1 . A few months ago, I got a terrible cold which ended in a cough that was hard to get rid of (摆脱). No matter how many different medicines I tried, I
Then one day after class, a student came up to me and
A few minutes later, the treatment started to produce a
| A.still | B.even | C.also | D.certainly |
| A.upset | B.amazing | C.unusual | D.inconvenient |
| A.recommended | B.confirmed | C.adopted | D.treated |
| A.benefits | B.wonders | C.functions | D.ways |
| A.nervous | B.excited | C.hesitant | D.optimistic |
| A.Currently | B.Gradually | C.Surprisingly | D.Immediately |
| A.shot | B.look | C.miss | D.break |
| A.ear | B.nose | C.tongue | D.teeth |
| A.hospitals | B.doctors | C.patients | D.machines |
| A.unsatisfied | B.frightened | C.attracted | D.injured |
| A.damaging | B.cooling | C.relieving | D.inspiring |
| A.pain | B.pressure | C.recovery | D.relaxation |
| A.strength | B.ability | C.behavior | D.condition |
| A.lessen | B.worsen | C.better | D.deepen |
| A.fine | B.gone | C.worthwhile | D.different |
2 . The biomedical world is flooded in data. We have a lot of genomic information from mouse to human, precious health measurements from clinical tests, and a large amount of so-called real-world data from insurance companies and drugstores. Using powerful computers, scientists have carefully researched it with some fine results, but it has become clear that we can learn much more with an assist from artificial intelligence. Over the next decade deep-learning neural networks will likely transform how we look for patterns in data and how research is conducted and applied to human health. This special report explores the future of this new transformation.
Right now the biggest assumptions are being placed in the field of drug discovery, and for good reason. The average cost of bringing a new drug to market nearly doubled between 2003 and 2013 to $2.6 billion, and because nine out of ten fail in the final two periods of clinical tests, most of the money goes to waste. Every large drug company is working with at least one AI-focused start-up to see if it can raise the return on investment.
Machine-learning algorithms (算法) can get through millions of chemical compounds, narrowing the choices for a particular drug target. Perhaps more exciting, AI systems — free by leading theories and biases — can identify entirely new targets by spotting tiny differences at the level of cells, genes or proteins between a healthy brain and one marked by Parkinson’s — differences that might avoid or even puzzle a human scientist.
That same sharp-eyed ability is also being used to explain medical scans. Some systems can already discover early signs of cancer that might be missed by a radiologist or see things that are simply beyond human capacity — such as evaluating cardiovascular (心血管) risk from a retinal scan. The Food and Drug Administration is approving imaging algorithms at a rapid click. Other AI applications lie a bit further down the road.
Will the inefficiencies of today’s electronic health records (EHRs) be solved by smart systems that prevent prescribing mistakes and provide early warnings of disease? Some of the world’s biggest tech giants are working on it.
Despite fears that machines will replace humans, most experts believe artificial and human intelligence will work cooperatively. The bigger concern is a shortage of people with both biomedical knowledge and algorithm proficiency. If this human problem can be solved, the key to creating successful AI applications may depend on the quality and quantity of what we provide them with. “We rely on three things,” says the CEO of one deep-learning start-up. “Data, data and more data.”
1. Why do large drug companies work with AI-focused start-up?| A.Because it is required by the government to do so. |
| B.Because it helps to explore new medicine with others. |
| C.Because it saves costs for drug companies to explore AI. |
| D.Because it’s used to check if the return on investment can be increased. |
| A.Positive. | B.Negative. | C.Neutral. | D.Unclear. |
| A.Why New Technology Will Change Our Life |
| B.How Artificial Intelligence Will Analyze Data |
| C.How Artificial Intelligence Will Replace Humans |
| D.How Artificial Intelligence Will Change Medicine |
CP: Central Point P: Point Sp: Sub-point (次要点) C: Conclusion
A.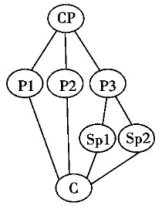 | B.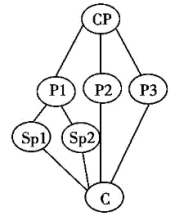 |
C.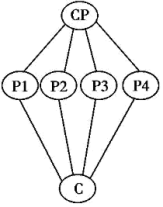 | D.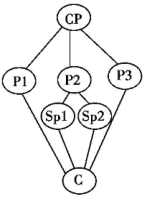 |
3 . “New and improved. “These words are put in so many marketing campaigns that we tend to accept them as linked. But many new drugs aren’t an improvement over the best existing drug for a given condition, and the fast drug-approval processes in recent years have added to the uncertainty about their advantages.
A recent report in the British Medical Journal, “New Drugs: Where Did We Go Wrong and What Can We Do Better? “Analyzed the issue. The authors looked at 216 drugs approved between 2011 and 2017:152 were newly developed, and 64 were existing medicine approved for new uses. Only 25%offered a major advantage over the established treatment, and fully 58%had no confirmed added benefit to reduce symptoms or improve health-related quality of life.
“This doesn’t mean there’s no added benefit, “lead author Wissler said. “It just means we have no positive proof. Either we have no studies or have studies not good enough. “Wissler and her co-authors work for a German institute which evaluates new treatments and advises on whether the country’s health care system should pay a premium(补贴)for them. Such organizations, known as health technology assessment(HTA)agencies, work a little differently in the US, says Sean Tunisia researcher in Baltimore: “If payers think a new drug isn’t better than an existing drug, these agencies will require that hospitals try the cheaper drug first.”
Germanys HTA demands trials to prove that a new treatment beats the existing standard. This isn’t always practical. For one thing, such studies can be expensive and time-consuming, with no guarantee of success. Secondly, it can discourage companies from attempting to develop new alternatives. This is already happening. Drug developers are increasingly focused on areas where there are no good treatments to compete with, such as rare diseases.
This lack of meaningful data to guide patients is a major point of Wissler’s paper. With accelerated approval, there are more products approved, with a greater amount of uncertainty about risks and benefits. But there are other solutions besides drug trials. One idea is to require postmarked studies to track the effectiveness of newly approved drugs—a step too often neglected.
1. What message does the recent report convey?| A.Improved drugs have advantages over old ones. |
| B.Many new drugs have no improved advantages. |
| C.Before 2017 no improvement was made to drugs. |
| D.The approval processes for new drugs are too fast. |
| A.Get hospitals to use the cheaper drugs. |
| B.Remove government premium on them. |
| C.Arrange financial support for the patients. |
| D.Put new drugs on further trials and studies. |
| A.Getting patients to depend on the government for support. |
| B.Making drug companies think of illegal ways to cut cost. |
| C.Holding companies back from improving existing drugs. |
| D.Pushing companies to try alternatives for existing drugs. |
| A.The Advantage of Existing Drugs |
| B.A Dilemma with New Drug Alternatives |
| C.Misunderstanding of New and Old Drugs |
| D.People’s Preference for New or Old Drug |



