Kevin Randall, a teacher, who teaches biology at Grandville High School, runs the environmental club at the high school which has around 2, 000 students. The club is known as the GHS Green Team, and it aims to raise awareness among students and teachers of sustainability(可持续性). It also works on projects to reduce the environmental footprint of the building itself.
One of the club’s recent projects focused on reducing waste in the school cafeteria. Randall said their cafeteria supervisor told them that the school went through 54, 000 plastic forks every year. The club applied for financial help, built recycling centers for the cafeteria and bought metal silverware.
And now every student uses a durable metal fork or spoon instead of disposables(一次性用品). “And that’s just one way we’re trying to capture the low-hanging fruit,” Randall said.
The efforts of Randall and his students have earned Grandville High School the Michigan Green School certification from the state. In addition to their work reducing waste in the cafeteria, the GHS Green Team has also built a garden with flowers and vegetables on campus. Over the years, Randall and his students have also been working on raising money to install solar panels(太阳能电池板) on the roof of the high school.
Randall said he was inspired to take the lead on environmental issues for his school because he wanted his students to have someone to turn to in the building who understands what’s at stake(有风险) when it comes to climate change.
“And I also felt like I need to do more in my life for my own two children at home,” Randall added. “They need to know that their dad is working as hard as he can to reduce the effects of climate change and to make sure that other students out there are learning about this just the way they are at home.”
1. What’s the purpose of the GHS Green Team Club?| A.To inspire students’ love for biology. |
| B.To promote environmental protection. |
| C.To finish projects given by the school. |
| D.To prepare students for their future jobs. |
| A.The service of the cafeteria is improved. |
| B.The fresh fruit will be offered to students. |
| C.The financial trouble of the cafeteria is solved. |
| D.The use of plastic forks has been reduced greatly. |
| A.The activities organized by the club. |
| B.The function of the projects. |
| C.The features of the club. |
| D.The future of the club. |
| A.All students know the stake of climate change now. |
| B.Many people took part in the project for material rewards. |
| C.Randall thinks it necessary to set a good example for his children. |
| D.Randall was unwilling to take the lead on environmental issues at first. |
相似题推荐
【推荐1】Contributing to climate change efforts and biodiversity conservation have been the priority of the ongoing work for global beverage leader the Coca-Cola Co. in China, as it has operated more than 50 water management programs in the country.
Since 2007, Coca-Cola has been working with the WWF, UNDP and other partners to protect the freshwater resources of the Yangtze River, in which rare species such as pandas, snow leopards, white cranes, porpoises and Chinese dragonflies were bred. Coca-Cola’s actions over a decade have effectively contributed to the protection of more than 200, 000 hectares of high-ecological value are, as part of the efforts to conserve the biodiversity and communities of 2 million hectares of wetland ecosystems in the basin.
Coca-Cola China has also been working on responsible agriculture. Since 2012, together with the UNDP, Coca-Cola China has helped double the production of sugar cane in Chongzuo, Guangxi Zhuang autonomous region, by establishing an irrigation (灌溉) system for the first time, which uses wastewater byproducts to irrigate the fields.
“The water coming from the sugar processing facility needed to be treated, but once it’s treated it can be used,” Goltzman said. “You don’t have to withdraw from the ecosystem to water those crops.”
The Coca-Cola Company used a smart “golden triangle” model in all sustainability proposals. The innovative (创新) model gives full play to the advantages and expertise of governments, businesses, nongovernmental organizations and other sectors of society, to meet the increasingly serious environmental challenges, and protect water and biological diversity.
Zhang said, “We act in ways to create a more sustainable and better shared future. Sustainability remains core to what we do.”
1. Which of the following can best describe the Coca-Cola Co.?| A.Peace-conscious. | B.Fully-equipped. |
| C.Earth-friendly. | D.Recently-built. |
| A.Processed wastewater byproducts are used. |
| B.The sugar processing facility is set up. |
| C.The irrigation system has been changed. |
| D.The ecosystem has been improved. |
| A.It consists of new conservation proposals. |
| B.It is created by nongovernmental organizations. |
| C.It is employed to solve the problem of water shortage. |
| D.It makes the most of social resources to help nature. |
| A.In an essay. | B.In a fashion magazine. |
| C.In a newspaper. | D.In a biology book. |
【推荐2】Amphibian (两栖动物) species are disappearing at an alarming rate across the globe due to habitat loss, pollution, and disease. FrogWatch trainings cover the importance of amphibians in the environment, how monitoring our local frog population helps to protect them, factors to consider in choosing a site to monitor, how to identify frog species by their calls and how to report findings to FrogWatch USA. Become a citizen scientist with FrogWatch USA, and help save our frogs!
Date: Saturday, June 4, 1:00 p.m.—3:00 p.m.
Price: $10household (includes up to 2 adults and 2 children age 8+)
Training instruction:
FrogWatch trainings cover the importance of amphibians in the environment. The instruction focuses on how to:
1. monitor our local frog population to protect the species;
2. determine factors when choosing a site to monitor;
3. recognize frog species by their calls;
4. report findings to FrogWatch USA.
After passing a test on identifying frog calls at the end of the training, certified volunteers then commit themselves to monitoring a local amphibian habitat (such as a pond or lake) approximately once a week for about 15 minutes, and collecting /submitting data on what they hear. Data collected will be added to a national FrogWatch USA database. In 2020, Rhode Island FrogWatch citizen scientists followed 80 sites almost 900 times! In those 900 observations, FrogWatchers, heard more than 1,220 frog choruses.
Questions: Contact Programs@rwpzoo.org or call (401)785-3510 ext. 358.
Please note: FrogWatch trainings will cover a large amount of information and protocols (规程). While FrogWatching is a great after-dark family activity for all ages, the trainings are designed for interested older children and adults.
1. How can you tell frog species apart?
| A.By their colors. | B.By their shapes. | C.By their voices. | D.By their sizes. |
| A.To collect data about frogs. | B.To set up a database for frogs. |
| C.To take a test on frog knowledge. | D.To guard frog habitats once a week. |
| A.Frogs need to be watched by a family. |
| B.It is dangerous to watch frogs at night. |
| C.Small children aren’t suitable for trainings. |
| D.People have to take notes about frog information. |
【推荐3】It turns out that plants are getting help from their friends underground—quite a bit more than scientists had realized. A global team of researchers has calculated that around 36% of the carbon released into the atmosphere each year from the burning of fossil fuels is captured and delivered to a complicated system of fungi that lives beneath our feet.
Plants take carbon dioxide from the air and use it to make sugars and fats. These are sent down to their roots, where they are taken up by so-called mycorrhizal (菌根) fungi. In exchange, the fungi provide the plants with water and essential nutrients from the soil. The more carbon these fungi are able to draw in, the more carbon dioxide gets captured by plants.
Mycorrhizal fungi helped plants get established on land several hundred millions of years ago, and today’s plants would have a hard time functioning without their partners under the ground. Yet “mycorrhizal fungi have been largely overlooked,” said To by Kiers, executive director of the Society for the Protection of Underground Networks. “They represent an incredibly important part of the carbon cycle, and we are only just beginning to understand how they work,” she said. “The urgency to understand that and link it to biodiversity belowground is the most important.”
The researchers also said that plants associated with mycorrhizal fungi can take in eight times more carbon than plants that are not. Stephanie Kivlin, an ecologist at University of Tennessee, said the study is a crucial step toward improving our understanding of the plant-fungi duo’s role in reducing carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. “These mutualisms (互利共栖) can act as a critical carbon sink in many ecosystems on the land,” she said.
Not only do the fungi take in carbon from plants, they also help keep that carbon safely belowground by creating a sticky compound that holds the soil together. Although mycorrhizal fungi have short life spans-only a few years—their usefulness doesn’t end after death. “This is my favorite part,” Kiers said. “After they die, they make a dead underground network that acts as a scaffolding to hold the soil together, locking the carbon in place. ”
1. What do the researchers find?| A.Fungi absorb carbon from plants. | B.Carbon is essential to plants. |
| C.Carbon is released into the air. | D.Plants exchange food with fungi. |
| A.Carbon sink reduces carbon dioxide. | B.Carbon cycle is linked to biodiversity. |
| C.Plants nowadays take in carbon as usual. | D.Plant-fungi system functions efficiently. |
| A.They become sticky scaffolding. | B.They help prevent carbon release. |
| C.They provide vital nutrients. | D.They change into fossil fuels. |
| A.A complicated problem. | B.An overlooked plant. |
| C.An underground green guard. | D.A useful ecosystem. |

Wolves have a certain undeserved reputation: fierce, dangerous, good for hunting down deer and farmers’ livestock. However, wolves have a softer, more social side, one that has been embraced by a heart-warming new initiative.
In a bid to save some of Europe’s last wolves, scientists have explored the willingness of these supposedly fierce creatures to help others of their kind. Female wolves, the scientists have discovered, make excellent foster parents to wolf cubs that are not their own. The study, published in Zoo Biology, suggests that captive-bred wolf cubs(幼兽) could be placed with wild wolf families, boosting the wild population.
The gray wolf was once the world’s most widely distributed mammal, but it became extinct as a result of widespread habitat destruction and the deliberate killing of wolves suspected of preying on livestock. Fear and hatred of the wolf have since become culturally rooted, fuelled by myths, fables and stories.
In Scandinavia, the gray wolf is endangered, the remaining population found by just five animals. As a result, European wolves are severely inbred and have little genetic variability(变异性), making them vulnerable to threats, such as outbreaks of disease that they can’t adapt to quickly. So Inger Scharis and Mats Amundin of Linkoping University, in Sweden, started Europe’s first gray wolf-fostering program. They worked with wolves kept at seven zoos across Scandinavia. Eight wolf cubs between four and six days old were removed from their natural parents and placed with other wolf packs in other zoos. The foster mothers accepted the new cubs placed in their midst.
The welfare of the foster cubs and the wolves’ natural behavior were monitored using a system of surveillance cameras. The foster cubs had a similar growth rate as their step siblings in the recipient litter, as well as their biological siblings in the source litter. The foster cubs had a better overall survival rate, with 73% surviving until 33 weeks, than their biological siblings left behind, of which 63% survived. That rate of survival is similar to that seen in wild wolf cubs. Scientists believe that wolves can recognize their young, but this study suggests they can only do so once cubs are somewhere between three to seven weeks of age.
If captive-bred cubs can be placed with wild-living families, which already have cubs of a similar age, not only will they have a good chance of survival, but they could help dramatically increase the diversity of the wild population, say the researchers. Just like the wild wolves they would join, these foster cubs would need protection from hunting. Their arrival could help preserve the future of one of nature’s most iconic and polarizing animals.
1. What’s the theme of the passage?| A.Giving wolf cubs a new life | B.Foster wolf parents and foster cubs |
| C.The fate of wild wolves | D.Changing diversity of wild wolves |
A.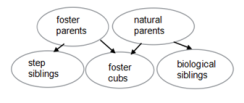 | B.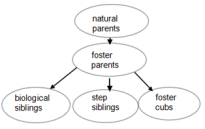 |
C.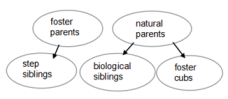 | D.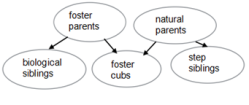 |
| A.Female wolves are willing to raise wolf cubs of 3 to 7 weeks old. |
| B.Foster cubs are accepted by foster parents and are well bred. |
| C.Man’s hostile attitude towards wolves roots in myths, fables and stories. |
| D.Foster cubs and their biological siblings have similar growth rate and survival rate. |
| A.To help wolves survive various threats |
| B.To improve wolves’ habitat and stop deliberate killing |
| C.To save endangered wolves by increasing their population |
| D.To raise man’s awareness of protecting wolves |
【推荐2】A four-wheeled pod shaped like a space capsule on riverside roads trundles slowly among people who run, walk, cycle and lead dogs. At a maximum speed of 10 mph, the car beeps as it moves regularly between the Inter Continental Hotel in the west of the peninsula and apartment blocks in the east.
The biggest surprise about the vehicle is not its futuristic appearance but how it is controlled. While current safety rules require a human to monitor the vehicle’s performance and step in to avoid crashes, the pod largely drives itself. It is one of several experiments worldwide aimed at exploring how autonomous vehicles might mesh with city transport systems. All are looking at how a technology being developed mainly for US highways can work in the more confined, chaotic space of city streets.
At the heart of these efforts is an attempt to work out whether driverless vehicles will ease or worsen the impact that private car travel has had on many cities following the highway-building craze of the mid-20th century.
Some fear the technology could prompt more journeys by private motor vehicles rather than more space-efficient public transport. If the technology provides comfortable, stress-free, private journeys, it might also prompt people to commute daily from further afield, generating yet more traffic.
Experts concerned about such impacts on behaviour argue it is vital that the roll-out of autonomous vehicle technology goes hand-in-hand with a rethink of how it is used.
David Begg, a former chairman of the UK’s Commission for Integrated Transport, accepts that autonomous vehicles will use road space more efficiently but says the problem remains that cars take up too much space for the people they carry. On average, most vehicles contain little more than one person — the driver.
“There’s no doubt autonomous vehicles can allow us to squeeze more vehicles into a given amount of capacity because they’re bumper-to-bumper and side-by-side,” prof Begg says. “Unless we can increase vehicle occupancy up from 1.1, we’re moving too much fresh air and not enough people.”
1. What do we know about driverless vehicles?| A.Driverless vehicle travels at an average speed of 10 mph. |
| B.Driverless vehicle drives itself to a great degree. |
| C.Driverless vehicles’ appearance is the same as common cars. |
| D.Most driverless vehicles contain more than one person. |
| A.deserted | B.tidy. | C.straight. | D.narrow. |
| A.Disapproving. | B.concerned | C.Positive. | D.Sympathetic. |
| A.Entertainment. | B.Health. | C.Education. | D.Science. |
【推荐3】Western Australia may soon be home to the world’s tallest wooden building, after authorities plans for a 191.2-meter-tall tower constructed using mass wood. Perth’s Metro Inner-South Joint Development Assessment Panel (JDAP) approved the developer Grange Development’s proposal for the tall building.
The tall building, currently named the C6 building, would stand nearly twice as high as the current record holder. The developers say 42% of the building will be constructed from wood, with the columns and core made of concrete (混凝土). If completed, the high-rise will go beyond the current world’s tallest wooden building, the Ascent tower in Wisconsin, America, which stands at 25 stories or 86 meters. The structure, located in South Perth, Australia, will also be taller than the coming wood Atlassian Headquarters in Sydney, which is expected to claim the record from Ascent but is yet to be completed.
Like Atlassian Headquarters, the C6 building will combine wood beams (横梁) with a steel supporting structure to support the whole structure. According to Grange Development, the 50-story building will contain more than 200 apartments.
It will be Western Australia’s first carbon-negative residential building. Grange Development’s director, James Dibble, said, “Our desire with the building is to shift the focus towards a more climate-conscious approach.” The building will use 7,400 cubic meters of wood harvested from 600 trees. “We can’t grow concrete,” Dibble said, calling the plan “a new open sourced blueprint that uses construction methods to balance out the CO2 within our built environment, which is the single biggest trigger to climate issues”. “This is our opportunity to show that we genuinely care about the climate crisis we are doing very little about as an industry,” he added.
Philip Oldfield, head of the University of New South Wales’ School of Built Environment, said, “Typically we build tall buildings out of steel and concrete, Concrete is responsible for 8% of all CO release. So by replacing concrete and steel with a biological material such as wood, it is going to reduce the environmental impact of the building quite significantly.”
1. Where will the second tallest wooden building appear?| A.In South Perth, Australia. | B.In Sydney, Australia. |
| C.In New South Wales, Australia. | D.In Wisconsin, America. |
| A.Relief. | B.Limit. | C.Improvement. | D.Contributor. |
| A.Low-carbon. | B.High-risk. | C.Material-saving. | D.Energy-wasting. |
| A.The tallest wooden building has been all done in Australia |
| B.The tallest wooden building causes environmental worries |
| C.The tallest wooden building highlights more than its height |
| D.The tallest wooden building fits well the climate in Australia |



