| A. profitably | B. fallen | C. sell | D. dangerous | AB. dump | AC. efficiently |
| AD. plastic | BC. endless | BD. civilization | CD. throwaway | ABC. stylish |
The value of upcycling
Recycling is a well-known idea that refers to reusing waste materials in any way possible. But what about “upcycling”? It’s a new word, even though it’s something that has been going on since human
One answer to this question is that we reuse fewer and fewer things, and so have become a (n) “
So upcyclers have adopted this new word to focus people’s attention on how waste cannot simply be reused, but be reused
2 . Nearly 40 years ago, Peter Harrison, a marine ecologist witnessed the first recorded large-scale coral bleaching(珊瑚白化)event. Diving in the Great Barrier Reef(大堡礁), he was shocked by the scene before him. "The reef was made up of healthy corals and badly bleached white corals, like the beginnings of a ghost city," he says. Just months before, the same site was filled with colorful tropical life.
"Many of the hundreds of corals that I'd carefully tagged and monitored finally died," he says. "It was shocking and made me aware of just how weak these corals really are.”
Coral exists together with photosynthetic algae(藻类), which live in its tissues and provide essential nutrition(and coloration). But high temperatures and other stresses can turn algae poisonous. When this occurs, the algae may die or be removed by the coral, a process known as bleaching because the coral's clear tissue and white calcium carbonate skeleton(碳酸钙骨骼)are exposed. If the coral can't reestablish its link with algae, it will starve or become ill.
The widespread destruction Harrison saw in 1982 was repeated on many other Pacific Ocean reefs that year and the next. In 1997 and 1998 the phenomenon went global, killing some 16 percent of the world's corals. With rising temperatures, pollution, disease, increased ocean acidity, invasive species, and other dangers, Harrison's ghost cities are expanding
Scientists suppose that about four decades ago severe bleaching occurred roughly every 25 years, giving corals time to recover. But bleaching events are coming faster now—about every six years—and in some places soon they could begin to happen annually.
"The absolute key is dealing with global warming," says marine biologist Terry Hughes. "No matter how much we clean up the water, the reefs will die." In 2016, a record-hot year in a string of them, 91 percent of the reefs that consist of the Great Barrier Reef bleached.
1. Peter Harrison was shocked when diving in the Great Barrier Reef, because___________.| A.the reefs were made up of precious corals | B.the corals were ruined badly and quickly |
| C.he found a ghost city with tropical life | D.he saw the corals he had tagged before |
| A.the causes of coral bleaching | B.the weakness of corals and algae |
| C.the elements that make algae die | D.the process of building a link with algae |
| A.global warming | B.the polluted ocean | C.the white corals | D.invasive species |
| A.With algae living in its tissues, coral's white skeleton is exposed. |
| B.Solving global warming is the real solution to coral bleaching. |
| C.The reefs die because the water hasn't been cleaned thoroughly |
| D.The severest coral bleaching occurred about four decades ago. |
Wildlife Secrets of Nigeria’s Last Wilderness
Researchers from Chester Zoo, working with the Nigeria National Park Service, surveyed over 1,000 square kilometres of the national park. Known
The cameras
The chimp
Chester Zoo is funding guards for the rangers and providing training in wildlife monitoring and protection. “This work is helping us learn more about the secrets of one of our last wilderness areas and we must continue to work together to ensure
4 . "When I was 16 years old, I was diving in Greece, but I was disappointed because I saw more plastic bags than fish.” These are the words of Boyan Slat, an engineer who designed the world's first ocean plastic cleanup system.
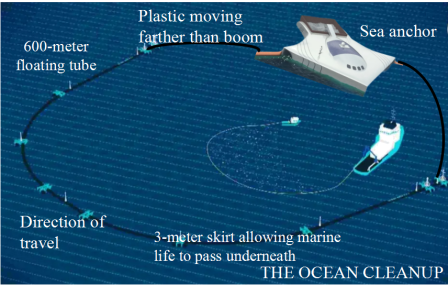
Every year, more than 8 million tons of plastics end up in our oceans, according to the UN Environment Programme. It is predicted that the weight of ocean plastics will match the weight of all the fish in our oceans by 2050. To prevent this from happening, in 2013 Slat created the Ocean Cleanup, an environmental non¬governmental organization, and put his plan for an ocean cleanup device into action.
After years of research and develop¬ment in the Netherlands, a device called System 001/B successfully started gathering plastics on October 2, 2019. The device uses a 600-meter-long C-shaped tube to gather all the floating rubbish. Unlike other cleanup methods, the system floats freely according to the direction of the waves, which allows waste to flow into and stay within the device. A sea anchor is attached to either end. This slows down the system as it floats through the water and allows the faster-moving rubbish, carried by the waves, to flow into its mouth. System 001/B can also collect waste below the surface using a 3-meter-deep skirt(挡板)attached to the end. After being gathered, the trash will be dragged back to shore by boat and recycled.
Right now, the system operates in the Great Pacific Garbage Patch, an area that is 3 times the size of France. Once operational, the Ocean Cleanup expects a full fleet to be able to clear 50% of the Great Pacific Garbage Patch in 5 years.
"It remains to be seen whether this dream will become a reality, but it is undeniable that humanity must work together to reduce our plastic use and repair the damage our waste has caused," Slat said. "We are starting to see a young generation that gets it and is excited about a sustainable (可持续的)future, but the question still comes down to: Are we going fast enough, and how much damage will have been done before we get there?"
1. The underlined word “match” in Paragraph 2 probably means “_________”.| A.compare | B.equal |
| C.measure | D.cover |
| A.To collect ocean plastic waste. |
| B.To help to invent System 001/B. |
| C.To protect the living environment of fish. |
| D.To do research on the ocean environment. |
| A.It can collect and recycle garbage at the same time. |
| B.It can only gather ocean waste which floats on the water. |
| C.It aims to clear up the Great Pacific Garbage Patch in five years. |
| D.It is an ocean-cleaning device which has already been put to use. |
| A.Young generations care less about the environment. |
| B.The future ecology of the oceans is deeply worrying. |
| C.People should work hard to decrease plastic pollution. |
| D.It's quite difficult to repair the damage to the environment. |
5 . Thieving Monkeys — Name Your Price
Human beings are not the only species able to negotiate a deal.
If you visit Uluwatu temple in Bali, be careful. The long-tailed macaques (猕猴) there are well-known thieves. They make a living by
Professor Leca and his colleagues conducted their experiment by wandering around the temple with video cameras, recording the activities of the monkeys. Every time they saw a monkey show interest in a
To work out what was going on, they had first to establish the
To confirm which stealable objects are most
They found that monkeys do have a good sense of what they are doing —
In monkeys, as in people, guile(狡猾)is not a trick that is inborn. It has to be
| A.warning | B.robbing | C.reminding | D.clearing |
| A.deposit | B.dish | C.offer | D.prey |
| A.assign | B.assist | C.assure | D.assess |
| A.particular | B.principal | C.peculiar | D.progressive |
| A.impacts | B.details | C.attacks | D.motions |
| A.precise | B.scientific | C.optional | D.relative |
| A.in spite of | B.in honor of | C.with regard to | D.on behalf of |
| A.preferences | B.potentials | C.performances | D.predictions |
| A.individual | B.independent | C.collective | D.cooperative |
| A.identified | B.valued | C.exchanged | D.rewarded |
| A.refused | B.managed | C.bothered | D.happened |
| A.instead | B.otherwise | C.thus | D.meanwhile |
| A.in practice | B.at least | C.in all | D.at length |
| A.differences | B.distinctions | C.distributions | D.demands |
| A.acquired | B.reversed | C.managed | D.informed |
| A.The man is afraid that the coat color is not cool enough. |
| B.The man hasn’t received the coat he bought the other day. |
| C.The man has worn the coat during the previous season. |
| D.It’s not suitable to wear the coat in the warm weather. |
7 . Mapping Antarctica
Antarctica was on the map long before anyone ever laid eyes on it. Nearly 2,400 years ago, ancient Greek philosophers such as Aristotle believed that a great continent must exist at the bottom of the world. They though it was needed to balance out the continents at the top of the world. In the 1500s, mapmakers often included a fanciful continent they referred to as Terra Incognita(Latin for “unknown land”) at the bottom of their maps. But it was not until the 1800s -----after explorers had sighted and set foot on Antarctica----- that mapmakers got down to the business of really mapping the continent, which is one—and—a –half times rhe size of the U.S..
While the coastline could be mapped by ships sailing around the continent, it took airplanes—and later, satellites---to chart Antarctica’s vast interior(内陆). That job continues today. And it is a job that still require a mapmaker, or cartographer, to put on boots and head out into the wild.
Cole Kelleher is familiar with that. He is a cartographer with the Polar Geospatial Center(PGC), which is based at the University of Minnesota and has a staff at McMurdo Station. PGC teamed up with Google to use the company’s Trekker technology to capture images of Antarctica for the Internet giant’s popular feature, Street View. A Trekker camera, which is the size of a basketball, is set about two feet above a backpack. The camera records image in all directions. “It weighs about 50 pounds. I was out for two and a half days, hiking 10 to 12 hours each day,” says Kelleher. It was hard work, but really an incredible experience.” According to Kelleher there are plans to use the technology to create educational apps for museums.
The PGC staff at McMurdo Station provides highly specialized mapmaking services for the U.S. Antarctic Program. For one project, Kelleher used satellite images to map huge cracks in the ice. That helped a team of researchers know whether they could safely approach their field camp on snowmobiles. Another recent project was to help recover a giant, high—tech helium(氦气) balloon used to carry scientific instruments high into the atmosphere. These balloons are launched in Antarctica because there is no danger that they will hurt anyone when they fall back down to Earth. Using satellite images, Kelleher and colleagues created maps of where the balloon could be found.
Antarctica may no longer be Terra Incognita, but it still holds countless mysteries. Cartographers and the maps they make will continue to be essential in helping scientists unlock those secrets.
1. From the passage, we can infer that Antarctica was on the map in the 1500s when________.| A.mapmakers knew it was much larger than the U.S. |
| B.Aristotle named the continent Terra Incognita |
| C.no one had ever seen or been to the continent |
| D.it was such an interesting continent as was often referred to |
| A.It needs much work for the mapmakers to head out into the wild. |
| B.The interior can only be mapped by planes and satellites. |
| C.It is relatively easy to map Antarctica’s coastline by ship. |
| D.Antarctic is a vast but still mysterious continent. |
| A.to capture images of Antarctica for Street View |
| B.to test the company’s Trekker technology |
| C.to create educational apps for museums |
| D.to hike for an incredible experience |
| A.satellite images which are used to map huge cracks in the ice |
| B.a high-tech helium balloon for carrying scientific instruments |
| C.how to safely approach the researcher’s field camp and the balloon |
| D.the specialized mapmaking services provided by the PGC staff |
Lower Oxygen Levels Threaten Marine Life
Oxygen in the oceans is being lost at an alarming rate, with “dead zones” expanding rapidly and hundreds more areas showing oxygen dangerously exhausted, putting sharks, tuna, marlin and other large fish species at particular risk. Dead zones, where oxygen is effectively absent, have quadrupled(翻两番) in extent in the last half-century, and there are also at least 700 areas where oxygen is at dangerously low levels, up from 45 when research was undertaken in the 1960s.
The reasons behind this environmental collapse are multiple. Among all, pollutants generated by the industrial world have been the most destructive force to cause the unbalance, including a rising tide of plastic waste, as well as other pollutants. Seas are about 26% more acidic than in pre-industrial times because of absorbing the excess carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, according to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, with damaging impacts on shellfish in particular.
Low oxygen levels are also associated with global heating, because the warmer water holds less oxygen and the heating causes stratification(分层), so there is less of the vital mixing of oxygen-rich and oxygen-poor layers. Oceans are expected to lose about 3-4% of their oxygen by the end of this century, but the impact will be much greater in the levels closest to the surface, where many species are concentrated, and in the mid to high latitudes.
Another major cause for lower oxygen is intensive farming. When excess artificial fertilizer from crops, or wastes from the meat industry, runs off the land and into rivers and seas, it feeds algae(藻类) which bloom and then cause oxygen consumption as they die and decay.
The problem of dead zones has been known about for decades, but little has been done to tackle it. Now is high time to take actions and help the oceans function better.
___________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Eating jellyfish could save endangered fish
According to the IUCN Red List 32,000 species are threatened with extinction — everything from birds and mammals. Despite national and international efforts being gathered to protect threatened species, we actively fish for many of them. For those of us who enjoy the odd fish and chips, this isn't great news,
Between 2006 and 2014, 92 vulnerable or endangered species of seafood were being caught, recorded, and sold. When they are sold, it is rare that fish and invertebrate (无脊椎的) species
The research team stresses the fact
There are some ways to untie the mess we're creating in the world's oceans, including
Of course, there are other ways to help keep endangered species
And the informed choice, at least in some places, is
10 . One picture in the Wonder Book of knowledge I had as a little boy showed a man reading a book while floating in the Dead Sea. What a miracle! How would it feel to lie back in water so thick with salt that it was impossible to sink?
Fed by the Jordan River and smaller streams, the Dead Sea is the lowest point on the earth’s surface, and its water is ten times saltier than the Mediterranean. With evaporation its only outlet, salt and other minerals become super-concentrated.
Earlier this year, I drove down the long, steep hill to realize my dream. The shoreline was a broad area of bare salt-mud, but the water edge was far out of sight. Had somebody pulled the Dead Sea’s plug? I wondered. Eli Dior, an Israeli official, explained the problem: “The Dead Sea is drying up. Every year, the surface drops about one meter, and as the water level falls, shadow areas are left high and dry.”
Over the last half-century, the five neighboring countries have collectively diverted nearly all the water flowing into the Dead Sea to meet human and agriculture needs. Result: the Dead Sea is being emptied.
With population in the region set to double at least in the next 50 years, there is little hope of restoring the water being diverted for human consumption. No country has a drop to spare for the Dead Sea, where they know it will just evaporate. To dream of opening the dams and restoring natural balance is plainly unrealistic.
Yet one ambitious high-tech dream may turn out to be not only the salvation of the Dead Sea but also a ticket to peace around its shores. The “Red-Dead” is a proposed $5 billion project to bring sea water some 240 kilometers by pipeline and canal from the Red Sea to the Dead Sea. The Red-Dead may be the only solution, but even if the project is carried out successfully, the Dead Sea will be 10 to 20 meters lower than now and two thirds of its current size.
Whatever the future holds, the Dead Sea’s magical mix of sun, mud, sea and salt will surely survive. Many might complain that the Dead Sea is half empty—but for me the Dead sea will always be half full.
1. What’s the passage mainly about?| A.Dead Sea – miracle of the world. |
| B.Save the environment of the Dead Sea. |
| C.Slow shrinking of the Dead Sea. |
| D.Why is the Dead Sea so salty. |
| A.a severe reduction of the water flowing into the sea |
| B.rapid evaporation of the water in the Dead Sea area |
| C.the increasing quantity of water drawn from the sea |
| D.very low annual rainfall in the Dead Sea Area |
| A.With no outlet to any ocean, the Dead Sea has become by evaporation most dense waters on earth. |
| B.Though burdened with the growing population, the neighboring countries haven’t cut off the sources of the Dead Sea. |
| C.All the countries in the area will consider diverting less water from the Jordan River. |
| D.The Red-Dead Project has not only brought water to the Dead Sea, but peace to the area as well. |
| A.If the Dead Sea dried up, great natural disasters would happen in the region. |
| B.The Dead Sea will not survive no matter what people do to save it. |
| C.The five neighboring countries should stop diverting water from the Jordan River. |
| D.Though the Dead Sea is shrinking gradually, it will not die. |



