1 . In 1953, when visiting his daughter’s maths class, the Harvard psychologist B.F. Skinner found every pupil learning the same topic in the same way at the same speed. Later, he built his first “teaching machine”, which let children tackle questions at their own pace. Since then, education technology (edtech) has repeated the cycle of hype and flop (炒作和失败), even as computers have reshaped almost every other part of life.
Softwares to “personalize” learning can help hundreds of millions of children stuck in miserable classes—but only if edtech supporters can resist the temptation to revive harmful ideas about how children learn. Alternatives have so far failed to teach so many children as efficiently as the conventional model of schooling, where classrooms, hierarchical year-groups, standardized curriculums and fixed timetables are still the typical pattern for most of the world’s nearly 1.5 billion schoolchildren. Under this pattern, too many do not reach their potential. That condition remained almost unchanged over the past 15 years, though billions have been spent on IT in schools during that period.
What really matters then? The answer is how edtech is used. One way it can help is through tailor-made instruction. Reformers think edtech can put individual attention within reach of all pupils. The other way edtech can aid learning is by making schools more productive. In California schools, instead of textbooks, pupils have “playlists”, which they use to access online lessons and take tests. The software assesses children’s progress, lightening teachers’ marking load and allowing them to focus on other tasks. A study suggested that children in early adopters of this model score better in tests than their peers at other schools.
Such innovation is welcome. But making the best of edtech means getting several things right. First, “personalized learning” must follow the evidence on how children learn. It must not be an excuse to revive pseudoscientific ideas such as “learning styles”: the theory that each child has a particular way of taking in information. This theory gave rise to government-sponsored schemes like Brain Gym, which claimed that some pupils should stretch or bend while doing sums. A less consequential falsehood is that technology means children do not need to learn facts or learn from a teacher—instead they can just use Google. Some educationalists go further, arguing that facts get in the way of skills such as creativity. Actually, the opposite is true. According to studies, most effective ways of boosting learning nearly all relied on the craft of a teacher.
Second, edtech must narrow, rather than widen, inequalities in education. Here there are grounds for optimism. Some of the pioneering schools are private ones in Silicon Valley. But many more are run by charter-school groups teaching mostly poor pupils, where laggards (成绩落后者) make the most progress relative to their peers in normal classes. A similar pattern can be observed outside America.
Third, the potential for edtech will be realized only if teachers embrace it. They are right to ask for evidence that products work. But skepticism should not turn into irrational opposition. Given what edtech promises today, closed-mindedness has no place in the classroom.
1. According to the passage, education technology can ________.| A.decrease teachers’ working load |
| B.facilitate personalized learning |
| C.help standardize curriculums |
| D.be loved by schoolchildren |
| A.The students who are better at memorization tend to be less creative. |
| B.Schools with bans on phones have better results than high-tech ones. |
| C.Shakespeare was trained in grammar but he penned many great plays. |
| D.Lu Xun’s creativity was unlocked after he gave up studying medicine. |
| A.at the service of teaching |
| B.limited in use among pupils |
| C.aimed at narrowing the wealth gap |
| D.in line with students’ learning styles |
| A.To stress the importance of edtech. |
| B.To introduce the application of edtech. |
| C.To discuss how to get the best out of edtech. |
| D.To appeal for more open-mindedness to edtech. |
2 . Armed with a toolkit of techniques and tricks to calm the mind and bring focus back to your body, you can stop stressful situations from sabotaging your day, says Katy Georgiou.
GROUND YOURSELF
Making contact with the ground is your baseline go-to response for stress. This technique can be especially helpful if you find your stress regularly turns into panic. Wherever you are, whatever you’re doing, place your feet flat on the ground so that you feel stable, and then close your eyes. If you’re able to sit on the floor cross-legged or to lie down flat, then even better.
Think of this as earthing: really connect with the ground beneath your body. Some studies suggest that this simple act can help reduce or relieve symptoms of stress such as pain and fatigue, reduce blood pressure, and improve sleep. If you’re feeling disconnected from the world, it can also remind you that you belong to it and are a crucial part of it — the ground will always be there for you.
LOVE THYSELF
Adopting regular, daily or weekly routines for self-care can be very containing, creating consistency amid all sorts of stressful life events happening around you. Looking in the mirror each day can actually remind you that you exist, so feel free to factor some reflective gazing into your daily routine, whether it’s while applying moisturiser, shaving, or brushing your hair. Studies have shown that being confronted with your reflection can have powerful effects, taking us out of our heads and into the immediate present. For added effect, pay attention to the way your products interact with your hair and skin as you apply them.
Playing around with smells, colours and textures in your hands will also engage your senses. Using a scented shampoo or smoothing on body lotion after a warm bath can be easy ways to do this.
CLEAR YOUR MIND
Abandon all your thoughts and try to focus only on your surroundings. What can you see, hear, smell, taste and touch? Identify three things you can hear, one thing you can taste, four things you can see and two things you can feel on your skin. Pick out colours in the room you are sitting in, notice textures and different kinds of light. If somebody is with you, tell them what you are experiencing. The point here is that your senses are your best and easiest route back to feeling calm, by coming out of your head and rooting yourself back in the present. This is incredibly helpful if you’re having a panic attack or flop response.
1. If your friend Jane always feels worn out and suffers from sleep deprivation, which of the following techniques will you especially recommend to her?| A.Connect her body to the ground beneath her. |
| B.Adopt a daily gaze at her reflection in the mirror. |
| C.Exchange her scentless shampoo for an aromatic one. |
| D.Focus on what she can see, hear, smell, taste and touch. |
| A.Lying down flat can better relieve your stress. |
| B.Grounding yourself can give you a sense of belonging to the world. |
| C.Brushing your hair while looking in the mirror can remind you of your existence. |
| D.Those having a panic attack should shut their senses down. |
| A.help people understand themselves better |
| B.introduce some practical methods for stress management |
| C.emphasize the significance of exploiting multiple senses |
| D.promote a mindset of living in the moment |
3 . How Did You Get Five Fingers?
Your arms and toes began as tiny buds that sprouted from your sides when you were just a four-week-old embryo (胚胎). By six weeks, these limb buds had grown longer and five rods of cartilage 软骨) had appeared in their flattened tips. By week seven, the cells between the rods had died away, forming five small fingers or toes from once-solid masses of flesh.
Now, a team of scientists led by James Sharpe from the Centre for Genomic Regulation in Barcelona has discovered that these events are carefully orchestrated by three molecules. They mark out zones in the embryonic hand where fingers will grow, and the spaces in between that are destined to die. Without such molecules, pianos and keyboards wouldn’t exist, and jazz hands would be jazz palms.
These three molecules work in a way first envisioned by Alan Turing, a legendary English mathematician and code-breaker. Back in 1952, Turing proposed a simple mathematical model in which two molecules could create patterns by spreading through tissues and interacting with each other. For example, the first molecule might activate the second, while the second blocks the first. Neither receives any guidance about where to go; through their dance, they spontaneously organize themselves into spots or stripes.
Since then, many scientists have found that these Turing mechanisms exist. They’re responsible for a cheetah’s spots and a zebrafish’s stripes. For 30 years, people have also suggested that they could sculpt our hands and feet, but no one had found the exact molecules involved.
Sharpe knew that these molecules would need to show a striped pattern. Sox9 seemed like the most promising candidate. It is activated in a striped pattern from a very early stage of development. By comparing cells where Sox9 is active or inactive, Jelena Raspopovic and Luciano Marcon found two other groups of genes—Bmp and Wnt—also formed striped patterns. Bmp rises and falls in step with Sox9 and both are active in the digits. Wnt is out of phase; it’s active in the gaps. The three molecules also affect each other: Bmp activates Sox9 while Wnt blocks it; and Sox9 blocks both of its partners. It looked like these were the molecules the team was searching for not a pair, as Turing suggested, but a trinity. To confirm this, they created a simulation of a growing limb bud and showed that Sox9, Bmp and Wnt could organize themselves into a pattern of five stripes, by activating and blocking each other.
There’s still a lot to discover, though. For example, I’ve used Bmp and Wnt as shorthands here—in reality, each represents a class of several molecules, and the team still needs to work out which specific member is part of the Turing’s proposal.
1. The underlined sentence in the second paragraph means that ________.| A.some certain molecules are necessary for the growth of human fingers |
| B.the development of embryos is dependent on some certain molecules |
| C.without some certain molecules, music won’t exist in this world |
| D.the molecules work in a way that Alan Turing once offered |
| A.Molecules interact by following a strict mathematical model. |
| B.Molecules have a strong will to form patterns in nature. |
| C.The formation of patterns in nature may be dominated by molecules. |
| D.Alan Turing was able to track down the movement of molecules. |
| A.A protein that determines humans’ development in childhood. |
| B.A gene especially important for the development of our limbs. |
| C.A striped pattern that always interacts with Bmp and Wnt. |
| D.A simulation of growing limbs that activate and block each other. |
| A.How human limbs are developed may well be similar to how animal spots are shaped. |
| B.The way Sox9 interacts with Bmp and Wnt is still a mystery that needs further studying. |
| C.Sox9 can activate both Bmp and Wnt to form our limbs, according to scientific research. |
| D.Sox9, Bmp and Wnt are three specific molecules that determine the growth of fingers. |
4 . Group-Centered Societies Have Just as Much Creativity
What does culture have to do with creativity? The answer could be “a lot”. For decades, psychologists trying to understand the roots of creative imaginations have looked at the ways in which two different types of cultures can come to have an effect over its artistic and
Individualism has long been thought to have a creative
The new work comes from comparing communities in different parts of China. Though it scores high, as a nation, on measures of cultural
In the new creativity study, researchers investigated innovation with these two groups in mind. The team used a drawing test that had been created by psychologists. They gave kids a sheet of paper with just a few basic elements printed on it: some dots here, squiggles (弯曲的线条) there, and a rectangle that suggested a drawing frame. The children got 15 minutes to use the elements already on the page to draw whatever they wanted. They could get “adaptive creativity” points for doodling in ways that connected the squiggles and lines into an original and
The researchers gave the test to 683 middle school students from north and south of the Yangtze River. When the scientists got the scores back, they discovered that there were no differences in the children’s overall creativity. When they broke down the results into components, they found that students from collectivistic regions scored
The findings are also a warning against cultural chauvinism (极端民族主义). Western countries have tended to lead the way in innovation — at least as defined by the metrics (指标) we Westerners have created. Perhaps we have been
| A.theoretical | B.inventive | C.productive | D.regular |
| A.prioritize | B.deprive | C.tolerate | D.abandon |
| A.satisfy | B.stimulate | C.cherish | D.sacrifice |
| A.shelter | B.edge | C.border | D.alternative |
| A.embrace | B.propose | C.resist | D.create |
| A.However | B.Therefore | C.Meanwhile | D.Moreover |
| A.broadly | B.objectively | C.seriously | D.narrowly |
| A.individualism | B.identity | C.collectivism | D.flexibility |
| A.selfish | B.collective | C.individualistic | D.realistic |
| A.fall apart | B.fit in | C.give in | D.show off |
| A.separate | B.ugly | C.unified | D.tiny |
| A.catch | B.miss | C.target | D.misuse |
| A.higher | B.averagely | C.lower | D.vaguely |
| A.capturing | B.approaching | C.imitating | D.overlooking |
| A.improvements | B.drawbacks | C.insights | D.attempts |
5 . Making beers on the moon might seem like a pipe dream to many, but for a group of students from the University of California at San Diego, there is a chance to take their research beyond Earth’s surface.
The Lab2Moon competition, held by TeamIndus, is offering students the chance to secure a spot on the TeamIndus rocket this year.
Taking craft beer to the next level, the students want to test whether it’s possible for yeast(酵母) to work and create beer on the moon. However, they believe the experiment is not just a creative concept for astronauts, it’s also important for the development of drugs and yeast-containing food, like bread.
“The idea started out with a few laughs among a group of friends,” said Neeki Ashari, a fifth-year bioengineering students at UC San Diego. “We all appreciate the craft beer. When we heard that there was an opportunity to design an experiment that would go up on India’s moonlander, w e thought we could combine our hobby with the competition by focusing on the practicality of yeast in outer space.”
The preparation work for the beer — up to the stage of adding yeast — will all be done on Earth, and rather than separating the fermentation ( 发酵) and carbonation stage of making beer, the team plans to combine them.
This removes the need to release CO2 accumulated in the process, which may result in cleanliness and safety issues out in space.
If selected, Team Original Gravity will be the first to make beer in outer space, and the fermentation will take place in a container no bigger than a soda can.
All teams competing for the place will showcase their ideas in Bangalore, India, in March.
Sadly, you won’t be enjoying moon beer in your local craft beer bar anytime soon, as no samples will be brought back. However, this small experiment could provide important data on just how practical it is for us to make and create our own resources on other planets and moons by learning how consumables (消耗品) behave in different environments.
1. How did the students feel when they got the chance to design the experiment ?| A.Excited. | B.Nervous. |
| C.Confident. | D.Casual. |
| A.The mixing of two stages. | B.Adding yeast on Earth. |
| C.The preparation work on Earth. | D.Fermentation and carbonation. |
| A.It has been designed based on similar experiments. |
| B.It’s quite competitive compared with other designs. |
| C.It’s design has already been approved by TeamIndus. |
| D.Its process was adapted to make it safer and greener. |
| A.It seems like a pipe dream. | B.It’s extremely complicated. |
| C.It’s meaningful and hopeful. | D.It’s creative but impractical. |
6 . Some of the greatest problems we face today are concerned with the gradual destruction of our environment. Brown clouds; wildlife
But does it do any good?
I recently learned something about flamingos (火烈鸟). These beautiful birds gather in
However, the next day they
The
Then one day something
A few can make a
If you believe in a cause (事业), don’t
| A.protection | B.extinction | C.migration | D.separation |
| A.questions | B.costs | C.examples | D.problems |
| A.drive | B.run | C.cycle | D.stand |
| A.tiny | B.different | C.huge | D.similar |
| A.comes | B.passes | C.varies | D.moves |
| A.all | B.any | C.none | D.most |
| A.gather | B.try | C.sing | D.appear |
| A.attract | B.require | C.escape | D.pay |
| A.plan | B.trend | C.activity | D.movement |
| A.since | B.though | C.unless | D.while |
| A.responsibility | B.notice | C.chance | D.measure |
| A.put off | B.cut off | C.carried out | D.worked out |
| A.approaches | B.works | C.changes | D.disappears |
| A.significant | B.reasonable | C.adequate | D.small |
| A.continues | B.delays | C.finishes | D.begins |
| A.familiar | B.strange | C.magnificent | D.unrealistic |
| A.point | B.decision | C.difference | D.mistake |
| A.useless | B.tireless | C.extra | D.special |
| A.give up | B.give in | C.give away | D.give out |
| A.identify | B.understand | C.predict | D.solve |
7 . The Last Robot-Proof Job in America?
You can get most food, such as warm cookies or vodka, to your doorstep in minutes. But try getting a red snapper (红鲷鱼). Until recently, if you could obtain it, it would likely have been pre-frozen and shipped in from overseas.
A new tech startup is aiming to
There is one thing,
“
By 1 a.m. each night, the company collects
Then, what can a fishmonger see that a computer can’t? DeGregorio showed me his part of the
Is he ever
| A.maintain | B.remedy | C.substitute | D.recognize |
| A.free | B.overseas | C.separate | D.fresh |
| A.therefore | B.otherwise | C.however | D.thus |
| A.ensure | B.propose | C.concede | D.remind |
| A.overpriced | B.misidentified | C.displaced | D.modified |
| A.computer | B.cuisine | C.fish | D.marketing |
| A.Rather than | B.Thanks to | C.Except for | D.Prior to |
| A.fund-raising | B.online-grocery | C.fish-selling | D.non-profit |
| A.significant | B.worthy | C.responsible | D.ridiculous |
| A.sales | B.orders | C.alternatives | D.statistics |
| A.analyze | B.supply | C.prioritize | D.feed |
| A.require | B.process | C.predict | D.value |
| A.calculation | B.decoding | C.correction | D.selection |
| A.smash | B.touch | C.wipe | D.roll |
| A.concerned about | B.eager for | C.delighted with | D.capable of |
8 . Mathew White, an environmental psychologist, is on a mission to give Mother Nature the respect he thinks she deserves when it comes to human health. For decades, scientists and health-care professionals have recognized that exposure to green spaces, such as public parks or forests, is linked with lower risks of all sorts of illnesses common in the world. Experimental work has demonstrated various physiological responses that occur when people spend time in natural environments: blood pressure drops, heart rate decreases, immune function improves, and the nervous system directs the body to rest and digest.
As humans increasingly populate urbanized areas, they are spending less and less time in natural environments. But before doctors can start advising their patients to head to the nearest park, there is an important outstanding question, says White: How much time in nature do you need to generate these apparent benefits? Most of the research that has linked health outcomes with exposure to the natural world didn’t use frequency or duration of park visits, but rather the amount of green space within a certain distance of a person’s home, White says. But “it’s not so much where you live; it’s whether you use it or not.”
So he collected data to estimate what dose(剂量) of nature was needed to show benefits to a person’s health. White’s group found the answer he was after: Spending at least two hours in nature per week was strongly correlated with self-reports of being in good health or having high wellbeing. “I was very surprised, to be honest,” says White, who had been expecting a much longer time. “We had no idea that such a clear threshold of time per week would emerge from the data.”
He was further surprised to learn that it didn’t seem to matter how many trips to a park people took, so long as they got in their two hours per week. It could be a long visit one day, a couple of hour-long trips, three visits of 40 minutes, or four half-hour excursions. He and his colleagues speculate that, if nature’s apparent health benefits are a result of being able to de-stress, then whatever pattern of green space exposure fits one’s schedule is probably the best way to achieve that goal.
Health-care recommendations for people to spend time in nature are probably years away, but the movement has begun. Several organizations around the world are working to promote awareness of nature’s contribution to health. Some researchers have used the term “a dose of nature” to evaluate the amount of exposure needed to gain benefits. “That was kind of the deliberate medicalization of the language around nature and health,” says White.
1. White’s research focused on_______.| A.required amount of green space |
| B.benefits from the exposure to nature |
| C.necessary time length of nature visits |
| D.physical responses to outdoor activities |
| A.Maximum time. | B.Minimum time. |
| C.Adequate time. | D.Average time. |
| A.is confident about his mission |
| B.is willing to cooperate with others |
| C.has persuaded others to accept his idea |
| D.has adopted the term for his research result |
| A.Respect for Nature | B.Nature as Medicine |
| C.Present from Nature | D.Mission in Nature |
9 . We’ve all had the experience of wanting to get a project done but putting it off to a later date. So why do we delay things? Are we built to operate this way sometimes?
These questions are central to my research on goal pursuit (追求). It all starts with a simple choice between working now on a given project and doing anything else. The decision to work on something is driven by how much we value accomplishing the project in that moment — what psychologists call its subjective value. And delay, in psychological terms, is what happens when the value of doing something else outweighs the value of working now.
This way of thinking suggests a simple trick to defeat delay. For example, instead of cleaning my house, I might try to focus on why grading papers is personally important to me. It’s simple advice, but sticking to this strategy (策略) can be quite difficult.
People are not entirely wise in the way they value things. For example, a dollar bill is worth exactly the same today as it is a week from now, but its subjective value — roughly how good it would feel to own a dollar—depends on other factors besides its face value, such as when we receive it. The tendency for people to devalue money and other goods based on time is called delay discounting. For example, receiving $100 three months from now is worth the same to people as receiving $83 right now. People would rather lose $17 than wait a few months to get a larger reward.
Getting something done is a delayed reward, so its value in the present is reduced: the further away the deadline is, the less attractive it seems to work on the project right now. The tendency to delay things closely follows economic models of delay discounting. One way to manage it is to make the finish line seem closer. For example, vividly imagining a future reward reduces delay discounting.
1. Which of the following best explains “outweighs” in Paragraph 2?| A.Is equal to. | B.Is greater than. |
| C.Is involved in. | D.Is central to. |
| A.Avoid setting a deadline too strictly. |
| B.Consider doing nothing temporarily. |
| C.Increase the subjective value of working now. |
| D.Realize great fun of working immediately. |
| A.Time and tide wait for no man. |
| B.A bird in the hand is worth two in the bush. |
| C.One of these days is none of these days. |
| D.Don’t count your chickens before they are hatched. |
| A.Asking for nothing in return. |
| B.Lowering our high expectations. |
| C.Searching for instant satisfaction. |
| D.Making future rewards more inviting. |
10 . Up and down the economic ladder, many Americans who work—and especially those raising kids—are pressed for time, wishing they had more of it to devote to leisure activities (or even just sleeping). At the same time, research has indicated that people who are busy tend to be happier than those who are idle, whether their busyness is purposeful or not.
A research paper released late last year investigated this trade-off, attempting to pinpoint (精确指出) how much leisure time is best. Its authors examined the relationship between the amount of “discretionary time” people had—basically, how much time people spend awake and doing what they want—and how pleased they were with their lives.
The paper, which analyzed data covering about 35,000 Americans, found that employed people’s ratings of their satisfaction with life peaked when they had in the neighborhood of two and a half hours of free time a day. For people who didn’t work, the optimal (最佳) amount was four hours and 45 minutes.
The research traced a correlation (关联) between free time and life satisfaction, but didn’t provide any definitive (最后的) insight into what underlies that correlation—“which is exciting, because this is a work in progress,” says Cassie Mogilner Holmes, a professor at UCLA’s Anderson School of Management and a co-author of the paper, which hasn’t yet been peer-reviewed or published in an academic journal.
An experiment that the researchers arranged hinted at (暗示) a possible explanation of the correlation they found. They asked participants to picture and describe what it would be like to have a certain amount of daily free time, and then report how they’d feel about that allotment (分配). “What we find is that having too little time makes people feel stressed, and maybe that’s obvious,” says Holmes. “But interestingly, that effect goes away—the role of stress goes away—once you approach the optimal point.” After that point, Holmes says, the subjects started to say they felt less productive overall, which could explain why having a lot of free time can feel like having too much free time.
It’s not clear what an individual is to do with these findings, since the amount of free time people have usually has something to do with a variety of factors, such as having children or a degree of control over work schedules. Holmes shared her research with the MBA students in her class on happiness, and some of the most time-crunched among them were comforted by the findings: “I think that two and a half hours creates a nice goal that even if you increase a little bit more of your discretionary time use, you can expect that it will translate into greater life satisfaction.”
1. According to the passage, what happens to Americans occupied with their work?| A.They allow themselves more leisure time. |
| B.They keep themselves busy on purpose. |
| C.They know how much leisure time is best. |
| D.They experience higher level of satisfaction. |
| A.Researchers have cast light on the cause of the correlation. |
| B.Unemployed people need more leisure time to feel content. |
| C.The paper on the correlation has achieved peer recognition. |
| D.Employed people enjoy more leisure time in the neighborhood. |
A.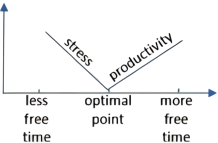 | B.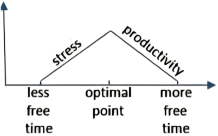 |
C.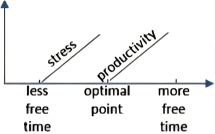 | D.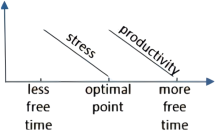 |
| A.Holmes is optimistic about the influence of her findings |
| B.individuals are encouraged to control their work schedules |
| C.people with tight schedules can’t benefit from the findings |
| D.the MBA students find no free time to obtain life satisfaction |



