1 .
| A.The harm done by single-use plastics. |
| B.The topic for the woman’s composition. |
| C.Environmental issues. |
| D.Some recent hot news. |
2 . We should all have at least one fire extinguisher somewhere in our home, but it’s not enough to simply keep one under the kitchen sink. If there is a fire, your safety — and the safety of your home — depends on knowing how to use that fire extinguisher correctly. In case your fire extinguisher has been sitting around collecting dust, here’s everything you need to know before brushing it off and fighting a fire in your home the right way.
Choose the right fire extinguisher
The first thing you need to know is the different classifications of fires. Most household fires fall into one of the following categories:
Class A: Fires fueled by solid combustibles like wood, paper, and cloth.
Class B: Fires fueled by flammable liquids such as oil and gasoline.
Class C: Fires started or fueled by faulty wiring and appliances.
Class D: Fires started or fueled by cooking oils, animal facts, and vegetable fats.
All fire extinguishers are labeled to indicate which classes of fire they are designed to combat. Most household fire extinguishers are considered multipurpose and labeled for use in A, B, and C classes. Class K extinguishers are heavier duty and will need to be bought separately. Household fire extinguishers are also rated for the size of fire that they can safely handle. The higher the rating, the larger the fire the extinguisher can put out. Higher-rated extinguishers are often heavier.
Steps for proper extinguisher use
Once you understand the different types of fire extinguishers and their uses, you need to be able to properly operate one.
Step 1: Identify a clear exit/escape routeBefore operating the fire extinguisher, make sure you have a clear evacuation path. If you cannot put out the fire, you’ll need to make a safe exit. Also, make sure everyone else is being evacuated from the building.
Step 2: Call the fire departmentEven if the fire appears manageable, you should always have the fire department on the way. Once firefighters arrive, they can double-check whether the fire has been completely extinguished.
Step 3: Stand backFace the fire and keep your back to the clear exit. You should stay between 1.8 and 2.5 meters away from the flames as you prepare to operate the fire extinguisher.
Step 4: Operate the extinguisherIt can be difficult to think clearly during an emergency. Thankfully, there is a long-standing acronym(首字母缩略词)— PASS — to help you recall the steps involved in operating your fire extinguisher.
P: Pull the pin (保险销) on the fire extinguisher.
A: Aim low. Point the nozzle at the base of the fire instead of the flames.
S: Squeeze the handle or lever to discharge the extinguisher.
S: Sweep the nozzle back and forth until the flames are extinguished.
Step 5: Keep an eye on thingsAfter the flames appear to be out, continue to watch the fire area to make sure it doesn’t reignite. If the fire does start up again, repeat the “PASS” process.
Step 6: Get to a safe placeOnce the fire is out, or if you are unable to put it out, leave the scene. Find a place out of reach of the fire.
1. According to the passage, what is the top priority in a fire emergency?| A.Find out how to escape. | B.Operate a fire extinguisher. |
| C.Call the fire department. | D.Escape and leave everything behind. |
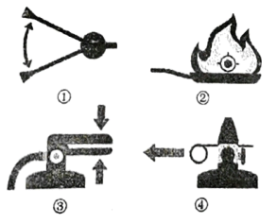
| A.③②④① | B.④②③① |
| C.③④①② | D.④③①② |
| A.leave the fire area at once | B.repeat the “PASS” process |
| C.inspect the fire area carefully | D.have the fire department on the way |
3 . Tiny trash factories
Not all waste has to go to waste. Most of the world’s 2.22 billion tons of annual trash ends up in landfills or open dump. Veena Sahajwalla, a materials scientist and engineer at the University of New South walks, has created a solution to our massive trash problem: waste microfactories. These little trash processors house a series of machines that recycle waste and transform it into new materials with thermal technology. The new all-in-one approach could leave our current recycling processes in the dust.
Sahajwalla launched the world’s first waste microfactory targeting electronic waste in 2018. A second one began recycling plastics in 2019. Now, her lab group is working with university and industry partners to commercialize their patented Microfactoric technology. She says the small scale of the machines will make it easier for them to one day operate on renewable energy, unlike most large manufacturing plants. The approach will also allow cities to recycle waste into new products on location. With a micro-factory, gone are the days of needing separate facilities to collect and store materials, extract elements and produce new products.
Traditionally, recycling plants break down materials for re us c in similar products. It is like melting down plastic to make more plastic things. Her invention evolved this idea by taking materials from an old product and creating something different. “The kids don’t look like the parents,” she says.
For example, the microfactories can break down old smart phoned and computer monitors and extract silica and carbon, and then combine them into silicon car bide nanowires. This generates a common ceramic material with many industrial uses. Sahajwalla refers to this process as “the fourth R,” adding “
In 2019, just 17.4 percent of e-waste was recycled, so the new ability offers a crucial new development in the challenge recycling complex electronic devices. “We can do so much more with materials,” says Sahajwala.” Traditional recycling has not worked for every recycling challenge.” She and her team are already working to install the next waste microfactory in the Australian town of Cootamundra by early 2021, with the goal of expanding around the country over the next few years.
1. Which of the following is the feature of the waste microfactory?| A.It can restore the waste to their original forms. |
| B.It is cleaner than the traditional recycling plant. |
| C.Waste can be recycled where they are dump at. |
| D.There is only one machine in the waste microfactory. |
| A.Establishing the first waste microfactory. |
| B.Expanding the variety of waste it can recycle. |
| C.Trying to make a profit from microfactory technology. |
| D.Developing renewable energy to operate microfactories. |
| A.recall | B.reform | C.release | D.reverse |
| A.Traditional recycling is actually useful for only a small part of waste recycling. |
| B.Microfactories make it possible for scientists to create various things with wastes, |
| C.Microfactories can directly make waste electronic device into household utensils. |
| D.By now, Australia is the first country in the world that has realized the popularization of waste microfactofies. |



