1 . As Earth’s climate continues to change, a plant’s ability to adapt to its changing environment is important to its survival. Often, to stay alive, a plant must move locations by releasing its seeds, but plants are rooted in the ground and cannot move themselves. Instead, they are dependent on animals or the wind to carry their seeds to a new location.
Playing an essential part in an ecosystem (生态系统), plants create resources like food and medicine for us human beings. A team of researchers developed the model to better understand how plants can stay resiliency (韧性) when facing challenges like climate change.
“Once seeds are released from a plant, we wanted to know how far they can go because as wind conditions shake, the seeds will be moved around differently because of various weights, sizes, and shapes,” says Binbin Wang, an assistant professor at the University of Missouri.
Changes in one part of the ecosystem can create a “snowball effect” on other parts. That’s why understanding seed spread is important. Plants can only make this move once during their life — as a seed, says Lauren Sullivan, an assistant professor at Michigan State University.
“Understanding how plants move as seeds year-round is important for us to analyze how they’ll be able to handle climate change,” Sullivan says. “This movement is also important for how we can increase diversity (多样性) in the ecosystem.” “We’re now able to partner with researchers. This innovative approach can help us develop accurate models that are simple enough to make good predictions in a short time.”
The model, which makes predictions based on seed and plant type, plant height, and wind speed, can develop an entire year’s worth of predictive data in just one or two days. As part of their future work, the team will develop educational programming for K-12 and college students. For example, they will provide opportunities for college students to explore how different disciplines, such as agriculture, biological sciences, and engineering, can work together to solve different real-world problems.
1. Why did the researchers develop the model?| A.To learn how plants handle challenges like climate change. |
| B.To find out what helps seeds travel to different places. |
| C.To study the effects climate change has on plants. |
| D.To create more food and medicine resources. |
| A.Its weight. | B.Its location. | C.Its size. | D.Its shape. |
| A.It is caused by the change of the climate. |
| B.It can happen during the whole life of a plant. |
| C.It has an effect on other parts of the ecosystem. |
| D.It’s hard to be predicted for the diversity of ecosystem. |
| A.Explore different disciplines for college students. |
| B.Work together to solve different real-world problems. |
| C.Develop educational programming for students to explore. |
| D.Make valuable predictions about the type and height of the plants. |
1. What makes potted roses easier to plant?
| A.Lower nutrition requirement. |
| B.Stronger cold resistance. |
| C.Better root development. |
| A.They need less soil. |
| B.They are easier to transport. |
| C.Their planting time is fixed. |
| A.Damp condition. | B.Heavy sunshine. | C.Continuous watering. |
| A.Types of roses. | B.Ways of rose packing. | C.Tips on rose growing. |
3 . Plants do not suffer in silence when thirsty or stressed, according to a new study published today in Cell.
Plants that need water or have recently had their branches cut produce up to roughly 35 sounds per hour, the authors found. But well-watered and uncut plants are much quieter, making only about one sound per hour.
The reason why you have probably never heard a thirsty plant make noises is that the sounds are so high-pitched that very few humans could hear them. Some animals, however, probably can. Bats, mice and moths could possibly live in a world filled with the sounds of plants, and previous work by the same team has found that plants respond to sounds made by animals, too.
To overhear plants, Lilach Hadany at Tel-Aviv University in Israel and her colleagues placed tobacco and tomato plants in small boxes provided with microphones. The microphones picked up any noises made by the plants, even if the researchers couldn’t hear them. The noises were particularly obvious for plants that were stressed by a lack of water or recent cutting.
Plants do not have vocal cords (声带) or lungs. Hadany says the current theory for how plants make noises centers on their xylem (木质部) that transport water and nutrients from their roots to their branches and leaves. Water in the xylem is held together by surface tension, just like water moving through a drinking straw. If an air bubble (气泡) forms or breaks in the xylem, it might make a little popping noise; bubble formation is more likely during dry seasons. But the exact system requires further study, Hadany says.
The team produced a machine-learning model to check whether a plant had been cut or was water-stressed from the sounds it made, with about 70% accuracy. This result suggests a possible role for the audio monitoring of plants in farming and gardening.
To test the practicality of this approach, the team tried recording plants in a greenhouse. Pilot studies by the authors suggest that tomato and tobacco plants are not exception. Wheat, corn and wine grapes also make noises when they are thirsty.
1. What is the new research mainly about?| A.Plants can react to animals. | B.Plants can produce sounds. |
| C.Well-watered plants keep silent. | D.Branchless plants need watering. |
| A.They can create more bubbles. | B.They can feel less stressed. |
| C.They require less nutrient supply. | D.The y need lungs to breathe more. |
| A.Fruit growing. | B.Crop selection. |
| C.Water source protection. | D.Noise pollution test. |
| A.How Plants Are Thirsty | B.When Nature Expresses Itself |
| C.How Plants Cry for Their Needs | D.When Creatures Hear Each Other |
Scientists in Florida have
According to Professor Anna-Lisa Paul, all the plants looked the same
DNA testing showed that those Thale Cress 2
NASA Administrator Bill Nelson believes this research will help future space missions and that resources on the moon and Mars
5 . It has long been known that plants communicate when they are stressed. You need only observe a houseplant to realize that a plant wilts (枯萎) when it needs water. Some plants may also emit a terrible taste to prevent some insects from hurting them.
Now, a new study that was conducted by researchers at Tel Aviv University, shows that not only do plants express themselves in the above ways when stressed, they also make sounds, like talking.
According to the researchers, plants make sounds at frequencies (频率) between 40 to 80 KHZ — out of the range of human ears — but within the range of some animals. “Bats make sounds in these ranges all the time, and mice, dogs and cats can partially hear within it,” Dr. Lilach Hadany, a Professor at Tel Aviv University, and one of the authors of the study said.
One of the primary breakthroughs (突破) of Hadany’s study is that the researchers have managed to understand and classify the sounds that plants make for the first time. Plants that are not stressed make about one noise per hour, but plants that are stressed or injured make many hundreds of sounds per hour. And each of these sounds seemed to be specific to the type of stress the plant was under.
This type of information could be important for agriculture. Knowing what sounds their plants are making could help farmers determine whether their crops are in danger of drought or disease and allow them to make the necessary changes to help their plants.
Amazingly enough, the researchers are not actually sure how the plants make sounds. But anyway, the discovery is still a game-changer for plant science, and potentially for the future of agriculture. One day soon your plants may be able to tell you if they are hungry, thirsty, or just feeling lonely.
1. What does the underlined word “emit” in Paragraph 1 probably mean?| A.Give off. | B.Add to. |
| C.Clear up. | D.Take in. |
| A.Humans. | B.Bats. |
| C.Mice. | D.Dogs. |
| A.They’ve found plants can communicate with each other. |
| B.They’ve used plants’ sounds to improve agriculture. |
| C.They can understand and classify plants’ sounds. |
| D.They’ve discovered how plants make sounds. |
| A.Scientists Discover the Language of Plants |
| B.Animals Understand Plants’ Language |
| C.Plants Communicate in Various Ways |
| D.Stress Makes Plants Talk |
6 . Tomatoes taste great. With a lot of vitamins, they are good for you, too! People around the world enjoy this amazing fruit.
Not all tomatoes are red. They can be yellow, orange, pink or white. All tomatoes are green before they are ready to be picked. Then the tomatoes turn their true color. That’s when they are ready to eat!
Tomatoes first grew in the Americas. The Incas (印加人) grew them over 1,000 years ago. They were introduced to Europe by the Spanish in the early 16th century. The Spanish and Italians seem to have been the first Europeans to accept them as food. In France, people grew tomatoes in the garden just to enjoy their beauty. Many people there thought tomatoes would make them sick. It was years before some of them would eat tomatoes.
Tomatoes are fruits. They grow from seeds. They won’t grow in cold weather. But with water, sunlight and warmth, tomatoes grow fast. They can grow in pots or in the ground. As the plant grows taller, people may tie it to a stick. Next is the blooming stage. Flowers appear. The flowers turn into fruit. Some kinds of tomatoes can be picked in about six more weeks. Some tomatoes are large. One kind of tomato can weigh as much as two pounds.
You can eat raw tomatoes. First, wash them. Then, cut them up for salads or sandwiches. Tomatoes can be cooked, too. They can be grilled, boiled, or even fried. Do you use ketchup (番茄酱)? It is made from tomatoes. Tomatoes don’t have a smell. But they taste great in foods around the world. Many dishes from India use tomatoes. Italians use them to make spaghetti sauce and pizza, too.
1. What can we know from the passage?| A.Tomatoes come in different colors. | B.Tomatoes grew in Europe first. |
| C.Tomatoes can grow in all weathers. | D.Tomatoes have a special smell. |
| A.Time. | B.Board. | C.Set. | D.Flower. |
A. 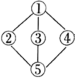 | B. | C.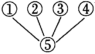 | D.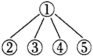 |
| A.Family. | B.Food. | C.Science. | D.Health. |
7 . Warmer oceans can cause coral (珊瑚) bleaching. Bleaching happens when the coral, colonies of tiny animals called polyps, lose colored algae (藻类) living in their bodies and turn completely white. Without the algae, the coral loses its main food source and can die.
In 2021, the United Nations reported a 14 percent loss of corals across the world largely from rising sea temperatures in the previous 13 years. Australia declared mass bleaching events in 2022 across large parts of the Great Barrier Reef, the fourth since 2016.
Reefs in Hawaii, Florida, and the Caribbean were all severely affected, but thankfully some coral areas were not. Scientists looked into the characteristics of these corals and their ecosystems to see how others could be protected. Warm water reefs in the tropics are the worst affected by bleaching, but they also contain corals with better heat resistance.
Research is focused on finding genes for heat tolerance so that they can be passed on to future generations. Biologists mix corals that are more resilient to higher temperatures with those that are not and the resulting hybrid generation has a better chance of survival.
Researchers in Florida’s reefs have been using ocean nurseries to replant coral with batches that contain genes resistant to heat, acidification, and disease. Those areas have recovered within a year.
Other projects like Revive and Restore are using methods like preserving older coral populations’ sperm and eggs (biobanking) and using corals with better adaptability characteristics in breeding. The project also believes that boosting biodiversity by restoring (恢复) seabirds to islands, and ridding them of invasive species like rats, helps coral reefs thrive.
Ultimately, scientists say that without a serious reduction in greenhouse gas emissions, 99 percent of the world’s coral reefs will be gone by the end of the century. There is a limit to how quickly coral can adapt, especially given the rate of climate change. Computer simulations have shown that mild or moderate warming allows coral to adapt, but if temperatures rise rapidly then extinction is certain.
1. What mainly causes coral bleaching?| A.Loss of algae. | B.Lack of food. |
| C.Warm oceans. | D.Ocean pollution. |
| A.Coral reefs in tropics are easier to bleach. |
| B.Some corals are found better to resist heat. |
| C.Coral reefs in some areas are badly affected. |
| D.Ecosystems in some coral areas are destroyed. |
| A.Breeding hybrid generation with heat resistance. |
| B.Replanting batches of corals containing diseases. |
| C.Restoring seabirds of islands and invasive animals. |
| D.Setting no limitation of greenhouse gas emissions. |
| A.Botany. | B.Culture. | C.Nature. | D.Education. |
8 . Increased human activity and climate change have caused a rise of algae (藻类植物) in water bodies around the world—sometimes choking ecosystems of sunlight and oxygen. In more extreme cases, they can produce dangerous poisons that can sicken or kill people and animals. But the plenty of algae could prove crucial as our population rises beyond eight billion people worldwide because algae are crops that don’t need land, freshwater, or fertilizer to fill nutritional gaps.
And even though they are so closely associated with human’s bad impact on Earth, algae could also play vital roles in slowing climate change and helping fight against pollution, viruses, and more. With microplastic pollution documented in almost all habitats related to water, a study showed that algae can help filter microplastics from water. Algae can also filter chemicals that can be used for fertilizer.
Algae can produce more effective biofuel than traditional sources. Rescarchers at a German algae growing facility are already using it to fuel plane. Researchers believe this and other sustainable fuels could reduce carbon released from airplanes by up to 80 percent.
Animal feed containing a kind of red algae reduces harmful methane(甲烷)released from cattle by more than 80 percent. The addition works by changing the environment in a cow’s stomach, stopping the production of methane before it can be released.
Red algae can stop the copies of some viruses, and have been shown to stimulate the body’s immune (免疫的) system and could become a powerful anti-HIV medicine.
In 2019, freshwater algae were launched into space to change the CO2 breathed out by astronauts on the International Space Station into oxygen. Since algae are also high in protein, they could replace up to 30 percent of astronaut food in the future.
1. What can we know about algae from the first paragraph?| A.Better late than never. | B.Every coin has two sides. |
| C.All is well that ends well. | D.Two heads are better than one. |
| A.They avoid climate change. | B.They absorb pollutants in the air. |
| C.They reduce microplastics in the water. | D.They filter most poisonous chemicals. |
| A.Change animal feed into methane. |
| B.Store carbon released from airplanes. |
| C.Help researchers to create traditional sources. |
| D.Create biofuel and reduce methane in cows’s stomach. |
| A.By helping fight against diseases. | B.By increasing human’s strength. |
| C.By producing more oxygen than other plants. | D.By replacing much food for astronauts. |
9 . Forests are feeling the heat. In places like the American West, rising temperatures and drought mean less water for trees. Now, scientists have found that thinning early in forest growth creates tougher trees that can endure climate change. What’s more, these thinned forests can suck carbon out of the air just as fast as thick forests.
“When it comes to carbon storage and climate change adaptation, we can have our cake and eat it too,” says Andrew Larson, forest ecologist and author of the new study. “It’s a win-win.”
As trees grow, they convert carbon dioxide to food and store it in their leaves, trunks, and roots. But if trees get too crowded, they compete for light and water. Removing some trees can ease the competition, letting the remaining trees grow big and healthy. But scientists worry that removing trees can reduce forest carbon storage.
To see whether the climate trade-off truly exists, scientists tapped into a long-term experiment in northwestern Montana. In 1961, U.S. Forest Service officials started the experiment in a young forest of western larch. The forest was broken up into plots. In some plots, the 8-year-old trees were thinned from tens of thousands per hectare down to 494 per hectare. These trees grew thick trunks and broad tree shades. Other plots were left alone, and the trees there grew tall and skinny as they competed for sunlight. The original study was rooted in an interest in growing timber rapidly. But the scientists at the University of Montana sprouted a new question: How did tree density (密度) influence carbon storage?
To find out, they measured tree height, diameter, and width of branches to estimate the amount of carbon stored. They also calculated the carbon contained in other plants, dead wood, and forest floor debris. The research showed total carbon was nearly the same in both forests. The un-thinned forest had more trees, but the thinned forest compensated with bigger trees.
1. What is scientists’ finding about forests?| A.The tougher trees in thinned forests stand climate change. |
| B.Thinned forests have as much carbon as thick forests. |
| C.The American forests are suffering sever heat wave. |
| D.The thick forests grow rapidly than thinned ones. |
| A.We are able to produce and enjoy a cake together. |
| B.Carbon storage and climate stability are the final goals. |
| C.We can choose between carbon storage and climate change. |
| D.Carbon storage and climate adaptation can be achieved meanwhile. |
| A.Through observing forests grow. |
| B.Through comparative experiments. |
| C.By providing examples to illustrate. |
| D.By collecting massive amounts of data. |
| A.To achieve how to plant trees scientifically. |
| B.To test how much carbon forests contain. |
| C.To prove the advantages of thinned forests. |
| D.To see how tree density affects carbon storage. |
Herbal tea has v



