Food from the air
Everyone has seen plants growing, but have you ever thought
First, he dried some soil, put it into a pot and weighed it. Next, he weighed a small tree, planted it in the pot and added rain water. Then, he watered it
After five years, he removed the tree from the pot and weighed it again. He found that the tree had gained
We now know that plants and trees make their own food. Their leaves, when exposed
1. How does the woman feel at first?
| A.Curious. | B.Surprised. | C.Excited. |
| A.Flowers. | B.Mushrooms. | C.Trees. |
| A.Two. | B.Three. | C.Four. |
| A.On Thursday. | B.On Friday. | C.On Saturday. |
| A.From not enough water. |
| B.From not enough sun. |
| C.From not enough plant food. |
4 . It’s breathtaking to watch the delicate spring wildflowers come out from their blanket of leaves, bloom, develop and disperse (传播) fruit, all in a matter of a few short days or weeks.
Although they look fragile, these are tough little plants, each focusing its efforts on spreading its species. They have evolved to have a wide range of flower structures and colors, some with fragrances, attracting many different insect species to assist them in pollination (授粉).
There is one strategy (策略) that a surprising number of spring blooming native plants have evolved in common: seed dispersal by ants. As many as thirty percent of the spring flowering plant species in the forests of eastern North America have evolved to take advantage of this situation to benefit themselves. These species have evolved to provide food attached to their seeds to encourage ants to disperse those seeds. This food, called an elaiosome, is a specialized fat body whose chemical composition more closely matches that of the insects that ants prefer than it does that of a seed.
When a fruit opens to disperse its seeds, the elaiosomes are an instant attraction for ants. They take the seed with its attached elaiosome back to their nests for consumption there, but they just eat the elaiosome, their preferred food, and dispose of the seed on their trash pile. This tends to be an environment that is rich in nutrients, and will benefit the growth of the new plant. Just to make sure the ants don’t eat the seeds in addition to the elaiosome, some plant species have hard seed coatings that ants can’t really bite through.
This evolutionary adaptation is somewhat similar to the strategy of plants that have evolved to surround their seeds with fleshy fruits to attract birds to assist them with seed dispersal. Given the fact that there are fewer birds available in early spring to help with seed dispersal, it makes sense that the early blooming plants evolved to partner instead with the ants for this service.
Did you ever wonder how your Spring Beauty managed to pop up in new locations in your lawn or garden? Thank an ant!
1. How many methods do wildflowers have to attract animals according to the text?| A.Two. | B.Three. | C.Four. | D.Five. |
| A.It’s hard to digest. | B.It’s impossible for ants to resist. |
| C.It makes the earth rich in nutrients. | D.It’s often thrown into the trash pile. |
| A.Ants are creative and hardworking. |
| B.Ants are better at dispersing than birds. |
| C.The birds in the early year are not enough. |
| D.The birds are not interested in their fleshy fruits. |
| A.Thank Ants for Wildflowers |
| B.Wildflowers Discover Their Treasures |
| C.New Species of Wildflowers are Found |
| D.Ants Are Superheroes Protecting Environment |
Nature’s Lungs
We know that trees are nature’s purifier (净化器): They absorb carbon emissions (碳排放)and release oxygen. But their
According to the study, there are
This may sound like a lot,
Yet, planting trees is still considered the most effective way
6 . Scientists have been experimenting with playing sounds to plants since at least the 1960s, during which time they have been exposed to everything from Beethoven to Michael Jackson. Over the years, evidence that this sort of thing can have an effect has been growing. One paper, published in 2018, claimed that an Asian shrub known as the telegraph plant grew substantially larger leaves when exposed to 56 days of Buddhist music — but not if it was exposed to Western pop music or silence. Another, published last year, found that marigolds and sage plants exposed to the noise of traffic from a busy motorway suffered growth difficulty.
Plants have been evolving (进化) alongside the insects that eat them for hundreds of millions of years. With that in mind, Heidi Appel, a botanist now at the University of Houston, and Reginald Cocroft, a biologist at the University of Missouri, wondered if plants might be sensitive to the sounds made by the animals with which they most often interact. They recorded the vibrations made by certain species of caterpillars (毛毛虫) as they chewed on leaves. These vibrations are not powerful enough to produce sound waves in the air. But they are able to travel across leaves and branches, and even to neighbouring plants if their leaves touch.
They then exposed tobacco plant — the plant biologist’s version of the laboratory mouse — to the recorded vibrations while no caterpillars were actually present. Later, they put real caterpillars on the plants to see if exposure had led them to prepare for an insect attack. The results were striking. Leaves that had been exposed had significantly higher levels of defensive chemicals, making them much harder for the caterpillars to eat. Leaves that had not been exposed to vibrations showed no such response. Other sorts of vibration — caused by the wind, for instance, or other insects that do not eat leaves — had no effect.
“Now speakers with the right audio files are more often being used to warn crops to act when insects are detected but not yet widespread,” says Dr. Cocroft. “Unlike chemical pesticides, sound waves leave no dangerous chemicals.”
1. What can we learn about plants from the first paragraph?| A.They may enjoy Western music. | B.They can’t stand Buddhist music. |
| C.They can react to different sounds. | D.They can make different sounds. |
| A.Plants can make a cry for help. | B.Plants evolve alongside insects. |
| C.Plants are sensitive to the sounds. | D.Plants have been studied for years. |
| A.They can recongnize harmful vibrations. | B.They look like laboratory mice. |
| C.They can threaten the caterpillars. | D.They can release poisonous chemicals. |
| A.Disadvantages of chemical pesticides. | B.Application of the experimental results. |
| C.Interaction between plants and insects. | D.Warning system of widespread insects. |
7 . Suzanne Simard, a professor of forest ecology who called herself a “forest detective”, was raised in mountains in Canada. Few scientists make much impact with their PhD thesis, but, in 1997, she did just that. Her research on the “wood wide web” made the cover of Nature and transformed our understanding of forests. What was then a challenge to traditional ideas is today widely accepted.
A mushroom is the part of a fungus (真菌) that sticks up above the ground. Thin, white threads grow from its stem deep into the soil. These threads are called hyphae (菌丝). Hyphae connect themselves to tree roots. They also stretch from root system to root system, like an underground network. This network may go for miles. Hyphae pick up nutrients and water from soil. The fungus threads that connect to tree roots share their nutrients and water with the trees. In return, they sip a bit of the sugar the trees make. Sharing helps both trees and mushrooms live. It’s also how trees communicate.
When a tree is being eaten by bugs, it makes chemicals to shoo them away, sort of like bug repellent (驱虫剂). The chemicals travel through the tree, down its roots, and into the hyphae network. Other trees connected to the network taste the chemicals. That tells them a nearby tree is under attack, so they start to make their own bug repellent. Trees do more than share warnings through the hyphae. They also help each other. In the fall, paper birch trees drop their leaves and can no longer make sugar. So, a fir tree that stays green all winter uses the network to send extra sugar to the birch until spring comes again. This system of sharing information and nutrients through the hyphae is sometimes called the “wood wide web”, because it works a bit like the Internet.
Local climate sets the stage for the wood wide web, researchers say. In cool temperature and boreal forests, where wood and organic matter decay slowly, network-building EM fungi rule. By contrast, in the warmer tropics where wood and organic matter decay quickly, AM fungi dominate. These fungi form smaller webs and do less intertree swapping, meaning the tropical wood wide web is likely more localized.
Ecologist Thomas Crowther’s results suggest that as the planet warms, about 10% of EM-associated trees could be replaced by AM-associated trees. Microbes in forests dominated by AM fungi deal with carbon-containing organic matter faster, so they could liberate lots of heat-trapping carbon dioxide quickly, potentially accelerating a climate change process that is already happening at a frightening pace.
1. What do we know about Suzanne Simard?| A.She was a professor and a forest detective. |
| B.Growing up in the countryside, she made the cover of Nature. |
| C.Like many other scientists, she made big influence on her PhD thesis. |
| D.Her idea of the “wood wide web” used to challenge people’s thoughts. |
| A.They facilitate tree communication. | B.They form an underground network. |
| C.They produce sugar and share it with trees. | D.They share nutrients and water with the trees. |
| A.They release warning signals through leaves. |
| B.They produce real bug repellent to kill insects. |
| C.They make use of hyphae to produce chemicals. |
| D.They send chemical signals through the network. |
| A.It might slow down carbon release. | B.It would break down organic matter. |
| C.It might speed up climate change. | D.It might lead to faster tree growth. |
8 . The candy we eat, the tea we drink, the lotion we use---they all likely contain ingredients from wild plants. While natural ingredients can be beneficial to buyers, the way those plants are harvested could harm ecosystems. In a recent United Nations report, medicinal plant experts revealed the risks behind several of them, including Brazil nuts, frankincense, goldenseal, gum arabic, and licorice.
Plant derivatives (衍生物) in household products “sit there somewhere in the middle of the ingredients list” on product labels, often going unnoticed, says Caitlin Schindler, lead author of the report. Even if consumers do take note, there’s no information about what’s involved in obtaining or processing the derivatives.
Many of these plants are threatened with extinction from overharvesting, disease and pests, climate change, and habitat loss. The endangered state of more than 20,000 medicinal plant species has never been assessed, which means it’s impossible to know whether their use is sustainable.
Meanwhile, the trade in wild plants is booming. U. S. consumers spent more than $12.3 billion on herbal dietary supplements in 2021---up more than 9 percent from 2020. Wild plants have been used locally for centuries, but today’s global demand puts many at risk. And international customers often have no idea where these products originate.
Should consumers stop buying the products? No. Schindler says, because “the ingredients are really critical to a lot of people’s livelihoods.” Solutions for transforming the trade in wild plants are rooted in awareness. The first step for consumers is to “just notice that you’re buying something that has a wild ingredient,” she says. It’s generally safer to purchase local products and splurge on more expensive ones, if possible.
Consumers can also look for organic and fair-trade certifications. Various programs evaluate wild-plant supply chains for sustainability, and many companies advertise these certifications, either on the product or online. One of the most prominent is Fair Wild, which assesses environmental risks and recommends best sourcing practices. If certifications are missing, Schindler encourages people to challenge companies to do better. “Until businesses get a bit more pressure from consumers, we won’t see any changes happening,” she says.
1. What can we learn about wild plants according to the report?| A.Their current situation is ignored. | B.They are limited on a global scale. |
| C.They have been evaluated regularly. | D.Their process information is on the label. |
| A.Get rid of. | B.Spend much money on. |
| C.Pay attention to. | D.Conduct many experiments on. |
| A.They confirm the quality of the wild plants. |
| B.They offer consumers rights to assess the products. |
| C.They ensure the use of wild plants at a steady level. |
| D.They inspire companies to make more advertisements. |
A.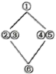 | B.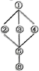 | C.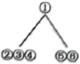 | D.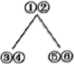 |
9 . In 1986, when he was only a prince. King Charles told a television interviewer that it was important to talk to plants. He was widely laughed at. But his wisdom seems to have been ahead of its time, for there is now plenty of evidence that plants can detect (察觉) sound, react to it, and even perhaps produce it.
Scientists have been experimenting with playing sounds to plants since at least the 1960s, during which time they have been exposed to everything from Beethoven to Michael Jackson. Over the years, evidence that this sort of thing can have an effect has been growing. One paper, published in 2018, announced that an Asian plant grew much larger leaves when exposed to 56 days of Buddhist chants — but not if it was exposed to Western pop music, or silence. Another, published last year, found that plants exposed to the noise of traffic from a busy motorway suffered slow growth, and produced a range of stress compounds (成分).
Another research reports that certain frequencies (频率), played in some environments like greenhouses, can affect seed growth and even improve crop production. And plants can make noises, too. Earlier this year a group of researchers at Tel Aviv University published an article in Cell Press, reporting that several plants gave out different noises in response to different stresses — although not at the sorts of frequencies that humans can hear. Humans can only hear frequencies of up to 16 kilohertz. Scientists discovered sounds given out by plants were up to 250 kilohertz.
If all that sounds strange, perhaps it should not. After all, sound carries useful information.
From an evolutionary point of view, there is no reason to expect that information to be applied only by animals.
1. What was most people’s attitude to Charles’ opinion?| A.Unclear. | B.Positive. | C.Cautious. | D.Negative. |
| A.Different sounds have different effects on plants. |
| B.Buddhist chants don’t make a difference to plants. |
| C.Western pop music does good to plants’ growth. |
| D.The noise of traffic produces stress compounds. |
| A.The sounds are strange. | B.The plants grow in greenhouses. |
| C.The plants are under great stress. | D.The sounds are at high frequencies. |
| A.It’s the important to talk to plants. |
| B.Sounds make a difference to plants. |
| C.Plants can discover and even make sound. |
| D.Humans can’t hear sounds produced by plants. |
10 . In times of intense stress, people sometimes let it out with a scream and a new study suggests that plants might do the same. Researchers at Tel Aviv University in Israel has found that plants let out ultrasonic (超声的) screams when damaged or stressed by drought.
The noises, falling within a range of 20 to 100 kilohertz, are too high-frequency for humans to hear, but other plants and some animals perceive them. Insects might be listening for sounds from stressed plants to assess their condition before laying eggs on their leaves. A moth (蛾) may decide against laying eggs on a plant that sounds water-stressed.
Researchers attached recording devices directly to plants to listen for secret sounds inside their stems (茎). In drought, air bubbles formed, burst and caused vibrations (振动) within the tissue that normally carries water up the plants’ stems. The process was picked up by the attached recording devices, but researchers wanted to know if any plant sounds could travel through the air.
So the team placed microphones 10 centimetres from stressed-out tomato and tobacco plants. They subjected one set of crops to drought and another to physical damage. A third group was untouched.
The microphones did pick up distinct sounds. On average, drought-stressed tomato plants let out about 35 ultrasonic screams per hour, while those with cut stems made about 25. Drought-stressed tobacco plants let out about 11 screams per hour, and cut crops made about 15 sounds in the same time. The average number of sounds from untouched plants fell below one per hour.
The researchers also attempted to identify each plant group just based on its screams. Using a type of artificial intelligence calculations, the team picked out distinct features in each set of sounds and successfully sorted their plants into three kinds: “dry, cut or untouched.”
If it is not too costly to set up the recording in a field situation, farmers might be able to hear these stress signals too. In future, enabling farmers to listen for water-stressed plants could “open a new direction”, which will be increasingly important as climate change exposes more areas to drought.
1. The moth is mentioned in paragraph 2 to show __________.| A.moths need enough water when laying eggs |
| B.some animals are able to hear plants scream |
| C.some insects are picky about their surroundings |
| D.wildlife species depend on each other when stressed |
| A.Plants’ sounds couldn’t be detected by humans. |
| B.Plants can be grouped according to their features. |
| C.Plants’ screams are related to stress types in a way. |
| D.Air bubbles contribute to the lack of water in plants. |
| A.Supporting evidence for the research result. |
| B.Potential application of the research findings. |
| C.A further explanation of the research methods. |
| D.A reasonable doubt about the research process. |
| A.Plants’ Vibrations: Way to React to Stress |
| B.Stress Signals: Secret Newly Found in Plants |
| C.Green Screams: Plants Make Noises When Stressed |
| D.Ultrasonic Screams: Discovery Opens a New Chapter |



