Given the fact that chemical pesticides and artificial fertilisers can fight crop disease and increase production, they
1. What is the woman doing?
| A.Joining a protest. | B.Interviewing the man. | C.Giving a speech. |
| A.She is looking for her husband. |
| B.Her salary hasn’t been paid by the boss. |
| C.The factory is polluting the environment. |
| A.The woman’s husband. |
| B.People in the community. |
| C.The workers in the factory. |
| A.To shout with her. |
| B.To go to the government. |
| C.To cover the event. |
The beautiful Li River and its amazing surrounding scenery is one of the most well-known tourist destinations in China. However, the
1. 水污染的原因描述;
2. 水污染的危害;
3. 你的建议。
注意:
1.词数80左右;2.首句已给出,不计入总词数。
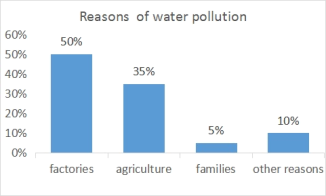
With the development of society, water pollution is getting more and more serious.
__________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________5 . Pollution is one of the biggest problems in the world today. In many places, rubbish is thrown into lakes and rivers.
In some cities, the air is filled with pollution.
If we do not act to improve the environment, more living things will be killed by pollution.
If we can do these, we will make the world a better place to live in.
| A.This makes some old people and children ill. |
| B.As well as people, animals are also harmed by pollution. |
| C.We can make our lakes and rivers cleaner and cleaner. |
| D.It’s time for all of us to take action right away! |
| E.Because of this, these places have already been polluted. |
| F.Trees reduce dust and help keep the air clean. |
| G.A few of us should take action to protect the environment. |
6 . Microplastics — tiny pieces of plastic waste less than five millimetres long that have been degraded by waves, wind and ultraviolet rays — have been discovered in the deepest oceanic trenches and within the stomachs of the organisms that live there, but we have little idea about where the great majority of them end up. More than eight million tonnes of plastic enters our oceans every year, comprising between 80 and 85 percent of all marine trash, but with inadequate data, there are concerns that these figures could be underestimates.
Currently, most of the data we have on microplastics are accidentally captured by research ships, which use plankton nets to collect marine-microorganism samples. However, researchers Christopher Ruf and Madeline Evans from the University of Michigan have discovered an innovative way to identify and track concentrations of microplastics in the ocean.
The technique relies on NASA’s Cyclone Global Navigation Satellite System (CYGNSS), a constellation of eight micro-satellites used to predict hurricanes that calculate wind speeds above the ocean by measuring the roughness of surface waters. As the satellites are continuously recording, Ruf and Evans realised that they collect a great deal of additional data. It was while analysing these data that they noticed some differences-times where the surface of the ocean appeared to be much smoother than it should, given the prevailing wind (盛行风) conditions.
Knowing that water isn’t roughened as much when it contains a lot of floating material, Ruf and Evans identified a pattern that linked areas of unusual smoothness and predicted microplastic distributions. They found that the difference between their measurements, and how much rougher the surface would be if winds of the same speed were blowing across clear water, was “highly correlated with the presence of microplastics, and the degree of the difference also correlated with the concentration of the plastics.”
The research reveals that there are seasonal variations,where the concentrations of microplastics tend to be higher in the summer and lower in the winter in a very clean, periodic way, which Ruf explains mirrors the way in which the ocean circulation changes throughout the year. It also confirms, as was previously thought, that rivers are the main source of ocean microplastics.
Raising awareness of the issue of ocean microplastics among the public and politicians is just one of the researchers’ future aims; they are also in conversation with Duteh non-profit The Ocean Cleanup and Finnish clean-technology specialist Clewat, which are interested in using the information to more efficiently target their trash-collection campaigns.
So far, only one year’s worth of data have been processed since CYGNSS was launched in 2016. By looking at a longer time period, Ruf and Evans aim to determine whether the seasonal pattern is repeatable, and whether the concentration of micmplastics in the ocean is getting worse.
1. What is Paragraph 1 mainly about?| A.The limited knowledge about ocean microplastics. |
| B.The harm of ocean microplastics to sea creatures. |
| C.The methods of degrading ocean microplasties. |
| D.The previous research on ocean microplasties. |
| A.has offered data about the repeatable seasonal pattern |
| B.guides research ships to gather data about sea animals |
| C.provides unexpected data about the changes of sea surface |
| D.was designed to measure the distribution of ocean microplastics |
| A.Microplastics will end up in the stomachs of the ocean organisms. |
| B.Mlicroplastics play a vital role in the yearly ocean circulation changes. |
| C.The surface of the ocean can get smoother with more microplastics in it. |
| D.The new way of tracking microplastics has helped prevent ocean pollution. |
| A.To introduce the technology of CYGNSS. |
| B.To present a way to study ocean microplastics. |
| C.To test an assumption on ocean microplastics. |
| D.To propose a new means of protecting the ocean. |
7 . Multispectral cameras (多光谱摄像机) keep a watch on the polluted Ganges (恒河), where thousands of people suffer from water-borne diseases by the river.
The 1.500-mile-long Ganges originates in the Himalayan range and snakes across to the coastal state of West Bengal. In Rishikesh, the river is still relatively clear, but when it reaches the city of Kanpur, the Ganges turns a deep grey with raw waste and is faced with serious pollution. 764 industries along the river consume 1,123 million liters of water and flow back about half that volume as wastes.
Large-scale plans ever launched to clean the river prove unsatisfying. due to a lack of a clear understanding of what pollutants are in the water and how they affect it.
Dipro has been working on high tech solutions to the first survey and the analysis of the pollutants. To collect data on the water composition. he sent a plane into the sky, fitted with four multispectral cameras that use sensors to remotely monitor pollutants in the river, which create a long pathway easily studied from the sky. The reflection of lights from the surface of the liquid depends on the amount of various matters in it. At a higher concentration, these changes are visible to naked eyes, but in low concentrations, he uses specialized optical filters (光学过滤) and calculations to separate the wavelengths of light being reflected. Sometimes he creates false color composite images, which add color to the wavelengths to better distinguish different parts of the liquid with concentrations of floating pollutants. People can trace them back to the sources accurately and identify the polluters responsible.
When asked to develop this remote sensing method further to handle polluters better from the sky. Dipro says, "With new and affordable drones (无人机) available in the market, anyone can send one up and help collect relevant data."
1. What's the main idea of paragraph 2?| A.The link between the Himalaya and the river. |
| B.The development of industries along the river. |
| C.The formation of the Ganges |
| D.Severe pollution of the Ganges |
| A.Wavelengths of light. | B.Floating pollutants |
| C.False images. | D.Different parts of the liquid. |
| A.More drones will be adopted to address river pollution. |
| B.It's everyone's duty to engage in the work of drones. |
| C.Drones perform perfectly in river pollution control. |
| D.Drones serve as a must for a better environment |
| A.How to Operate Multispectral Cameras | B.How to Clean Ganges from the Sky |
| C.Dipro's Ambitious Invention | D.Ganges' Serious Pollution |
8 . A handful of old mobile phones lay in a grey bucket. These outdated devices, which are about to be chopped into thousands of pieces, will be given a second life as recycled e-waste. But many phones won't.
According to the latest estimates, the world gets rid of approximately 50 million tonnes of waste annually. E-waste is full of dangerous materials that can cause damage to human health and the environment if not managed properly. But only 20 percent of global e-waste is recycled.The rest ends up in landfill, or burned—or is not recycled at all.
And yet,Switzerland is a good example of how to deal with the growing environmental issue. The country collects and recycles roughly 7S percent of this discarded material. This is thanks to a strong voluntary take-back system, where consumers can take e-waste to a reclining collection point or any electronic shop retailer(零售商). A recycling station can be found within at most 300 meters from any residential area. Everyone gets involved. Switzerland's e-waste system is unique and can't be easily copied-due to a strong recycling culture within the country.
However, Switzerland faces the same global challenges as every nation.The built-in lithium batteries(锂电池)aren't easy to take out. The only way to remove these potentially dangerous components is with a bar and hammer. This poses a significant risk to those handling the goods. As such, producers need to be more transparent(信息透明的) and show more clearly where the harmful substances are, and how they can be removed.
Once the battery is removed, e-waste is sorted into different component parts—-metals, plastics and other materials. Roughly 70 percent of the device can be recycled. The material that cannot be recycled is used for other purposes like construction material or is burned to generate energy. Mobile phones—from a material perspective (角度), from a value perspective,and also from an environmental impact perspective -are very important.
For the past 15 years, Switzerland has been actively encouraging and supporting electrical waste disposal practices. They are happy to share their knowledge, experience, lessons learned, and they are happy if other people pick up on it.
1. What can we know about the global e-waste?| A.Only 20% of the e-waste is useful. |
| B.It is becoming an environmental problem. |
| C.Most of it has been given a second life. |
| D.It has been the major cause of pollution. |
| A.It is unique and easy to copy. |
| B.It features many devoted volunteers. |
| C.It gains great support and understanding. |
| D.It is complicated and not easily accessible. |
| A.Remove harmful substances. |
| B.Use less dangerous components. |
| C.Offer customers free bars and hammers. |
| D.Help make the removal easier and safer. |
| A.How to fight against e-waste. |
| B.Why E-waste gets out of control. |
| C.How to be champion of recycling. |
| D.How to lead an Eco-friendly lifestyle. |
9 . Most of our everyday plastic items end up in landfill, left to rot away for many years. But some of it blows away, spoiling the countryside and causing damage to the natural environment and harming wildlife. The problem is most severe in our oceans. Research has found a deserted island in the South Pacific is littered with the highest density (密度) of plastic waste anywhere in the world.
The study described how remote islands act as a ‘sink’ for the world’s rubbish. They become collecting points for fishing items and everyday things including toothbrushes, cigarette lighters and razors-things that we throw away. Dr Jennifer Lavers from the University of Tasmania says “Almost every island in the world and almost every species in the ocean is now being impacted one way or another by our waste.”
This highlights the potentially deadly effect of our disposable (用后即丢弃) culture. When we throw something away, it doesn’t just disappear, it goes somewhere and because of the nature of plastic, it takes a long time to rot away and stays there causing great damage to the ocean’s ecology (生态). And worse still, plastic is broken down into tiny particles over a long period by the wind and the waves, then sea creatures at the bottom of the food chain swallow them. These creatures are eaten by the fish that we eventually consume.
The solution to this problem would be to use less plastic. Several countries now charge for using plastic carrier bags which reduces the amount used and some products now use natural and recyclable materials.
1. What does the author really want to tell us in the first parapraph?| A.It is a good idea to end plastic items in a landfill. |
| B.Plastic items blow away easily in the strong wind. |
| C.It is a bad habit to throw away plastics everywhere. |
| D.Plastic pollution in oceans is a most serious issue. |
| A.The islands begin to sink with much rubbish on them. |
| B.The islands have become gathering places for rubbish. |
| C.The islands are ideal places to hide the plastic products. |
| D.The islands are inaccessible due to the white pollution. |
| A.Impact on sea species. | B.Thrown-away rubbish. |
| C.The nature of plastic. | D.The ocean’s ecology. |
| A.Breaking the balance of ocean ecology. | B.Causing many sea creatures to die out. |
| C.Presenting potential risks to our health. | D.Cutting off the food chain of sea creatures. |
10 . In recent years, Ethiopia has become a regional leader in solid waste management. Last year, the country transformed the landfill (垃圾填埋场) in Addis Ababa into a new waste-to-energy plant, the first such project on the continent. The plant incinerates up to 1, 400 tonnes of waste every day, about 80 percent of the city's rubbish, supplying the capital with 25 percent of its household electricity needs.
However, despite these important steps, challenges remain in Ethiopia. Although the country has permitted the Basel, Stockholm and Rotterdam conventions, laws and policies for environmentally sound management of hazardous (有害的) wastes are still not effective in pre- venting littering waste illegally.
To help Ethiopia meet these challenges, the Chemicals and Waste Management Program is supporting the country with a three-year project to enhance its capacity for sound management of hazardous wastes.
In the initial stages, a project management unit will be formed, made up of many representatives from government departments and private organizations. This unit will be responsible for reviewing and assessing Ethiopia's current legal system, which, despite numerous advances in recent years, does not specifically target the recycling of hazardous waste. Once legal gaps are identified, the project will seek to update existing policies and strategies.
Many people in Ethiopia are not aware of the possible effect of environmental damage and the need to report such crimes to the police. To resolve this pressing issue, Ethiopia will be conducting a series of capacity-building activities, including creating awareness-raising programs, training trainers and providing equipment.
Ethiopia will also work to establish a national mechanism for chemicals and waste management by engaging government departments and civil society groups. Authorities will also make budgetary provisions (预算拨款) in national, regional and institutional planning to ensure funding for these activities is sustainable even after the project's completion.
1. Which can replace the underlined word “incinerates” in paragraph 1?| A.Produces. | B.Burns. | C.Gathers. | D.Absorbs. |
| A.The relevant laws are not sound. | B.The shortage of workers is severe. |
| C.The pollution level is too high. | D.The funds are not sufficient. |
| A.Restrict their environmental movement. | B.Call on them to start some programs. |
| C.Reward them with budgetary provisions. | D.Raise their environmental awareness. |
| A.Ethiopia is facing serious environmental problems. |
| B.Ethiopia has achieved success in waste management. |
| C.Ethiopia is putting efforts into waste management. |
| D.Ethiopia has reduced environmental pollution levels. |



