1 . Population:Is 8 billion people too many?
The world’s population has reached 8 billion people.
For now, we can both acknowledge the downsides of the 8 billionth human and believe this is an occasion worth celebrating.
| A.We’ve reached this milestone |
| B.Actually, some population alarmism is appropriate |
| C.The end of population expansion is now foreseeable |
| D.The truth is that the population in developed nations has remained stable |
| E.With any luck, the massive challenge of global aging will spur innovation |
| F.The increasing global population will put more pressure on resources and produce far more emissions |
| G.In contrast, various experts have been put forward “nightmare consequences” about overpopulation since 1960s |
2 . For almost all of human history, the Earth's population has tended to be younger. But since the last World Population Day on July 11, a major shift occurred: There are now more people aged 65 and older than there are under age five.
World Population Day was established by the United Nations Development Program in 1989 to bring attention to population issues. Having more people on the planet is not the only concern, though, since a population's age structure matters too.
Increased lifetime is a remarkable human success story, but having more elderly people also creates a number of socioeconomic concerns. The global population will continue to age as these two groups grow in opposite directions. By 2100, the percentage of the population aged 65 and older will rise to nearly 25 percent — about five times that of children under five.
“Most developed countries have been aging for a century, giving them time to prepare for the changes. But developing countries will become old before they become rich,” says researcher Toshiko Kaneda. Many countries in Latin America and Asia are aging much faster and have less time and resources to prepare health-care systems.
What are the consequences of an older global population? Supporting elderly people is more expensive than caring for young ones. Pressing issues arise like how to provide long-term care, and maintain a labor force. In developed regions like Europe, where 10 percent of the population over age 50 is childless, elderly care is a major worry.
“Not a single country has been able to change declining trends in fertility (生育) despite government requests for people to reproduce as has been done across Europe and in Japan,” Kaneda says. “The aging trend is continuous. ”
But declining fertility rates can have positive effects too, says Kaneda. When fertility rates decline but the population hasn't aged yet, governments can spend more on secondary and higher education, and benefit the economy. Both Thailand and South Korea have seized the opportunity during this ideal period.
1. What do we know about the global population?| A.It tended to be younger until now. |
| B.People are living longer and having fewer kids. |
| C.Age structure matters more than population size. |
| D.Developed countries are facing tougher challenges. |
A.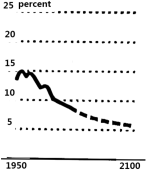 | B.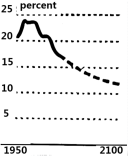 |
C. | D.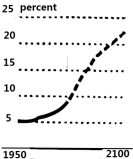 |
| A.Critical. | B.Objective. | C.Optimistic. | D.Doubtful. |
| A.The declining trend in the fertility rates. |
| B.The consequences of the aging population. |
| C.The establishment of World Population Day. |
| D.The present situation of the global population. |
| A. double B. intense C. pressures D. stock E. agriculture F. trapped G. withdrawal H. availability I. drive J. expanding K. rising |
Throughout history, people have fought bitter wars over political ideology, national sovereignty and religious expression. How much more
Less than three percent of the planet’s
Global



