On the edge of the Saudi Arabian desert beside the Red Sea, a city called Neom is due to be built. The city-complete with flying taxis and robotic domestic help—is planned to become home to one million people. And what energy product will be used to power this city? Not oil. Instead, Saudi Arabia is banking on a different fuel—green hydrogen.
A large US gas company, Air Products & Chemicals, announced that as part of Neom it has been building a green hydrogen plant in Saudi Arabia for the past four years. The plant claims to be the world's largest green hydrogen project.
Experts say that green hydrogen could be an ideal power source for many industries.
In Japan, a new green hydrogen plant opened near Fukushima—an intentionally symbolic location given the plant's proximity to the site of the 2011 nuclear disaster. It will be used to power fuel cells.
Europe is also investing in green hydrogen. The European Union drafted a strategy for large-scale green hydrogen expansion. "Large-scale deployment (部署) of clean hydrogen at a fast pace is key for the EU to achieve its high climate ambitions", the European Commission wrote.
Green hydrogen is a promising zero-emission technology for aircraft. But Airbus recently released a statement saying that significant problems need to be overcome, including safely storing hydrogen on aircraft, the lack of a hydrogen facility at airports, and cost.
And on the ground, green hydrogen has been identified as an alternative to some road vehicles. In the UK, hydrogen trains, trucks and buses are welcomed.
There are even plans for smaller-scale hydrogen systems that can power individual homes. In Australia, the University of New South Wales has created a home-based system that uses solar energy to create and store green hydrogen, which is changed into electricity as needed.
1. What do we know about the city Neom?| A.It is located off the coast of the Red Sea. |
| B.It will be crowded with robotic taxis. |
| C.It will be powered by a unique power source. |
| D.It has the world's largest gas company. |
| A.Nearness. | B.Significance. |
| C.Remoteness. | D.Similarity. |
| A.Some experts state that it could be applied to almost any field. |
| B.The European Union took great interest in its fast- paced expansion. |
| C.It can be employed in all road vehicles as a zero-emission technology. |
| D.Storing it safely on aircraft was impossible to handle. |
| A.Advertisement. | B.Travel guide. |
| C.Science report. | D.Newspaper. |
相似题推荐
【推荐1】There are a couple of ways to forecast the destructive potential of a hurricane so that people in the way can take adequate precautions (预防措施). Satellite images of cloud patterns can be analyzed to estimate peak wind speeds, but the estimates are often way off the mark. Specialized aircraft can fly into a storm to measure the winds directly, but the flights are costly.
Researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology come up with a third way: listening to a storm underwater.
In a paper to be published in Geophysical Research Letters, Nicholas C. Makris and a former graduate student, Joshua D. Wilson, report a strong connection between the intensity (强度) of sound recorded by an undersea microphone in the mid-Atlantic and the wind power of a hurricane that passed over it. They say that such microphones, known as hydrophones, could be a safe and relatively inexpensive means of estimating hurricane force.
Dr. Makris and Dr. Wilson, who are now with Applied Physical Sciences Corporation, worked out the theory of underwater acoustic (声音的) monitoring of storms in a 2005 paper. “To be very frank with you, it’s a mystery what makes storms noisy underwater.” Dr. Makris said. The most popular idea currently is that it has something to do with oscillating air bubbles (气泡振动).
The researchers then went looking for experimental data to back their theory, and found it from a hydrophone placed at a depth of 2,500 feet by the National Atmospheric and Oceanic Administration. It happened that Hurricane Gert passed over the area in September 2009, and a hurricane-hunter plane directly measured the wind speed at the same time. The hydrophone data showed sound intensity rose when the storm’s outside wind “wall” passed over, and again when the inside wall, the most destructive part of the storm near the eye, passed over. “We got a beautiful connection,” Dr. Makris said, “between the hydrophone data and the actual wind speeds as measured by the aircraft.”
Dr. Makris is conducting additional experiments, working with the Mexican Navy off the west coast of Mexico. The eventual goal, he said, would be permanent hydrophones in known hurricane zones or temporary ones that could be easily laid by plane or ship in the path of a coming storm.
1. Compared with the traditional methods, the new way of measuring is_____.| A.more expensive | B.more direct |
| C.less accurate | D.less dangerous |
| A.The scientists gained support from different fields. |
| B.Dr. Makris and Dr. Wilson have figured out what makes storms noisy underwater. |
| C.The relationship between sound intensity and the force of the hurricane has been found. |
| D.There are several ways for people to forecast the force of the coming hurricane. |
| A.To place permanent hydrophones in some zones. |
| B.To collect more images of cloud patterns. |
| C.To be secure in carrying out their experiments. |
| D.To get more information from the hurricane-hunter planes. |
| A.Ways to Stop the Destructive Force of a Hurricane. |
| B.Measuring a Hurricane by Sound Underwater. |
| C.Connection between the Intensity of Sound and the Wind Power of a Hurricane. |
| D.Hydrophones, Safe but Expensive Means of Estimating Hurricane Force. |
【推荐2】Hadi Partovi,founder of Code.org believes every student should learn the basics of computer science just like they do math,physics,or biology,regardless of what they want to do in the future.The expert says knowledge about the subject is important to understand how the world around us works and compares it to learning about photosynthesis(光合作用),even though not every student is going to be a botanist.To spark students’interest,he created the“Hour of Code,”which introduces the world of computing to anyone,from ages 14 to 104,in a fun,interactive manner.Observed annually during Computer Science Week,the event now draws tens of millions of kids from over 180 countries.
The“Hour of Code”,which can be scheduled anytime during Computer Science Week,begins with an introductory video on computer science.Participants can then select from hundreds of fun assignments that are sorted by both grade level and coding experience.Though each project is designed to last just sixty minutes,beginners can deal with as many challenges as they desire.
To help introduce computer science in classrooms on a more regular basis,Code.org has also developed a catalog of online courses that can be incorporated(纳入)in a school’s regular curriculum.Since the nonprofit began offering the courses in 2013,over 704,000 teachers have signed up to teach introductory computer science to over 22 million students worldwide.
Thanks to the efforts of the pioneer,about 40 percent of US schools now offer computer science as a subject.The numbers are even higher—an impressive 70 percent—if after-school offerings such as robotics clubs are included.Even more encouraging,eight years ago,just 19,390 students took an Advanced Placement Computer Science exam.By the spring of 2017,the number had jumped 415 percent to 99,868.
1. Why did Hardi Partovi create the“Hour of Code”?| A.To train computer scientists for the future. |
| B.To introduce the world of computing to teachers. |
| C.To add a programme to Computer Science Week. |
| D.To help people learn computer science in a fun way. |
| A.it is observed annually |
| B.it can be scheduled anytime |
| C.its projects last sixty minutes each |
| D.its tasks can be sorted by coding experience |
| A.Schools can use them regularly in their classrooms. |
| B.They help the developer make lots of money. |
| C.Over 704,000 teachers have been learning them. |
| D.They have existed for over 10 years up to now. |
| A.The efforts of Hadi Partovi. |
| B.The influence of robotics clubs. |
| C.The effect of Hadi Partovi’s efforts. |
| D.The development of many US schools. |
【推荐3】A living robot has been created out of frog skin cells. Xenobots, named after the frog species Xenopus laevis (非洲爪蝴) that the cells come from, were first described last year. Now the team behind the robots has improved their design and demonstrated new capabilities.
To create the xenobots, Michael Levin at Tufts University in Massachusetts and his colleagues obtained tissue from 24-hour-old frog embryos (胚胎) after very small physical operation. Where the previous version relied on the contraction (收缩) of heart muscle cells to move them forward by pushing off surfaces, these new xenobots swim around faster. They also live between three and seven days longer than their previous generation, which only lasted about seven days, and have the ability to sense their surroundings to some extent, turning red when exposed to blue light.
The fundamental finding here is that when you free skin cells from their normal context, and you give them a chance to build other things than what they normally build,” says Levin. “To me, one of the most exciting things here is that they are plastic. This idea that even normal cells, not genetically modified (更改), are in fact capable of building something completely different.”
Because they are created from cells, the xenobots eventually break apart and are totally biodegradable (能降解的), says team member Douglas Blackiston, also at Tufts University. He therefore hopes that they can be used for biomedical and environmental applications.
Previous attempts at creating living robots, such as a wirelessly controlled cockroach, have involved dealing with live animals, raising ethical (伦理的) concerns. Xenobots differ from these because they are made entirely of living cells. “The approach here is maybe ethically the least problematic because everything starts with cells. They have no neurons (神经元),so it’s not an animal,” says Auke ljspeert at the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology at Lausanne, who wasn’t involved in the research. “It’s really cells, so I find it maybe the cleanest way.”
1. How were the new xenobots created?| A.By making use of frog embryos. |
| B.By relying on heart muscle cells. |
| C.By sensing similar surroundings. |
| D.By exposing them to blue light. |
| A.fragile. | B.valuable. |
| C.flexible. | D.active. |
| A.The xenobots can’t break down easily. |
| B.The xenobots need to be further perfected. |
| C.The xenobots can be applied in other fields. |
| D.The xenobots have already been widely used. |
| A.The new approach starts with some neurons. |
| B.Xenobots have raised least ethical concerns. |
| C.The wireless controlled cockroach is a failure. |
| D.Previous living robots involve few living animals. |
【推荐1】14 million liters of water get wasted every year, just through the water we leave behind in restaurants. Are you shocked? Yes, but what can you do with it? The same question concerned Garvita Gulhati. But unlike the rest of us, who gave a shrug and moved on with our lives, she refused to let the fire in her die down.
She started by setting up Why Waste?, a non-profit organization with the help of four friends in 2016. They worked with restaurants by persuading them to serve half-full glasses of water. The Glass Half Full concept aims to help prevent wastage of water left in glasses while also educating the public as well as restaurants about the need of taking care of the limited water resources.
However, persuading restaurant owners was challenging. Most owners said it was against the basic rules of welcoming guests to keep a half-filled glass at the table where customers sat. But Gulhati refused to give up and came up with new strategies to try to persuade restaurant owners and staff to change their ways. Several campaigns (活动) were organized in public spaces to increase awareness.
“So far, the campaign has been successfully launched by over 80,000 restaurants across India. People have become more aware and this simple step has helped save millions of liters of water across the country,” says Gulhati, adding, “Next time you eat out, make sure your glasses are empty before leaving the food joint.” Gulhati further says, “After launching the Glass Half Full campaign, we wanted to design a module, which would attract more people to save water.”
1. Why did Gulhati come up with the Glass Half Full concept?| A.To publicize water safety. | B.To prevent water pollution. |
| C.To educate people to save water. | D.To help the restaurants recycle water. |
| A.Curious. | B.Angry. | C.Worried. | D.Interested. |
| A.Reuse our waste water. | B.Eat out less to save water. |
| C.Bring our own water when possible. | D.Empty the glasses when eating outside. |
| A.Brave and successful. | B.Responsible and determined. |
| C.Creative and confident. | D.Outgoing and humorous. |
【推荐2】Scientists have recently developed a method to 3D-print greener buildings using local soil that they say has the potential to revolutionize the construction industry.
Sarbajit Banerjee, a professor of chemistry and materials science and engineering at Texas A & M University, said 3D printing was extensively used and allowed them to print entire architectural facades (正面), although getting such structures to meet existing building regulations remained a significant challenge.
Concrete remains the primary material used in many construction projects but it cannot be recycled and requires a lot of energy to mix and transport. The research team’s aim is to print structures using the type of soil that can be found in any garden.
“While the widespread use of concrete has made housing accessible and enabled the growth of cities, this has come at a considerable environmental cost,” said Banerjee.
The move to 3D-print concrete threatens to worsen this problem. However, we imagine a new example of construction that uses naturally sourced materials. Using such materials will further pave the way for building designs that are specifically adapted to the needs of the local climate.
What’s more, the use of local materials would reduce the need to transport concrete long distances, further reducing the environmental impact of the buildings.
The research team’s plan to replace concrete with the earth beneath our feet depends on their ability to improve the soil’s ability to stand the weight of the whole house, to which Banerjee said “they are making excellent progress”.
Once they have a clearer idea of the limits of the technology, Banerjee and his team plan to further investigate how it might allow for building on other planets. For instance, they have worked on addressing the problem of building all-weather roads in the subarctic (亚北极区). They hope the technology could one day be used beyond Earth, to create settlements on the moon or even Mars.
1. What’s the latest development in construction?| A.Recycling concrete. |
| B.Reducing the construction cost. |
| C.3D-printing buildings from local soil. |
| D.Changing the construction regulations. |
| A.It reduces the need of long-distance transportation of concrete. |
| B.It helps to design buildings adjusted to the local climate. |
| C.It contributes to the development of housing and cities. |
| D.It places less burden on the environment. |
| A.The local climate. | B.The cost of transportation. |
| C.The environmental footprint. | D.The soil’s weight-bearing ability. |
| A.The prospect of further studies. | B.The explorations of the subarctic. |
| C.The limits of the new technology. | D.The barrier to building on other planets. |
【推荐3】How green are you? Do you know how to be green?
We all need a healthy environment, but we produce waste every day and it is harmful to our environment. Though we are young, we can still do something to help. Here are some ideas for you.
Reduce
Reduce means “use less”. Don’t waste things. This saves money and reduces pollution. Before we buy something new, think whether it is really necessary — or maybe the old one is still useful.
Reuse
Reuse means “use again”. When we buy things, make sure that they can last a long time. When something is broken, we should repair it instead of throwing it away and buying a new one. Don’t use a paper cup or a paper bag. It’s better to use a china (瓷) cup and a lunch box because you can use them again.
Recycle
Recycle means “change things into something else”. Though it takes energy to change something into something else, it’s better than throwing things away or burning them.
So please remember these words: reduce, reuse and recycle.
1. Which of the following is TRUE?| A.Always throw away old things. |
| B.Don’t waste things. |
| C.Always buy new things. |
| D.Never buy new things. |
| A.reuse | B.reduce |
| C.repair | D.recycle |
| A.menu | B.dictionary |
| C.storybook | D.magazine |
| A.How to produce things. |
| B.How to burn things. |
| C.How to be green. |
| D.How to help others. |
【推荐1】Warm water freezes more quickly than cold water. Sir Francis Bacon said that almost four hundred years ago. But few people believed him until 1970. In that year a Canadian scientist George Kill proved the English professor was right. Dr Kill filled an open oil pail (桶) with cold water. He filled another with warm water. He put both in the same low temperature. The warm water froze first. The lack of covers on the pails is the secret. Some of the warm water changed into vapor. This meant that less of the warm water was left to be frozen. And so the warm water froze faster than the cold water even though it had a greater temperature drop to make.
1. Hundreds of years ago, Sir Francis Bacon found _______.| A.the temperature of warm water drops faster than that of cold water |
| B.warm water is heavier than cold water |
| C.warm water has the same temperature as cold water |
| D.warm water is not as useful as cold water |
| A.cold water freezes first |
| B.warm water turns into ice before cold water |
| C.warm water and cold water freeze at the same time |
| D.much of cold water is changed into air. |
| A.Because some of the warm water turns to vapor, the amount becomes less than that of cold water. |
| B.Because warm water is lighter than cold water. |
| C.Because the temperature of warm water is lower than that of cold water. |
| D.Because cold water freezes with more difficulty than warm water. |
【推荐2】To give grasshoppers (蚱蜢) some credit -- jumping across yards and between branches takes a lot more expertise than it might appear. There are incredibly tiny factors to consider, such as the resistance in launch surface, as well as desired distance, speed, and landing.
Most jumping robots can’t compete with the insect, as their jumps are limited to starting atop extremely rigid surfaces. But a new bouncing robot developed by researchers in Carnegie Mellon’s College of Engineering is crossing those barriers, and showing promise for how autonomous devices could operate in the future.
A team of scientists led by professor of mechanical engineering Sarah Bergbreiter recently optimized a robot’s latch mechanisms (弹簧机制) used to boost it upward. Previously, these latches were primarily thought of as simple “on/off switches that enabled the release of stored energy. However, Bergbreiter and her team employed mathematical modeling to illustrate that these latches both were capable of controlling energy output, as well as controlling the transfer (传递) of energy between the jumper and the launch surface.
To test their work, the team positioned a small jumping robot atop a tree branch and recorded the precise energy transfers in its jumps’ first moments.“We found that the latch can not only mediate (调节)energy output but can also mediate energy transfer between the jumper and the environment that it is jumping from,” said Bergbreiter.
Now that researchers better understand the interactions at play in the opening moments of jumping, they can now begin working on ways to integrate this into future robotic designs. “It has been nearly impossible to design controlled insect-sized robots because they are launched in just milliseconds,“ explained Bergbreiter. “Now, we have more control over whether our robots are jumping up one foot or three. It’s really fascinating that the latch -- something that we already need in our robots -- can be used to control outputs that we couldn’t have controlled before.”
1. What does the author want to show about the new robot by mentioning grasshoppers?| A.It comes with technical difficulties. | B.It can beat the insect easily. |
| C.It is the first one designed for jumping. | D.It is shaped like the tiny creature. |
| A.They are better positioned in robots. | B.They help release more energy at a time. |
| C.They work in extreme environments. | D.They have more than a single function. |
| A.It has changed their research direction. | B.It inspires new applications of robots. |
| C.It brings them a sense of achievement. | D.It will make robots smaller and lighter. |
| A.A new model for future robots. | B.A step forward in robot design. |
| C.Jumping robots inspired by grasshoppers. | D.Efforts to develop insect-sized robots. |
【推荐3】Mosquitos can infect you with Malaria, yellow fever, and dengue. All can kill you. So we spray large areas with pesticides (杀虫剂) .But this negatively affects the whole ecosystem and your health. Now there’s a new device, which claims to keep you and your loved one’s mosquito free.
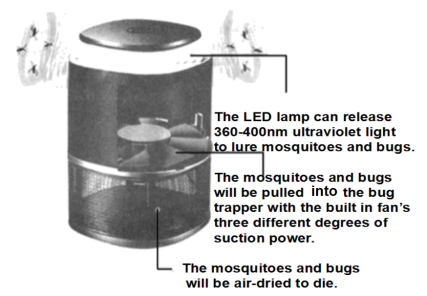
The device was designed by two German engineers who were fed up with being bitten while camping. They found solutions containing ‘DEET’ — a damaging chemical which could be both harmful to us and the environment — worked best, but still only for 45 minutes maximum and that the traditional anti-pest devices didn’t work well! So, they designed the brand new type of bug killer, Moskinator.
Instead of trying to keep the mosquitos away, it actually attracts them, then catches and kills them! It lures (引诱) the flies and mosquitos near using a safe, completely harmless LED light. The flying pests (害虫) can’t resist the UV-PT light! Next to the LED light is a powerful, yet efficient reverse fan that sucks (吸) the insects through a one-way trapdoor. Once trapped in the drying basket they are dried to death by the fan a matter of 2 minutes. You can simply empty the dead bugs into the trash, without even touching them.
Does Moskinator really work in real life? We had some of our customers try it out in their homes. The results speak for themselves:
“My wife would complain she had a headache in the mornings whenever we used chemical pesticides. Now we use our Moskinator, and we wake up bite and headache free!”— Shane Maguire
“This Moskinator really works and you don’t have to worry about breathing any harmful chemicals.”— Jake Shearer
1. What is the name of the new device?| A.DEET. | B.Moskinator | C.Malaria. | D.UV-PT. |
| A.It gives off natural light. | B.It attracts flying pests. |
| C.It sucks pests inside. | D.It dries pests to death. |
| A.Innovative and effective. | B.Traditional and cheap. |
| C.Power-saving and portable. | D.Chemical free and soundless. |
| A.To educate the readers. | B.To entertain the readers. |
| C.To introduce a new device. | D.To evaluate a new device. |



