1 . A few months ago, I got a terrible cold which ended in a cough that was hard to get rid of (摆脱). No matter how many different medicines I tried, I
Then one day after class, a student came up to me and
A few minutes later, the treatment started to produce a
| A.still | B.even | C.also | D.certainly |
| A.upset | B.amazing | C.unusual | D.inconvenient |
| A.recommended | B.confirmed | C.adopted | D.treated |
| A.benefits | B.wonders | C.functions | D.ways |
| A.nervous | B.excited | C.hesitant | D.optimistic |
| A.Currently | B.Gradually | C.Surprisingly | D.Immediately |
| A.shot | B.look | C.miss | D.break |
| A.ear | B.nose | C.tongue | D.teeth |
| A.hospitals | B.doctors | C.patients | D.machines |
| A.unsatisfied | B.frightened | C.attracted | D.injured |
| A.damaging | B.cooling | C.relieving | D.inspiring |
| A.pain | B.pressure | C.recovery | D.relaxation |
| A.strength | B.ability | C.behavior | D.condition |
| A.lessen | B.worsen | C.better | D.deepen |
| A.fine | B.gone | C.worthwhile | D.different |
1. Who did the woman just meet?
| A.A psychologist(心理学家). | B.Her doctor. | C.One of her friends. |
| A.Anxiety. | B.Too much work. | C.The pills she takes. |
| A.Exercising outdoors. |
| B.Talking more often to others. |
| C.Not using the computer for a while. |
| A.Take some sleeping pills. |
| B.Schedule an appointment with a psychologist. |
| C.Try the man’s suggestions. |
3 . Did you know it's possible to swim with whales in the ocean while lying on a hospital bed?Have you imagined experiencing your 74th birthday as a 20-something? Medical virtual (虚拟的) reality is an area with interesting and attractive possibilities. Although the field is brand new, there are already great examples of VR having a positive effect on health care. Here are some.
Have you ever lain down on a hospital bed counting the days until you leave the hospital? Brennan Spiegel and his team at the Cedars-Sinai hospital in Los Angeles introduced VR worlds to their patients to help them reduce stress and pain. With the special glasses, they could escape the four walls of the hospital and enjoy amazing scenery in Iceland, take part in the work of an art studio or swim together with whales in the ocean. So the hospital experience is improved.
As we know, the experience in a hospital is even more stressful for small children who miss their parents and friends. Now a Dutch company made their dream possible. Through a smart phone and virtual glasses, VisitU makes live contact possible with a 360 degree camera at the patient's home, school or special occasions like a birthday celebration or a football game. Though staying in hospital, young patients can relax and still enjoy their lives.
Did you wonder what it feels like to grow old? Embodied Labs created “We Are Alfred” by using VR technology to show young medical students what aging means. Everyone can be the imagined Alfred for 7 minutes, and experience what it feels like to live as a 74-year-old man. Thus it's possible to solve the disconnection between young doctors and elderly patients due to their huge age difference.
Mind MotionPro, produced by the Swiss Mindmaze allows patients with a brain injury to “practice” how to lift their arms or move their fingers with the help of virtual reality. The app makes the practice of repetitive (重复的) movements fun for patients. The mental effort helps their damaged nervous systems to recover much faster than lying helplessly in bed.
1. What is implied in the questions raised in Paragraph 1?| A.The characters of medical VR. |
| B.The function of medical VR. |
| C.The popularity of medical VR. |
| D.The imagination about medical VR. |
| A.Making patients adapt to their surroundings. |
| B.Improving the hospitals'services. |
| C.Relaxing patients in hospital. |
| D.Exposing patients to real life. |
| A.Spiegel's special glasses. |
| B.The application of VisitU. |
| C.The creation of “We Are Alfred”. |
| D.The use of Mind MotionPro. |
4 . The U. S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved a debatable Alzheimer's treatment, the first that promises to slow the disease's destruction in the brain.
The drug, aducanumab, is also the first new Alzheimer's treatment approved since 2003.However, in 2019, aducanumab was nearly abandoned after it appeared unlikely to succeed in two clinical trials. But after reanalyzing more data, the drug's developer Biogen saw signs indicating the drug might work, and decided to pursue FDA approval.
Still, today's decision concerns some doctors and scientists because they aren't convinced that the drug actually works. Approving a drug that's not effective would offer patients false hope, those experts argue. “This is a great day for Biogen but a dark day for the field of Alzheimer's research,” says Michael Greicius, a neurologist at Stanford. Pushing forward on the “illusion of progress,” he says, “will come at a cost to genuine progress in finding an effective treatment for this destructive disease.”
Others disagree that the evidence is slim, and are excited about having a new tool to fight a disease that has escaped an effective treatment for so long. “We have been waiting decades for this,” says Maria Carrillo, an expert at the Alzheimer's Association. A drug that delays decline due to Alzheimer's promises patients “to sustain independence and to hold onto memories longer,” she says.
The drug targets the sticky protein—A-beta(淀粉样蛋白). Some researchers suspect that in Alzheimer's, A-beta confuses connections between nerve cells and damages brain tissue, ultimately causing Alzheimer's symptoms. But that idea is still unsettled. Brain scans reveal that aducanumab is effective at reducing A-beta in the brain. What's less clear is whether this reduction comes with consistent improvements in people's quality of life.
1. What does paragraph 2 mainly tell us about aducanumab?| A.Its bitter failure in clinical trials. |
| B.Its tough path to getting recognized. |
| C.Its medical value in treating Alzheimer's. |
| D.Its challenging process of being produced. |
| A.Proof. | B.Significance. | C.Prospect. | D.Misunderstanding. |
| A.Unconcerned. | B.Doubtful. | C.Positive. | D.Intolerant. |
| A.A-beta in human body should be removed. |
| B.Aducanumab has potentially serious side effects. |
| C.A-beta's decrease improves people's quality of life. |
| D.Further tests on aducanumab need to be carried out. |
5 . The biomedical world is flooded in data. We have a lot of genomic information from mouse to human, precious health measurements from clinical tests, and a large amount of so-called real-world data from insurance companies and drugstores. Using powerful computers, scientists have carefully researched it with some fine results, but it has become clear that we can learn much more with an assist from artificial intelligence. Over the next decade deep-learning neural networks will likely transform how we look for patterns in data and how research is conducted and applied to human health. This special report explores the future of this new transformation.
Right now the biggest assumptions are being placed in the field of drug discovery, and for good reason. The average cost of bringing a new drug to market nearly doubled between 2003 and 2013 to $2.6 billion, and because nine out of ten fail in the final two periods of clinical tests, most of the money goes to waste. Every large drug company is working with at least one AI-focused start-up to see if it can raise the return on investment.
Machine-learning algorithms (算法) can get through millions of chemical compounds, narrowing the choices for a particular drug target. Perhaps more exciting, AI systems — free by leading theories and biases — can identify entirely new targets by spotting tiny differences at the level of cells, genes or proteins between a healthy brain and one marked by Parkinson’s — differences that might avoid or even puzzle a human scientist.
That same sharp-eyed ability is also being used to explain medical scans. Some systems can already discover early signs of cancer that might be missed by a radiologist or see things that are simply beyond human capacity — such as evaluating cardiovascular (心血管) risk from a retinal scan. The Food and Drug Administration is approving imaging algorithms at a rapid click. Other AI applications lie a bit further down the road.
Will the inefficiencies of today’s electronic health records (EHRs) be solved by smart systems that prevent prescribing mistakes and provide early warnings of disease? Some of the world’s biggest tech giants are working on it.
Despite fears that machines will replace humans, most experts believe artificial and human intelligence will work cooperatively. The bigger concern is a shortage of people with both biomedical knowledge and algorithm proficiency. If this human problem can be solved, the key to creating successful AI applications may depend on the quality and quantity of what we provide them with. “We rely on three things,” says the CEO of one deep-learning start-up. “Data, data and more data.”
1. Why do large drug companies work with AI-focused start-up?| A.Because it is required by the government to do so. |
| B.Because it helps to explore new medicine with others. |
| C.Because it saves costs for drug companies to explore AI. |
| D.Because it’s used to check if the return on investment can be increased. |
| A.Positive. | B.Negative. | C.Neutral. | D.Unclear. |
| A.Why New Technology Will Change Our Life |
| B.How Artificial Intelligence Will Analyze Data |
| C.How Artificial Intelligence Will Replace Humans |
| D.How Artificial Intelligence Will Change Medicine |
CP: Central Point P: Point Sp: Sub-point (次要点) C: Conclusion
A.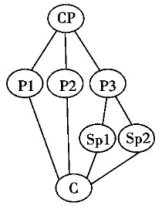 | B.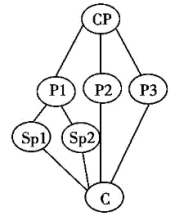 |
C.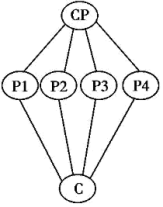 | D.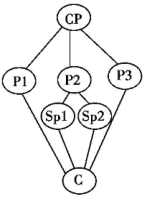 |
6 . “New and improved. “These words are put in so many marketing campaigns that we tend to accept them as linked. But many new drugs aren’t an improvement over the best existing drug for a given condition, and the fast drug-approval processes in recent years have added to the uncertainty about their advantages.
A recent report in the British Medical Journal, “New Drugs: Where Did We Go Wrong and What Can We Do Better? “Analyzed the issue. The authors looked at 216 drugs approved between 2011 and 2017:152 were newly developed, and 64 were existing medicine approved for new uses. Only 25%offered a major advantage over the established treatment, and fully 58%had no confirmed added benefit to reduce symptoms or improve health-related quality of life.
“This doesn’t mean there’s no added benefit, “lead author Wissler said. “It just means we have no positive proof. Either we have no studies or have studies not good enough. “Wissler and her co-authors work for a German institute which evaluates new treatments and advises on whether the country’s health care system should pay a premium(补贴)for them. Such organizations, known as health technology assessment(HTA)agencies, work a little differently in the US, says Sean Tunisia researcher in Baltimore: “If payers think a new drug isn’t better than an existing drug, these agencies will require that hospitals try the cheaper drug first.”
Germanys HTA demands trials to prove that a new treatment beats the existing standard. This isn’t always practical. For one thing, such studies can be expensive and time-consuming, with no guarantee of success. Secondly, it can discourage companies from attempting to develop new alternatives. This is already happening. Drug developers are increasingly focused on areas where there are no good treatments to compete with, such as rare diseases.
This lack of meaningful data to guide patients is a major point of Wissler’s paper. With accelerated approval, there are more products approved, with a greater amount of uncertainty about risks and benefits. But there are other solutions besides drug trials. One idea is to require postmarked studies to track the effectiveness of newly approved drugs—a step too often neglected.
1. What message does the recent report convey?| A.Improved drugs have advantages over old ones. |
| B.Many new drugs have no improved advantages. |
| C.Before 2017 no improvement was made to drugs. |
| D.The approval processes for new drugs are too fast. |
| A.Get hospitals to use the cheaper drugs. |
| B.Remove government premium on them. |
| C.Arrange financial support for the patients. |
| D.Put new drugs on further trials and studies. |
| A.Getting patients to depend on the government for support. |
| B.Making drug companies think of illegal ways to cut cost. |
| C.Holding companies back from improving existing drugs. |
| D.Pushing companies to try alternatives for existing drugs. |
| A.The Advantage of Existing Drugs |
| B.A Dilemma with New Drug Alternatives |
| C.Misunderstanding of New and Old Drugs |
| D.People’s Preference for New or Old Drug |
1. What is one of the symptoms of the woman?
| A.Fast heartbeat. | B.Shortness of breath. | C.Sharp neck pain. |
| A.About 10 minutes. | B.About 15 minutes. | C.About 20 minutes. |
| A.Have an operation. | B.Have some tests. | C.Have some medicines. |
8 . Each year there are at least five million people around the world who develop serious flu (流感), and almost half a million deaths. When someone we know gets the flu virus, we expect them to be very careful not to pass it on to others. Doctors and nurses working with flu patients also need to protect themselves from the virus. But what is the best way to do this? This is the question that flu expert Professor Jonathan
Van-Tam at Nottingham University is trying to answer. He wants to find out how flu is transmitted, so that he can stop doctors and nurses getting sick.
Van-Tam explains their method, "There are 41 volunteers in my experiment. Some healthy volunteers are made to get flu first. When they show symptoms (症状 ) , other volunteers, usually called recipients(接受者), enter the house. Everyone lives together in the small space for four days. Some of the recipients wear face masks, and wash their hands every 15 minutes, but some have no protection. In this way we can study who catches the flu and which ways of transmitting flu are important. During the four days when they are in contact with the virus, and for the ten days after that, the flu recipients are checked regularly."
The experiment is not simple and it is very expensive. It is difficult to design correctly, and it is also difficult to plan and carry out. Just one study like this takes about 18 months to organize and needs hundreds of people working on it. But Van-Tam believes it is worth because the results will help to decide what type of protection is needed for people working in hospitals with large numbers of flu patients around the world. And perhaps it could reduce the number of deaths from flu each year.
1. Which word can replace the underlined word “transmitted" in paragraph l ?| A.solved | B.passed | C.formed | D.stopped |
| A.to test the medicines for people who develop serious flu |
| B.to find the best way to protect doctors and nurses from the flu. |
| C.to reduce the number of people who die of flu |
| D.to find out who gets the flu easily |
| A.This type of study lasted 18 months. |
| B.The experiment is neither simple nor expensive. |
| C.Recipients were divided into at least 2 groups to perform the experiment. |
| D.Wearing masks was the best way to protect people from getting flu |
1. Why did Murphy go to a doctor?
| A.He thought his wife was deaf. |
| B.He wanted to get his hearing back. |
| C.He couldn’t make himself understood. |
| A.Stand about 15 meters from his wife. |
| B.Ask his wife some serious questions. |
| C.Talk to his wife in different distances. |
| A.Watching TV. | B.Cooking. | C.Setting the table. |
| A.Twice. | B.Three times. | C.Four times. |



