupiter. |
| A.Their conclusions. | B.Their measure to do the research. |
| C.Discussion of some problems of preciseness. | D.Their acknowledgements. |
| A.辐射 | B.红外线技术的 | C.太阳风 | D.红外线 |
| A.The strong magnetic is a good breakthrough point to research the auroral flares. |
| B.The X-ray pulses will last for several days on Jupiter. |
| C.The soft X-rays are caused by high-energy ions. |
| D.The X-ray pulses beat regular on Jupiter. |
注意:
1、词数100左右
2、可以适当增加细节,以使行文连贯;
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________



