When people think of threats facing the ocean, we often think of climate change, plastics, and overfishing. But research shows noise pollution is another essential thing we need to be monitoring. Scientists say the changes in the sounds of our oceans, seas, and other waterways affect many marine animals—from very small shrimps to huge whales.
Francis Juanes, an ecologist, explained, “For fish, sound is probably a better way to sense their environment than light.” Sounds help fish and other marine animals survive. They use sounds to communicate with each other. Sounds also help some ocean animals find food and avoid their hunters. Many ocean animals use sounds to find good places to mate (交配).
However, increased noise from humans is making it harder for these animals to hear each other. The noise is coming from shipping traffic, motorized fishing ships, underwater oil and gas exploration, offshore construction, and other noisy human activity. “For many marine species, their attempts to communicate are being masked by sounds that humans have introduced,” said Carlos Duarte, who co-wrote the paper with Juanes.
Experts at NOAA (the U.S. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration) explain the term masking on its website. Masking happens when one or more noises in the water block sound important to a marine animal's existence. NOAA experts state that masking is most noticeable when “a noise is at the same frequency and loudness as biologically important sounds, such as mating calls.”
The stress from human noise might also affect the immune system—an animal's natural defense system—as well as reproductive (生殖的)health or behavior. “Imagine having to raise your kids in a place that's noisy all the time,” said Joe Roman. He is a marine ecologist at the University of Vermont and was not involved in the research. Roman added that it should come as no surprise that many marine animals are showing higher levels of stress due to noise.
1. Why is it essential to monitor noise pollution in the ocean?| A.Noise pollution threatens the survival of marine animals. |
| B.Marine animals are less sensitive to light and plastic. |
| C.Marine pollution keeps changing the sounds of the ocean. |
| D.Noise pollution results directly from climate change. |
| A.Being unable to detect mate calls leads to decline of marine animals. |
| B.The noise only occurs when it is of the same frequency of animals' sounds. |
| C.The mixed noise prevents animals from detecting important sounds. |
| D.Human activities are involved in producing noise in the ocean. |
| A.The immune system of marine animals is the same as kids'. |
| B.Raising kids in a noisy environment leads to more pressure. |
| C.Noise pollution is easier to deal with than other ocean threats. |
| D.Marine animals suffer from stress in a noisy environment. |
| A.The Sharp Decline of Marine Animals |
| B.Humans Are Making Oceans Too Noisy |
| C.Time to Clean Up the Polluted Ocean |
| D.Importance of Sounds for Ocean Animals |
相似题推荐
【推荐1】Thousands of birds die each spring and fall when they crash with Chicago’s high-rise buildings, which lie on a major migration path between Canada and Latin America. But the birds don’t die in vain. Since the 1970s, many of them have been collected from the street by the city’s Field Museum. They were classified and recorded in detail there. This unique and detailed set of data has been a scientific windfall, showing that North American migratory birds appear to become smaller in size.
A new study of this data has highlighted an important trend: birds that have bigger brains, relative to their body size, are not shrinking as much as the smaller-brained members of their species. The study is the first to identify a potential link between awareness and animal response to human-made climate change, according to the researchers from Washington University in St. Louis. “As temperatures warm, body sizes are decreasing.” said Justin Baldwin. “But larger-brained species are decreasing less strongly than small-brained species.”
Relative brain size is often considered an indicator of behavioral flexibility in birds, according to the research. “The idea is causing a lot of disagreements when it’s applied to some other animals”, Baldwin said, “but it works for birds.” “Relative brain size connects with increased learning ability, increased memory, longer lifespans and others.” Baldwin said. “In this case, a bigger-brained species of bird might be able to reduce its risk to warming temperatures by searching for habitats with cooler temperatures, for example.” he said.
Birds that had big brains, relative to their bodies, had body-size reductions that were only about one-third of those observed for birds with smaller brains, the study found.
1. Why do some birds die on the way of migration?| A.The spring and fall change quickly. | B.The weather becomes extremely cold. |
| C.They crash into the tall buildings. | D.Barriers are set up on the migration path. |
| A.They were kept and studied later on. | B.They were buried in the same streets. |
| C.They were taken away from the path. | D.They were used to show migratory way. |
| A.Increasing | B.Decreasing | C.Strengthening | D.weakening |
| A.By finding cooler homes. | B.By having longer lifespans. |
| C.By increasing their memory. | D.By changing their behavioral flexibility. |
【推荐2】North Atlantic right whales now grow smaller than they did 40 years ago, and new research suggests a leading cause is the damage that human activity has done to the critically endangered species.
The findings, published in the journal Current Biology, reveal that when fully grown, a North Atlantic right whale born today would be expected to be about one meter shorter than a whale born in 1980. Currently, full-grown members of the species average 13 to 14 meters in length.
Researchers used high-resolution photographs to ’track size and body condition of 129 right whales. Their research indicated that a major reason for the animals’ recent growth problem is entanglement (缠绕) in rope and fishing equipment.
North Atlantic right whales typically move up and down the Eastern seaboard, from Florida to Canada. In recent years, more than half the population can be found from late winter to early spring off the coast of Cape Cod, where they sail through a deadly maze (迷宫) of rope and fishing equipment.
Entanglements in the equipment can lead to life-threatening infections, starvation, or drowning (溺水). Even when they don’t kill the whales, they can cause long-term harm, the researchers found. When the whales get caught in fishing equipment and end up dragging it around, it forces them to expend more energy fighting to survive, instead of growing or reproducing. Not only does entanglement contribute to reduced body size for an individual whale, but female North Atlantic right whales entangled while nursing produce smaller babies. That threatens the repopulation of a species with so few remaining members.
In response, conservationists say managers of fishing grounds need to better manage the fishing grounds, whose equipment on the seafloor is considered the primary cause of entanglements. One potential answer is greater investment in the development and testing of ropeless fishing technology.
“There is no time to wait,” researchers said. “The species can’t tolerate any further impacts, or it will have no future.”
1. What can we learn about North Atlantic right whales?| A.Overfishing slows their growth in size. |
| B.They could grow to 15 meters long decades ago. |
| C.They will soon become endangered due to human activity. |
| D.Hundreds of them suffer from entanglement every year. |
| A.Growth and reproduction. | B.Disease resistance. |
| C.Food-seeking. | D.Breathing. |
| A.Weight loss of nursing whales. | B.Decline in the number of whales. |
| C.Energy loss of individual whales. | D.Smaller size of the whales. |
| A.Making ocean fishing completely unlawful. |
| B.Banning the use of fishing equipment. |
| C.Improving the seafloor environment. |
| D.Investing more in rope-free fishing technology. |
【推荐3】Madagascar, an island nation off the southeastern coast of Africa, is home to some of the most unusual animals in the world. But many of these species may be in danger. Bushes and lowlying plants have started to take up too much space on the forest floor, providing fuel for wildfires. So scientists are considering using giant tortoises to help prevent the forest fires and thereby help the native wildlife in Madagascar.
Why? Long ago, giant tortoises lived all over Madagascar. They ate up many plants that grew on the forest floor. They also spread the seeds of native trees — keeping the ecosystem in check. But when humans settled on the island over 2,000 years ago, hunting caused the giant tortoises native to the island to become extinct.
Now, scientists plan to ship 300 close relatives of the extinct Madagascaran tortoises to the island. They hope that these tortoises will spread the seeds of native plants and chow down on the extra bushes — just like their relatives did long ago.
To find the relatives, scientists studied the fossils of Madagascar's extinct giant tortoises. They discovered that they were actually very similar to another group of giant tortoises that live on the Aldabra Atoll, a group of islands in the Indian Ocean. When the tortoises first arrive in Madagascar, they will live in an area closed off from the rest of the wildlife. There, researchers will watch the tortoises' every move to see how they will react to the native plants. If all goes well, the tortoises will be released into the wild.
Similar practice has been successful in other places. Take the island of Rodrigues, located east of Madagascar, for example. Seven years ago, tortoises were brought there. Now they are spreading seeds and keeping the bushes from taking over. If the same thing works in Madagascar, the giant tortoises may be used to help out other forests around the world.
1. The underlined phrase “chow down on” is the closest in meaning to “________”.| A.walk around | B.eat up | C.go through | D.live with |
| A.They will do an experiment with them. |
| B.They will always keep them off the wildlife. |
| C.They will make them adapt to native plants gradually. |
| D.They will compare them with the extinct tortoises in Madagascar. |
| A.the importance of the forests |
| B.tortoises are widely spread all over the world |
| C.it used to have the same problem as Madagascar |
| D.the giant tortoises can bring hope to Madagascar |
| A.Tortoises come to the rescue! | B.Madagascar's native tortoises brought to life! |
| C.Troubles caused by too many bushes | D.The relationship between tortoises and forests |
【推荐1】Sports can help you keep fit and get in touch with nature. However, whether you are on the mountains, in the waves, or on the grassland, you should know that your choice of sport might have great influence on the environment.
Some sports are resource-hungry(消耗资源). Golf, as you may know, eats up not only large areas of countryside, but also tons of water. Besides, all sorts of chemicals and huge amounts of energy are used to keep its courses(球场)in good condition. This causes major environmental effects. For example, in the dry regions of Portugal and Spain, golf is often held responsible for serious water shortage in some local areas.
There are many environmentally-friendly sports. Power walking is one of them that you could take up today. You don’t need any special equipment except a good pair of shoes; and you don’t have to worry about resources and your wallet. Simple and free, power walking can also keep you fit. If you walk regularly, it will be good for your heart and bones. Experts say that 20 minutes of power walking daily can make you feel less anxious, sleep well and have better weight control.
Whatever sport you take up, you can make it greener by using environmentally-friendly equipment and buying products made from recycled materials. But the final goal should be “green gyms(健身房;体育馆)”. They are better replacements(代替物)for traditional health clubs and modern sports centers. Members of green gyms play sports outdoors, in the countryside or some other open spaces. There is no special requirement for you to start your membership. And best of all, it’s free.
1. What do we know about golf from the passage?| A.It pollutes the environment with all sorts of chemicals. |
| B.It needs water and other energy to keep its courses green. |
| C.It is very popular in Portugal and Spain. |
| D.It causes water shortages around the world. |
| A.It is environmentally-friendly. | B.It improves our health. |
| C.It is simple and free. | D.It can make you put on weight. |
| A.Playing basketball in a gym. | B.Motor racing in the desert. |
| C.Cycling around a lake. | D.Swimming in a sports center. |
| A.To show us some major outdoors sports. |
| B.To encourage us to go in for green sports. |
| C.To discuss the influence of some popular sports |
| D.To introduce some environmentally-friendly sports. |
【推荐2】Xu Hai’ou has spent most of her life promoting environmental protection work in Beihai, a coastal city in the Guangxi Zhuang autonomous region, by cleaning beaches, protecting mi-grant birds and recycling kitchen waste.
Though her family originally comes from the eastern province of Shandong, the 60-year-old was raised in Guangxi and moved to Beihai for work at age 23, directly after graduating from college. Before she retired, she worked as a reporter for the Guangxi Daily Media Group, a news outlet in the region. In her free time, she became involved in voluntary work.
“In initially, in the 1990s, I helped impoverished children in Guangxi’s rural areas obtain financial aid from donors in Hong Kong, and set up my own NGO in 2004. At the time, it was Beihai’s only nonprofit social organization involved in volunteer work,” she said, “It’s very enjoyable to do this charity work and I have made many friends through it.”
She said her NGO focuses on environmental protection work and organizes a range of voluntary activities, including cleaning up beaches, and protecting mangrove forests and migratory birds.
In 2008, the organization joined a marine life protection event supported by the central government, the UN Environment Programme and the Global Environmental Facility.
Xu and her colleagues at the association arranged a number of voluntary events such as raising awareness of marine biodiversity among local residents and students, and beach-cleaning activities to help promote understanding of the need to protect marine animals and plants.
“Undertaking voluntary activities or charitable work has become my mission, and I want to contribute my own efforts to the nation’s environmental protection work, even if they only produce a small improvement. However, protecting the environment is very hard work. which can’t be done by a single person. I sometimes feel like my ability falls short of my wishes.”
According to Xu, her NGO is currently promoting the classification of waste in Beihai and recycling kitchen waste into compost. “We have mature technologies, but still face difficulties in promoting the program because many residents lack awareness of environmental protection. We hope the government can figure out better ways of managing the garbage after we classify it to make full use of this ‘waste’.”
1. What can we learn about Xu Hai’ou from the first two paragraphs?| A.She grew up in Shandong Province. |
| B.She graduated in Beihai at the age of 23. |
| C.She works as a journalist for a newspaper at present. |
| D.She is a retired reporter volunteering to protect the environment. |
| A.Rewarding. | B.Exhausting. | C.Amazing. | D.Embarrassing. |
| A.To clean beaches and recycle kitchen waste. |
| B.To get support from the central government. |
| C.To raise people’s awareness of marine biodiversity. |
| D.To help people understand the necessity of protecting marine life. |
| A.She wants to win a good reputation. |
| B.She wants to do what others don’t want to do. |
| C.She wants to do her part to protect the environment. |
| D.She wants to make the most of kitchen waste on her own. |
【推荐3】To be clear, plastic bags are rightly thought of as a threat that's harmful to human health. According to the National Resources Defense Council, over a decade ago, the average American family took home almost 1,500 plastic shopping bags a year, filling our cabinets, kitchen drawers, and landfills (垃圾填埋场). Today the numbers are slightly better: According to National Geographic, as of 2018, shoppers in the United States use almost one plastic bag per resident per day.
This is not a story on the evil of plastics, but on whether the reusable bag can justify its existence. Although more environmentally friendly than traditional single-use plastic bags, reusable bags, depending on what they are made of, are more energy-intensive (耗能) to recycle.
According to a report by the United Nations Environment Program, “depending on what they are made of, reusable bags might have to be deconstructed in a costly recycling process to separate the different materials. As a result, in many cases, reusable bags are not recycled." That means despite the best intentions, millions of reusable bags designed to replace the need for traditional plastic shopping bags, will also end up in landfills.
Another point to consider, not all reusable bags are equal in terms of their recyclability. There are a wide range of reusable bag options on the market, and reusable bags tend to be made of more than one material to give the bag added reinforcement (耐用) and added street fashion. On a life cycle basis, stronger, heavier bags-no matter what material they are made of-will have a more severe environmental effect. That's because heavier bags use more resources to produce as well as distribute.
Just like plastic bags did, reusable bags multiply rapidly. Used for promotional (促销的)purposes and marketing of all kinds, reusable bags' growing popularity means bags that have been used very little (or not at all) can be found piled in streets, in garbage cans in city parks, and basically everywhere. Therefore, consumers have come to see them as disposable, defeating their very purpose.
In the end, the best practice for reusable bags is to have no half measures: Either use them all the time or don't use them at all. Using a reusable bag once or twice, and then throwing it away, doesn't do the environment any favors.
1. What can we learn from the passage?| A.Plastic bags are refused by environmentalists. |
| B.Shops in America have limited the use of plastic bags. |
| C.The need of strong and fashionable reusable bags is more than the supply. |
| D.Reusable bags demand more resources to produce and recycle than expected. |
| A.being left in landfills |
| B.being used as much as possible |
| C.replacing plastic bags |
| D.promoting goods on the market |
| A.How to Recycle Reusable Bags |
| B.Disadvantages of Plastic Bags |
| C.Reusable Bags? Think Twice! |
| D.Plastic Bags, Less Popular? |
I: Introduction CP: Central Point P: Point Sp: Sub-point (次要点) C: Conclusion
A.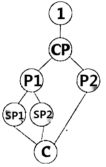 | B.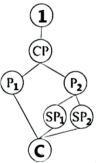 |
C.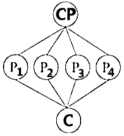 | D.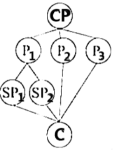 |
【推荐1】Family traditions are experiences or activities that are passed down between generations. These traditions can be as unique and special as the family itself. In addition to being something to look forward to, traditions also establish a foundation for family values and serve as special bonding (联系,连接) experiences.
Traditions can provide families with a sense of identity (身份) and belonging. They can inspire positive feelings and memories upon which family members can recall. Family traditions also provide a sense of continuity across generations. In other words, they are a way of transferring the family’s values, history, and culture from one generation to the next.
People create and maintain family traditions because they bring meaning to celebrations and foster (培养) special bonds. More importantly, traditions create positive experiences and memories for everyone by nurturing (培养,促进) a family’s connection and giving them a sense of belonging.
Family traditions also help children understand who they are and what is important to the family to which they belong. Traditions create a connection for children that comes from feeling like they are part of something that is unique and extraordinary. Family traditions can even contribute to children’ s self-esteem (自尊) and enhance (加强) their well-being (幸福). After all, children find comfort and security when things are predictable and consistent.
Family traditions don’t have to be formal nor do they have to cost money. All that is required to create a new family tradition is something meaningful to your family and a little creativity. Additionally, family traditions do not have to revolve (围绕) around the holidays. You can create family traditions for just about any time of year. Simply look for ways for your family to spend time together doing something they enjoy.
1. What does Paragraph 1 mainly tell us?| A.The way of creating family traditions. |
| B.The foundation of family values and bonds. |
| C.The definition and function of family traditions. |
| D.The effects of family traditions on family members. |
| A.Passing down. | B.Going against. |
| C.Taking away. | D.Referring to. |
| A.They help children love their parents more. |
| B.They help children behave well in the family. |
| C.They help children become successful in business. |
| D.They benefit the development of children’s body and mind. |
| A.Explain ways to spend holidays. | B.Advise creating family traditions. |
| C.Discuss how to enjoy family time. | D.Stress the importance of saving money. |
【推荐2】The Internet, search engines, virtual worlds. Have you ever got the feeling that you’re living in a science fiction?
Well, indeed you are.
For more than a century, inventors have been driven to create what sci-fi writers have imagined long before. Buck Rogers inspired a generation of scientists excited about space exploration. Ray Bradbury predicted home-theater systems. William Gibson dreamed up the Internet while writing Neuromancer on a typewriter. Not long after him, Neal Stephenson predicted virtual worlds in his 1991 novel Snow Crash. One of his readers was Philip Rosedale, who loved it so much that he wanted to build a virtual world based on it.
By the late 1990s, technology caught up to the novel, and Rosedale built the virtual world Second Life based on the “Metaverse” from the novel. With 1 million active users, Second Life offers virtual shops, bars, houses and even virtual television studios with virtual celebrities (名人) on virtual talk shows.
“I think it is pretty much what I imagined,” Stephenson says. “I just shoot for the stars, while he makes great things happen.”
But Snow Crash is a dark book. The world in the novel is filled with criminals, violence and environmental problems.
“Science fiction not only puts stars in our hands, it also helps us see the meaning of our work,” Philip Rosedale admits. “It makes it possible for us to see what all of our efforts could eventually lead to.”
In fact, most science fiction authors admit that their work is usually cautionary (警示性的). “While the inventors are rushing ahead and excited about this possibility or that possibility, we’re always standing there warning, ‘Hang on just a second. Let’s think about this a little more’” author William Gibson says. “But most of them will ignore you because they think they already know all things about any given hot topic of the day. But if you can convince them that you’re talking about a planet millions of miles away and hundreds of years in the future or the past, you can actually get them to examine more closely what’s going on right now.”
1. In which section of a newspaper may this text appear?| A.Book review. | B.Economy. |
| C.Technology. | D.Psychology. |
| A.Buck Rogers. | B.William Gibson. |
| C.Ray Bradbury. | D.Philip Rosedale. |
| A.He is satisfied with the “Metaverse”. |
| B.It is a very violent virtual world. |
| C.It is not based on his fiction strictly. |
| D.More activities should be added to it. |
| A.Sci-fi writers are much wiser than inventors. |
| B.Most inventors do not respect sci-fi writers. |
| C.People can easily get excited about the inventions. |
| D.Sci-fi can help inventors to think more carefully. |
【推荐3】Mathilda, 15, is Turkana, a native people that has survived by raising cattle in a semiarid region. Mathilda's school, like most schools in the area, doesn't have access to clean water and sanitation facilities for its students. So instead of spending their whole school day learning, Mathilda and her classmates start their day by spending two hours to the closest river fetching water—water that is anyway most likely not safe to drink. They do the same thing again in the afternoon, so they often lose around half of their school day fetching water.
Mathilda has to do the same thing outside of school hours to get the water her family needs at home, leaving her little time for studying. Because of rising temperatures, water has become harder and harder to find here, and people have to spend more and more time trying to find it.
This is just one small example of how climate change is making it harder to realise people's rights to water, education and security. Unfortunately, most higher-income countries remained silent on the issue.
This shows that communities already facing marginalization, such as women and children, mostly suffer from climate change. This is especially the case for those in countries with limited resources and fragile ecosystems.
Meanwhile, women consist of the majority of the world's poor, and so are more dependent for their livelihood on natural resources that are threatened by climate change. And around the world, women and girls are the most likely to be responsible for fetching water for their families.
This exposes them to danger and leaves them with less time to attend school, earn money, or simply to rest. But the fact is that the effects of climate change will be felt globally.
Despite the difficulties she is facing, trying to get an education, Mathilda says she hopes to serve her community in a leadership role when she grows up.
“All of the world's leaders need to work together to solve this problem that we are all facing,” she said.
1. Mathilda has to spend _____ fetching water every school day.| A.two hours | B.four hours | C.more than four hours | D.almost a whole day |
| A.the cause and effect of lack of water |
| B.one serious consequence of climate change |
| C.the difficulties in fetching water in the semiarid region |
| D.the hardship of life for the people in the semiarid region |
| A.climate change is everyone's business |
| B.water is becoming rare because of rising temperatures |
| C.fetching water takes up Mathilda's half of studying time |
| D.females are more responsible for fetching water for their families |
| A.rising temperatures | B.fetching water | C.climate change | D.water shortage |



