1 . Digital art is becoming increasingly popular among many artists.
Then make layers (图层).
On each layer you’ve created, start outlining the sketch (草图) with the brush tool.
| A.Draw your idea on paper. |
| B.Right now your draft is the only layer in the file. |
| C.The outline will make things easier to color later on. |
| D.Think about what you want to create before you work on it. |
| E.The more layers you add, the better the drawing will look. |
| F.Besides, you can add more layers and have more detail polished. |
| G.To make digital art, you first need a computer and a program for digital drawing. |
2 . Geothermal (地热的) power generation is one of our most stable renewable energy resources. Heat generated below the Earth’s surface can provide an almost unlimited supply to power and heat homes. And while geothermal electricity only accounts for around one percent of global generation, that is set to at least triple by 2050.
The Geysers in California is the world’s largest geothermal electricity complex. It produces enough electricity from its 18 power plants for 725,000 homes, totaling 20 percent of the state’s renewable energy. Superheated “dry steam” is channeled from a large sandstone reservoir heated by a large magma chamber (岩浆房) more than four miles beneath the surface.
Heat is captured from its passage through the rock and the heated water converts into electricity. Cooled water is then recycled and pumped back to gather more heat. EGS (enhanced geothermal systems) technologies will open up many more sites for geothermal energy. “You can effectively put a power plant anywhere,” said Will Pettit, director of the Geothermal Resources Council. “All you have to do is drill deep enough and you will find hot rock.”
Most geothermal plants actually use a flash steam technique, where hot water (at 360F or 180C) is drawn up, passed into lower pressure tanks and flashed into steam to power a turbine (涡轮机). Binary cycle (双元循环) plants are the growth technology because they can operate at lower water temperatures and more diverse geographical locations. They use moderately hot water to heat a secondary fluid with a lower boiling point—as low as 135F—to drive turbines.
Geothermal plants already emit 11 times less carbon dioxide per unit of electricity than the average US coal power plant. They can also operate 24 hours a day to provide a solid base load for homes and businesses.
There are drawbacks too. Seismic activity around drilling wells is a factor. High investment costs are another. But the US government is backing the sector with multi-million dollar funds to push forward advanced EGS research. Geothermal energy is set to play a big part in the low-carbon electricity future.
1. What is the significance of EGS (enhanced geothermal systems) technologies?| A.They have made geothermal energy less sustainable. |
| B.They have greatly reduced the need for drilling in geothermal sites. |
| C.They allow for more efficient use of geothermal resources. |
| D.They have opened up new methods of generating electricity from water. |
| A.Power plants are not affected by water. |
| B.Hot water is used to power a turbine directly. |
| C.Binary cycle plants are less restricted to sites. |
| D.A flash steam technique is a must in geothermal plants. |
| A.Perfect. | B.limited . | C.impractical. | D.promising. |
| A.Businesses have been competing to gain an advantage in geothermal power. |
| B.Geothermal power is likely to be a great chance to sustainable power. |
| C.Traditional power has been replaced by geothermal power in America. |
| D.EGS technologies have come into widespread application around the world. |
3 . For decades, scientists thought of the brain as the most closely guarded organ. Locked safely behind a biological barrier, away from the disorder of the rest of the body, it was broadly free of destruction of germs (病菌) and the battles started by the immune system.
Then, 20-odd years ago, some researchers began to ask a question: is the brain really so separate? The answer, according to a growing body of evidence, is no — and has important effects on both science and health care.
The list of brain conditions that have been associated with changes elsewhere in the body is long and growing. Changes in the make-up of the microorganisms resident in the gut (肠道), for example, have been linked to disorders like Parkinson’s disease. Some researchers think that certain infections could provoke Alzheimer’s disease and some could lead to emotional disorder in babies.
The effect is two-way. There is a lengthening list of symptoms (症状) not typically viewed as disorders of the nervous system in which the brain and the neural processes that connect it to the body play a large part. For example, the development of a fever is influenced by a population of neurons (神经元) that control body temperature and appetite. The effect of brain on body is underlined by the finding that stimulating a particular brain region in mice can ‘remind’ the body of previous inflammation (炎症) — and reproduce them.
These findings and others mark a complete shift in our view of the interconnectedness of brain and body, and could help us both understand and treat illness. If some brain conditions start outside the brain, then perhaps cures for them could also reach in from outside. Treatments that take effect through the digestive system, heart or other organs, for instance, would be much easier and less striking to give than those that must cross the blood-brain barrier, the brain’s first line of defence.
In the opposite direction, the effects of our emotions or mood on our capacity to recover from illness could also be used. There is an opening work under way testing whether stimulating certain areas of the brain that respond to reward and produce feelings of positivity could enhance recovery from conditions such as heart attacks. Perhaps even more exciting is the possibility that making changes to our behaviour — to reduce stress, say — could have similar benefits.
For neuroscientists, it’s time to look beyond the brain. And clinicians treating the body mustn’t assume the brain is above getting involved — its activity could be influencing a wide range of conditions, from mild infections to long-time fatness.
1. The author writes paragraph 1 mainly to ______.| A.evaluate an argument |
| B.present an assumption |
| C.summarize the structure |
| D.provide the background |
| A.Delay. | B.Cure. | C.Cause. | D.Disturb. |
| A.Treatments that cross brain-blood barrier are less used. |
| B.Previous diseases could cause the production of new ones. |
| C.Emotions could affect the capacity to fight against diseases. |
| D.Treatment of the brain takes priority over other treatments. |
I: Introduction P: Point Sp: Sub-point (次要点) C: Conclusion
A.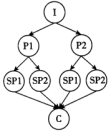 | B.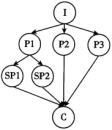 |
C.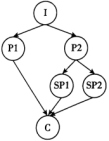 | D.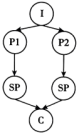 |
4 . As biologist Nicola Foster and her colleagues guided a remote-controlled monitor through the coral reefs (珊瑚礁) of the Indian Ocean’s Chagos Archipelago, they saw corals full of color near the surface. But nearly 300 feet below, in the darker and colder waters of what oceanographers call the “twilight zone,” some corals had turned terrible white, leaving them vulnerable (脆弱的) to disease and death.
“It wasn’t something we were expecting to see,” says Foster, who studies deeperwater coral ecosystems called mesophotic reefs. Mesophotic reefs would seem to be protected from rising sea-surface temperatures that white n higher-up corals. But this team’s 2019 observations show the deepest instance of bleaching (变白) ever recorded — suggesting similar reefs are more vulnerable than previously believed.
Bleaching often happens when warming water boosts corals to remove the colorful algae (水藻) that live in their tissues and help to sustain them. Although surface waters weren’t typically warm when Foster and her team took their measurements, the twilight zone waters neared 84 degrees Fahrenheit (华氏度) — far above the 68-to 75-degree range in which mesophotic corals are used to.
The researchers realized that bleaching is related to the timing of the Indian Ocean Dipole. This phenomenon shifts the region’s surface winds and ocean currents, says study co-author Phil Hosegood. Wind and waves shake the upper ocean, keeping it relatively warm and uniform in temperature. But the 2019 dipole deepened this well-mixed upper layer; the thermocline (the slice of ocean that separates warm upper waters from the cold depths) had become deeper than normal. Then, those corals were exposed to temperatures that are normally found at the surface.
This observation suggests mesophotic reefs elsewhere could also be bleaching. Fortunately, the corals in this study had largely recovered their color by 2022, Foster notes. But each bleaching stresses the corals and, if extended, can starve them. Future Indian Ocean Dipole patterns are likely to be more severe, Hosegood says, noting that data suggest “that these natural cycles are becoming increased with climate change.”
1. What are the first two paragraphs mainly about?| A.Corals in twilight zone become vulnerable because of bleaching. |
| B.Corals normally found at the surface were found in twilight zone. |
| C.Mesophotic reefs are much more vulnerable than higher-up reefs. |
| D.Mesophotic reefs and higher-up reefs need different temperature. |
A.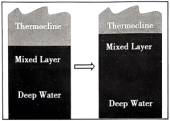 | B.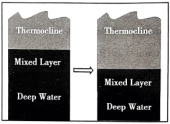 |
C.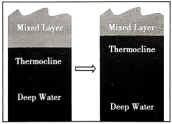 | D.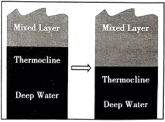 |
| A.excited | B.worried | C.curious | D.hopeful |
5 . A recent study conducted by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) has discovered that river erosion (侵蚀) can lead to increased biodiversity in areas with minimal tectonic (地壳构造的) activity. The researchers focused their attention on the Tennessee River Basin and examined how the erosion of various rock types by the river had led to the separation and diversification of a type of fish called the greenfin darter. As time passed, these separate fish populations evolved into distinct families with genetic differences.
Scientist Thomas Near observed that the greenfin darter was exclusively found in the southern half of the Tennessee River Basin. The researchers analyzed the genes of each fish in Near’s data set and constructed an evolutionary tree. This tree helped them comprehend the evolution and differences of the greenfin darter species. They discovered that the fish within the same branch of the river were more closely related to each other than to the fish in other branches.
This study provides evidence that river erosion significantly impacts biodiversity in regions with low tectonic activity. It illustrates how changes in the landscape caused by river erosion can lead to the division and diversification of species over time, even in peaceful environments. These findings enhance our understanding of the mechanisms (机制) that drive biodiversity and evolution, even in areas that are not typically associated with intense tectonic activity.
Subsequently, the team discovered a strong correlation between the habitats of the greenfin darter and the type of rocks present. The southern half of the Tennessee River Basin consists of hard, tightly packed rocks, resulting in turbulent (湍急的) waves in the rivers that flow through it. This characteristic may be favored by the greenfin darter. As a result, the team assumed whether the distribution of greenfin darter habitats had been influenced by the changing rock types, as the rivers eroded the land over time. To test this assumption, the researchers developed a simulation model. Remarkably, the results confirmed their assumption.
1. What is new about the MIT study?| A.It finds river erosion can enhance biodiversity. |
| B.It further proves the mechanisms of river erosion. |
| C.It proves the geographical features of biodiversity. |
| D.It classifies a type of fish called the greenfin darter. |
| A.Their appearances vary between families. | B.Their genetic constitutions have diversified. |
| C.They prefer the deep and slow-flowing river. | D.They go extinct in the changing landscape of rivers. |
| A.By creating an evolutionary tree of the fish. |
| B.By offering the fish’s genetic data. |
| C.By reasoning out the time the fish evolve and separate. |
| D.By analyzing the genetic similarity between different fish. |
| A.River Erosion Can Shape Fish Evolution | B.Genetic Change in the Greenfin Darter |
| C.Evolutionary Tree Analysis of the Greenfin Darter | D.The Impact of Climate Change on Fish Diversity |
6 . At the end of the day, most of us find ourselves on the couch, eyes glued to the television or to our smartphones, doing everything we can to conserve energy.
According to Michael Inzlicht, a social psychologist at the University of Toronto, we’re lazy and also, we’re not.
All humans, given equal options, will take the easy way out. Does it mean we’re lazy? Maybe.
But there are the times when humans are the opposite of lazy and do very difficult things for no apparent reason. Some rewards only come from extensive effort.
So, in that sense, effort is worth the effort. While humans are economically aware of effort most of the time, “in some cases, the effort itself is rewarding,” says Inzlicht.
| A.Think about things like running a marathon. |
| B.It’s not completely clear why humans behave this way. |
| C.It seems that we humans are gifted in the way of laziness. |
| D.We similarly love to space out, our brain tired of focusing. |
| E.But it certainly means that we’re economic with our effort. |
| F.Some people who appear to be lazy are suffering from much more serious problems. |
| G.Likewise, we might get a sense of pleasure or mastery from doing a crossword puzzle. |
7 . When we’re on the treadmill (跑步机), we’re more likely to bethinking about whether we’re going to make it another mile than’what’s in our workout clothing. But our favorite sports club are likely to be made from synthetic (合成的) fabrics, all of which are essentially plastic often created with harmful chemical additives. Now, a study conducted by the University of Birmingham shows the chemical additives from our workout clothing are available to be absorbed through our skin.
Previously, researchers have tended to focus on our exposure to plastic through diet,but the new study raises awareness that humans can be expesed to plastic chemicals through our skin, too. And because harmful chemicals accumulate lowly and stick around in our bodies, repeared and multi-source exposure can result in having high concentrations of chemicals inside us, potentially contributing to health effects.
The Birmingham study focused on a class of compounds (化合物) called brominated flame retardants (BFRs), which are used to prevent burning in a wide range of consumer products including fabrics, and are linked to adverse health effects such as hormonal disorders and mental problems.
It’s known that sweat contains oil. Researchers found the oil has a chemical nature that encourages the chemicals in plastic to dissolve and spread.“In short, oil substances in our sweat help the bad chemicals to come out of the microplastic fibers and become available for human absorption,”says Dr. Abdallah of the Urnversity of Birmingham. An easy way to avoid exposure to these chemicals is to wear clothing made of sustainably produced textiles, which dont contain the bad chemicals associated with plastic materials. Check fabric labels for items that are mostly organic cotton, he mp or merino wool. Visit brand websites to see if they make an effort to list their suppliers, and where their products come from, including their dye houses and mills. Abdallah says he minimizes synthetic fabrics in his home, meanwhile wearing natural fibers like cotton. “Why be exposed to these chemicals even at low levels?”he says.“Why not avoid the risks?”
1. What is found in the study by the Birmingham University?| A.Sports clothes are fit for treadmill exercise. |
| B.Plastic produces harmful chemical additives. |
| C.Gym clothes may release poisonous chemicals. |
| D.People are exposed to chemicals through plastic. |
| A.Unknown. | B.Harmful. | C.Similar. | D.Beneficial. |
| A.It frees bad chemicals out of clothes. |
| B.It produces bad chemicals with plastic. |
| C.It prevents harmful chemicals spreading. |
| D.It keeps chemicals in the fibers of clothes. |
| A.Choosing famous brands. | B.Contacting the suppliers. |
| C.Visiting the chemical plants. | D.Wearing pure cotton clothes. |
8 . Birders get nervous when they see landscapes covered in wind turbines (涡轮机). When the wind gets going, their blades (叶片) can turn around at well over 200km per hour. It is easy to imagine careless birds getting cut into pieces and wind turbines do indeed kill at least some birds. But a new analysis of American data suggests the numbers are negligible, and have little impact on bird populations.
Erik Katovich, an economist at the University of Geneva, made use of the Christmas BirdCount, a citizen-science project run by the National Audubon Society. Volunteers count birds they spot over Christmas, and the society gathers the numbers. He assumed, reasonably, that if wind turbines harmed bird populations, the numbers seen in the Christmas Bird Count would drop in places where new turbines had been built. Combining bird population and species maps with the locations and construction dates of all wind turbines, he found building turbines had no noticeable effect on bird populations.
Instead of limiting his analysis to wind power alone, he also examined oil-and-gas extraction (开采), which has boomed in America over the past couple of decades. Comparing bird populations to the locations of new gas wells revealed an average 15% drop in bird numbers when new wells were drilled, probably due to a combination of noise, air pollution and the disturbance of rivers and ponds that many birds rely upon. When drilling happened in migration centers, feeding grounds or breeding locations, bird numbers instead dropped by 25%.
Wind power, in other words, not only produces far less planet-heating carbon dioxide and methane than do fossil fuels. It appears to be significantly less damaging to wildlife, too. Yet that is not the impression you would get from reading the news. Dr Katovich found 173 stories in major American news media reporting the supposed negative effects that wind turbines had on birds in 2020, compared with only 46 stories discussing the effects of oil-and-gas wells.
1. What does the underlined word“negligible”in paragraph 1 mean?| A.Insignificant. | B.Inaccurate. | C.Inconsistent. | D.Indefinite. |
| A.Previous studies. | B.Relevant data. |
| C.Reasonable prediction. | D.Experiment results. |
| A.Oil-and-gas extraction has expanded in America. |
| B.Birds are heavily dependent on rivers and ponds. |
| C.Many factors lead to the decline of bird populations. |
| D.Well drilling poses a serious threat to birds' survival. |
| A.Wind turbines could share the sky with wildlife. |
| B.More evidence is needed to confirm the finding. |
| C.Wind power will be substituted for fossil fuels. |
| D.Wind turbines deserve wider media coverage. |
9 . When fighting sugar dependence, avoiding added sugar in the diet is key, which sounds simple — right? It certainly does, but things become a bit more complicated once we introduce alternative sweeteners into the mix.
Alternative sweeteners are everywhere.
Now that we know some of the common types of alternative sweeteners, let’s take a deeper dive into the problem with them. Research in animals has shown that removing calories from foods that taste sweet can interrupt the ability to control energy intake.
The other interesting thing about alternative sweeteners is that our brains don’t recognize them as “fake (假的)” sugar.
So what do I recommend? In order to fully put a definite end to sugar dependence, reducing your intake of alternative sweeteners should be the goal.
| A.The taste profile of alternative sweeteners varies. |
| B.We can’t forget about the ever-so-popular sugar alcohols. |
| C.There are countless alternative sweeteners on the market. |
| D.Our brain senses something sweet and thinks it is real sugar. |
| E.They may help reduce the calorie content of good-tasting foods and drinks. |
| F.Artificial sweeteners may also cause one’s body to prefer sweeter-tasting foods. |
| G.Alternative sweeteners are referred to as “low-calorie” or “no-calorie” sweeteners. |
10 . A shopkeeper’s son breaks a window, causing a crowd to gather. They tell the shopkeeper not to be angry: actually, the broken window is a reason to celebrate, since it will create work for the glazier (装玻璃的工人). In the story, written by a 19th-century economist, the crowd envisions the work involved in repairing the window, but not that involved in everything else on which the shopkeeper could have spent his money — unseen possibilities that would have brought him greater happiness.
If that window were to be broken these days, people might have a different reaction, especially if they were NIMBYs (Not In My Back Yard) who oppose any local construction that affects their quality of life. Their concern might be with the “embodied carbon”. The production of a piece of glass would carry a sizeable carbon cost. Similarly, the bricks and concrete in a building are relics of past emissions. They are, the logic goes, embodied carbon.
Conserving what already exists, rather than adding to the building stock, will avoid increasing these embodied emissions — or so NIMBYs often suggest. At its worst, this idea is based on a warped logic. Greenhouse gases released by the construction of an existing building will heat the planet whether the building is repaired or knocked down. The emissions have been taken out of the world’s “carbon budget”, so treating them as anew debit means double counting. The right question to ask is whether it is worth using the remaining carbon budget to repair a building or it is better to knock it down.
Choosing between these possibilities requires thinking about the unseen. It used to be said that construction emitted two types of emissions. Besides the embodied sort, there were operational ones from cooling, heating and providing electricity to residents. Around the world, buildings account for 39% of annual emissions, according to the World Green Building Council, of which 28% come from operational carbon.
These two types of emissions might be enough for the architects designing an individual building. But when it comes to broader questions, economists ought also to consider how the placement of buildings affects the manner in which people work, shop and travel. Density (密度) lowers the per-person cost of public transport, and this reduces car use. Research by Green Alliance, a pressure group, suggests that in Britain a policy of “demolish (拆除) and densify” — replacing semi-detached housing near public transport with blocks of flats — would save substantial emissions. Without such demolition, potential residents would typically have to move to the suburbs instead, saving money on rent but consuming more energy.
Targeted subsidies (补贴), especially for research and development into construction materials, could speed up the pace at which the built environment decarbonises. What will never work, however, is allowing the loudest voices to decide how to use land and ignoring the carbon emissions of their would-be neighbours once they are out of sight.
1. The first two paragraphs are written to ________.| A.exemplify an outlook on energy conservation |
| B.present a new way of relieving energy crisis |
| C.explain people’s reaction to a broken window |
| D.introduce an argument on carbon emission |
| A.Unsound. | B.Complicated. | C.Distinctive. | D.Underlying. |
| A.Operational carbon accounts for a larger share of carbon emission. |
| B.Repairing old buildings outweighs demolition in energy conservation. |
| C.Higher residential density near public transport may help reduce emission. |
| D.Stopping residents from living in new buildings is sensible to energy saving. |
| A.Interests of NIMBYs are worthy of consideration. |
| B.A comprehensive insight into emission is essential. |
| C.Upgrading construction materials should be prioritized. |
| D.Every resident should do their bit in reducing carbon emission. |



