1 . Nearly 40 years ago, Peter Harrison, a marine ecologist witnessed the first recorded large-scale coral bleaching(珊瑚白化)event. Diving in the Great Barrier Reef(大堡礁), he was shocked by the scene before him. "The reef was made up of healthy corals and badly bleached white corals, like the beginnings of a ghost city," he says. Just months before, the same site was filled with colorful tropical life.
"Many of the hundreds of corals that I'd carefully tagged and monitored finally died," he says. "It was shocking and made me aware of just how weak these corals really are.”
Coral exists together with photosynthetic algae(藻类), which live in its tissues and provide essential nutrition(and coloration). But high temperatures and other stresses can turn algae poisonous. When this occurs, the algae may die or be removed by the coral, a process known as bleaching because the coral's clear tissue and white calcium carbonate skeleton(碳酸钙骨骼)are exposed. If the coral can't reestablish its link with algae, it will starve or become ill.
The widespread destruction Harrison saw in 1982 was repeated on many other Pacific Ocean reefs that year and the next. In 1997 and 1998 the phenomenon went global, killing some 16 percent of the world's corals. With rising temperatures, pollution, disease, increased ocean acidity, invasive species, and other dangers, Harrison's ghost cities are expanding
Scientists suppose that about four decades ago severe bleaching occurred roughly every 25 years, giving corals time to recover. But bleaching events are coming faster now—about every six years—and in some places soon they could begin to happen annually.
"The absolute key is dealing with global warming," says marine biologist Terry Hughes. "No matter how much we clean up the water, the reefs will die." In 2016, a record-hot year in a string of them, 91 percent of the reefs that consist of the Great Barrier Reef bleached.
1. Peter Harrison was shocked when diving in the Great Barrier Reef, because___________.| A.the reefs were made up of precious corals | B.the corals were ruined badly and quickly |
| C.he found a ghost city with tropical life | D.he saw the corals he had tagged before |
| A.the causes of coral bleaching | B.the weakness of corals and algae |
| C.the elements that make algae die | D.the process of building a link with algae |
| A.global warming | B.the polluted ocean | C.the white corals | D.invasive species |
| A.With algae living in its tissues, coral's white skeleton is exposed. |
| B.Solving global warming is the real solution to coral bleaching. |
| C.The reefs die because the water hasn't been cleaned thoroughly |
| D.The severest coral bleaching occurred about four decades ago. |
2 . The lives of sea turtles begin on a beach when hatchlings crawl up out of their sandy nests and try to get to the sea as fast as they can. Those that aren’t eaten by killers on their way to the water swim out into the ocean until they find somewhere they can hide, eat and grow.
Ten to fifty years later, depending on the species, the sea turtles mate in shallow waters. Then the females return to the same beach where they were born to lay their eggs, and the cycle begins again.
SAVE ENDANGERED SEA TURTLES! Here’s how YOU can make a difference! 1. Only buy ethically harvested seafood. Seafood Watch. org's app will help you choose seafood providers who don't harm sea turtles. 2. Use reusable bags and water containers.Reduce your use of plastics and refuse to use plastic bags, disposable straws and water bottles. 3. Volunteer for beach clean-up activities. Help make our coastlines safer for sea turtles by removing harmful garbage like plastic bags and disposable straws. 4. Clear the beach of obstacles at night. Remove chairs and sandcastles and turn off any lights so sea turtles can more easily travel between their nests and the water. |
Turtles that successfully avoid the numerous threats to their existence can live up to 100 years. But predators, fishing nets and garbage are major problems, and only one out of every 1,000 hatchlings will reach adulthood. There are seven sea turtle species, and six of them are either threatened, endangered or critically endangered. Many organizations around the world are working hard to ensure that sea turtles will not disappear from our oceans.
1. After leaving their nests, how long will it be before the sea turtles are old enough to reproduce?| A.Ten to fifty months, depending on environmental factors |
| B.Six months, if they can survive that long in the open ocean |
| C.One to five weeks, depending on how much they find to eat |
| D.One to five decades, depending on the kind of sea turtle |
| A.Water pollution that harms sea turtles |
| B.Fishing industry practices that harm sea turtles |
| C.Other animals that eat sea turtles |
| D.Turtle overpopulation that makes food short |
| A.It gives the turtles a clear path from their nests to the ocean. |
| B.Tourists won’t trip on anything in the dark when they’re looking for turtles. |
| C.Waste on the beach ruins the view at night. |
| D.It makes it more difficult for killers to hunt the turtles. |
3 . "When I was 16 years old, I was diving in Greece, but I was disappointed because I saw more plastic bags than fish.” These are the words of Boyan Slat, an engineer who designed the world's first ocean plastic cleanup system.
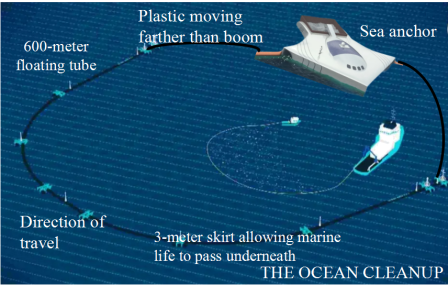
Every year, more than 8 million tons of plastics end up in our oceans, according to the UN Environment Programme. It is predicted that the weight of ocean plastics will match the weight of all the fish in our oceans by 2050. To prevent this from happening, in 2013 Slat created the Ocean Cleanup, an environmental non¬governmental organization, and put his plan for an ocean cleanup device into action.
After years of research and develop¬ment in the Netherlands, a device called System 001/B successfully started gathering plastics on October 2, 2019. The device uses a 600-meter-long C-shaped tube to gather all the floating rubbish. Unlike other cleanup methods, the system floats freely according to the direction of the waves, which allows waste to flow into and stay within the device. A sea anchor is attached to either end. This slows down the system as it floats through the water and allows the faster-moving rubbish, carried by the waves, to flow into its mouth. System 001/B can also collect waste below the surface using a 3-meter-deep skirt(挡板)attached to the end. After being gathered, the trash will be dragged back to shore by boat and recycled.
Right now, the system operates in the Great Pacific Garbage Patch, an area that is 3 times the size of France. Once operational, the Ocean Cleanup expects a full fleet to be able to clear 50% of the Great Pacific Garbage Patch in 5 years.
"It remains to be seen whether this dream will become a reality, but it is undeniable that humanity must work together to reduce our plastic use and repair the damage our waste has caused," Slat said. "We are starting to see a young generation that gets it and is excited about a sustainable (可持续的)future, but the question still comes down to: Are we going fast enough, and how much damage will have been done before we get there?"
1. The underlined word “match” in Paragraph 2 probably means “_________”.| A.compare | B.equal |
| C.measure | D.cover |
| A.To collect ocean plastic waste. |
| B.To help to invent System 001/B. |
| C.To protect the living environment of fish. |
| D.To do research on the ocean environment. |
| A.It can collect and recycle garbage at the same time. |
| B.It can only gather ocean waste which floats on the water. |
| C.It aims to clear up the Great Pacific Garbage Patch in five years. |
| D.It is an ocean-cleaning device which has already been put to use. |
| A.Young generations care less about the environment. |
| B.The future ecology of the oceans is deeply worrying. |
| C.People should work hard to decrease plastic pollution. |
| D.It's quite difficult to repair the damage to the environment. |
4 . How to deal with waste has been a problem since humans started producing it. As more and more people choose to live close together in cities, the waste-disposal problem becomes increasingly difficult.
During the eighteenth century, it was usual for several neighboring towns to get together to select a faraway spot as a dump site (垃圾填埋场). Residents or trash haulers (垃圾拖运者) would transport household rubbish, rotted wood, and old possessions to the site. Periodically some of the trash was burned and the rest was buried. The unpleasant sights and smells caused no problem because nobody lived close by.
Factories, mills, and other industrial sites also had waste to be disposed of. Those located on rivers often just dumped the unwanted remains into the water. Others built huge burners with chimneys to deal with the problem.
Several facts make these choices unacceptable to modern society. The first problem is space. Dumps, which are now called landfills, are most needed in heavily populated areas. Such areas seldom have empty land suitable for this purpose. Land is either too expensive or too close to residential neighborhoods. Long-distance trash hauling has been a common practice, but once farm areas are refusing to accept rubbish from elsewhere, cheap land within trucking distance of major city areas is almost nonexistent.
Awareness of pollution dangers has led to more strict rules of waste disposal. Pollution of rivers, ground water, land and air is a price people can no longer pay to get rid of waste. The amount of waste, however, continues to grow.
Recycling efforts have become commonplace, and many towns require their people to take part. Even the most efficient recycling programs, however, can hope to deal with only about 50 per cent of a city’s reusable waste.
1. The most suitable title for this passage would be “ _________ ”.| A.Places for Disposing Waste | B.Waste Disposal Problem |
| C.Ways of Getting Rid of Waste | D.Waste Pollution Dangers. |
| A.recycling it | B.burying it |
| C.burning it | D.throwing it into rivers |
| A.farm areas willingly accept waste from the city |
| B.there is cheap land to bury waste |
| C.ways to deal with waste stay the same as those in the past |
| D.it is no longer possible to have landfills, even in rural areas |
| A.suggest a better way to get rid of waste |
| B.warn people of the pollution dangers we are facing |
| C.call on people to take part in recycling programs |
| D.draw people’s attention to waste management |
5 . Each year, backed up by a growing anti-consumerist movement, people are using the holiday season to call on us all to shop less.
Driven by concerns about resource exhaustion, over recent years environmentalists have increasingly turned their sights on our “consumer culture”. Groups such as The Story of Stuff and Buy Nothing New Day are growing as a movement that increasingly blames all our ills on our desire to shop.
We clearly have a growing resource problem. The produces we make, buy, and use are often linked to the destruction of our waterways, biodiversity, climate and the land on which millions of people live. But to blame these issues on Christmas shoppers is misguided, and puts us in the old trap of blaming individuals for what is a systematic problem.
While we complain about environmental destruction over Christmas, environmentalists often forget what the holiday season actually means for many people. For most, Christmas isn’t an add-on to an already heavy shopping year. In fact, it is likely the only time of year many have the opportunity to spend on friends and family, or even just to buy the necessities needed for modern life.
This is particularly, true for Boxing Day, often the target of the strongest derision(嘲弄) by anti-consumerists. While we may laugh at the queues in front of the shops, for many, those sales provide the one chance to buy items they’ve needed all year. As Leigh Phillips argues, “this is one of the few times of the year that people can even hope to afford such ‘luxuries’, the Christmas presents their kids are asking for, or just an appliance that works.”
Indeed, the richest 7% of people are responsible for 50% of greenhouse gas emissions. This becomes particularly harmful when you take into account that those shopping on Boxing Day are only a small part of our consumption “problem” anyway. Why are environmentalists attacking these individuals, while ignoring such people as Russian billionaire Roman Abramovich, who has his own£1.5bn yacht with a missile defence system?
Anyway, anti-consumerism has become a movement of wealthy people talking down to the working class about their life choices, while ignoring the real cause of our environmental problems. It is no wonder one is changing their behaviours—or that environmental destruction continues without any reduction in intensity.
1. It is indicated in the 1st paragraph that during the holiday season, many consumers .| A.ignore resource problems |
| B.are fascinated with presents |
| C.are encouraged to spend less |
| D.show great interest in the movement. |
| A.has targeted the wrong persons |
| B.has achieved its intended purposes |
| C.has taken environment-friendly measures |
| D.has benefited both consumers and producers |
| A.madness about life choices |
| B.discontent with rich lifestyle |
| C.ignorance about the real cause |
| D.disrespect for holiday shoppers |
| A.anything less than a responsibility | B.nothing more than a bias |
| C.indicative of environmental awareness | D.unacceptable to ordinary people |
Sustainable Transport in Cities
Transporthas always shaped cities. In Medieval times crossroads gave birth to bloomingmarket towns. Many North American cities were created for the car. But how arethe cities of today being shaped by a need for more sustainable transport?
Manylocal governments are speeding up change through policy initiatives such asjoined transport, congestion charges and low emission zones, sustainablegaining and life-cycle costing, and opening data up to companies and academics.And these city level policies can move markets in more sustainable directions.
The least dense cities, for example, Houston, have per capita(人均价)carbonemissions nearly ten times higher than the densest, such as Singapore.
Light weighing and new engine and fuel technologies are helping to make existing road and rail vehicles more efficient.
| A.Many options require city - level investment in new facilities. |
| B.However, it is not yet clear which technologies and fuels cities will back. |
| C.Through their actions, city governments today are helping to shape the cities of the future. |
| D.For example, London is requiring all newly licensed taxis to be zero - emission capable from 2018. |
| E.City planners are using transport - oriented development to increase density while maintaining quality of life and property value. |
| F.Some cities, such as Delhi, are investing heavily in creating the mass transport systems needed to change how citizens travel. |
Acid rain is now a familiar problem in the industrialized countries in Europe. Harmful gases like Sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxide are produced by power stations and cars.
Acid rain is also capable of dissolving some rocks and buildings made of soft rock, such as limestone, are particularly badly affected. The acid rain attacks the rock, and so carvings and statues are worn away more quickly.
The acid rain is said to be caused by pollution from oil wells in the Gulf of Mexico. Car exhaust gases are also a problem. Local volcanic eruption make the problem even worse. Nevertheless, with enough money and effort, researchers say that many of the problems could be solved and the rate of dissolving reduced.
Mexico’s current lack of funds is also partly due to oil. The country has rich oil field and a few years ago, when oil was expensive, Mexico was selling large quantities of oil to the USA and earning a lot of money. The government was therefore able to borrow huge sums of money from banks around the world, thinking they would have no problem repaying their debts. However, the price of oil then dropped, and Mexico has been left owing enormous sums of money and with not enough income from oil sales to pay back the loans.
| A.However, the Mexican government does not have enough money to do the work, and needs to spend what money it has on the Mexican people. |
| B.That is enough to have caused some of the ancient carvings to become seriously damaged already. |
| C.So unless the price of rises, it is unlikely that Mexican will be able to afford to clean up the pollution and save its Mayan ruins from destruction. |
| D.These measures would reduce the pollution, but would not stop it completely. |
| E.The problem, however, is not a European one. |
| F.They dissolve in rainwater and this makes acid rain, which damages trees, rivers and streams. |
8 . In the classic novel The Day of the Triffids, giant plants terrorise humanity. Triffids can walk and are equipped with poisonous stingers, but their real power lies in their ability to communicate and so plot against us.
It sounds far-fetched, but since John Wyndham’s book was published in 1951, one aspect of this fiction has proved to be science fact: plants do talk to one another. It has long been known that insects such as pollinators (传粉者)and pests can distinguish between plants by the chemicals they release. What’s new is the idea that plants use their emissions to talk among themselves. “Plants release chemicals into the atmosphere—these can be viewed as a language in the sense that a plant releasing the chemicals can be viewed as ‘speaking’ and the plant receiving them as ‘listening’ and then responding,” says chemical ecologist James Blande at the University of Eastern Finland.
Now we are discovering that air pollution can disrupt these communications. In one study, Blande and his colleagues put individual bumblebees into a box containing paper flowers resembling those of black mustard (芥末). When the scientists injected the scent of real black mustard flowers that grew in either a clean or polluted atmosphere the bumblebees’ reactions were unequivocal: they were immediately attracted to the unpolluted scent, while that from polluted air left them flying around aimlessly.
It’s not just the clarity of plant language that gets disrupted,the “loudness” is affected, too. To find out how much things have changed since pre-industrial times, Jose Fuentes at the University of Virginia and his colleagues made a computer model that included historic air pollution levels. It revealed that scents(气味)produced by flowers that could once be picked up kilometres away now travel as little as 200 metres.
Even between clean and dirty environments today, a similar reduction in signal can be seen. Take lima beans. When one plant is attacked by spider mites, it emits chemical signals that make others nearby produce more sugary nectar. This, in turn, attracts predatory mites, which eat the attackers. If the atmosphere is clean, Blande found, the beans easily communicate with neighbours growing 70 centimetres away. But in polluted conditions, their warning cries can’t be heard more than 20 centimetres away.
1. The writer mentions the novel The Day of the Triffids in order to_________.| A.show how far-fetched the novel is |
| B.introduce the topic of the passage |
| C.warn readers of a possible danger |
| D.illustrate a new discovery of plants |
| A.familiar | B.unpredictable |
| C.different | D.inter-related |
| A.The scent of plants can’t travel in a shorter distance in polluted air |
| B.Classic novels are usually based on some proved scientific facts. |
| C.It was in pre-industrial times that pollution came into existence. |
| D.Warning cries made by insects are getting softer and softer. |
| A.Chemical signals vary with the age of plants. |
| B.Pollinators and insects either damage or benefit plants. |
| C.Pollution has an impact on the communication between plants. |
| D.Plants communicate with each other by means of what they emit. |
9 . A Swedish power plant is taking reuse and recycle to the next level by burning unusable clothing instead of coal, Bloomberg reports.
Retail giant Hennes & Mauritz, more commonly known as H&M, is helping the utility transition away from coal through its moldy (发霉的) or otherwise unsalable clothing.
The multi-fuel power and heating station in Västerås, central Sweden, is planning to be completely fossil-fuel free by 2020. It’s the largest station of its kind and Sweden claims it’s one of Europe’s cleanest. To kick its coal habit, the station is turning instead to other burnable materials including recycled wood, rubbish and yes, clothes.
“Our goal is to use only renewable and recycled fuels,” Jens Neren, head of fuel supplies at the utility company which owns and operates the Västerås plant, told Bloomberg.
Johanna Dahl, head of communications for H&M in Sweden, told Bloomberg that the company allows only the burning of clothes which are no longer safe to use.
“It is our legal obligation to make sure that clothes that contain mold or do not meet the requirements of our strict restriction on chemicals are destroyed,” she said.
The Västerås plant has burned around 15 tons of old H&M clothes so far this year, compared with about 400,000 tons of rubbish, Neren told Bloomberg.
Sweden has one of the world’s greener energy generating systems, and has invested in bioenergy, solar power and electric buses. In 2015, the Scandinavian country announced an ambitious aim to become one of the first nations in the world to end its dependence on fossil fuels. According to the Swedish government, the country has already heavily reduced its dependence on oil, which accounted for 75% of the energy supply in 1970, and now makes up a 20% share.
1. Which of the following can serve as fuel in the Västerås plant?| A.Fashionable coats in H&M chain store. | B.Old TV sets deserted as rubbish. |
| C.Wooden furniture in second-hand shop. | D.H&M clothes unsuitable for sale. |
| A.eliminating | B.adjusting |
| C.producing | D.circulating |
| A.The Swedish government discourages the development of bioenergy. |
| B.Clothes only take up a small proportion of the burning material. |
| C.Sweden’s fossil-fuel free plan is almost accomplished by now. |
| D.Sweden has an ambition to be the cleanest country in the world. |
| A.A Swedish power plant is burning unusable H&M clothes for fuel. |
| B.The Swedish government aims high and is taking effective action. |
| C.H&M is looking for a new way to strengthen its position in fashion. |
| D.Coal and oil are no longer regarded as the primary fuels in Sweden. |
Where is the Beef
Most people like to eat meat. As they grow richer they eat more of it. For individuals, that is good. Meat is nutritious. In particular, it packs much more protein per kilogram than plants do. However, animals have to eat plants to put on weight - so much so that feeding them accounts for about a third of harvested grain. Farm animals consume 8 per cent of the world’s water supply, and they produce around 15 per cent of unnatural greenhouse-gas emissions. More farm animals then, could mean more environmental trouble.
The simplest way to satisfy this demand is to concentrate on substitutes for familiar products. “Meat” made directly from plants, rather than indirectly, via an animal’s metabolism, is already on sale for the table and barbecue. Impossible Foods, a Californian firm, has deconstructed hamburgers, to work out what gives them their texture (质感) and flavour, and then either found or grown botanical equivalents to these.
For those who really want to eat steak while saving the planet, a second approach maybe more promising. That is “clean” meat made by taking animal cells and growing them in a factory to form strips of muscle. Steak is not yet on the menu, but burgers and meatballs may soon be. The field leader is Mosa Meat, a Dutch firm staffed by scientists.
There is one more novel source of meaty protein that does not involve farm animals -at least, farm animals of the conventional sort. This is insects. Locusts (蝗虫), for example, are about 70 per cent protein. Insects do have to be fed, but being cold-blooded, they convert more food into body mass than warm-blooded mammals do and, being boneless, more of that body-mass is edible.
| A.The first burger it made, in 2013, cost around $300,000. |
| B.It launched its plant-based burger in a number of restaurants in America last year. |
| C.Per edible gram, insects need only a twelfth of the food that cattle require. |
| D.The problem is marketing. |
| E.Plant-based "meat" products have made it onto menus and supermarket shelves. |
| F.Some consumers, particularly in the rich West, get this. |



