The over 48,000 orange trees in Seville, Spain, not only fill the city’s air with the pleasant smell of orange blossoms in spring, but they also produce over 16,500 tons of fruit every winter. Though that makes the capital of southern Spain’s Andalusia region Europe’s top orange-producing city, the fruit is too sour to be consumed fresh. While some of the produce is used to make orange jam and an alcoholic drink, most of it ends up in Seville’s landfills (填埋场). However, that may change soon thanks to a clever idea to use the oranges to produce clean energy.
The trial programme is being launched by the city’s council and park department in cooperation with Emasesa, Seville’s water supply and sanitation (卫生) division. Juice from 38.6 tons of oranges will be left to ferment (发酵) in a specialised facility. The methane (甲烷) released from the fermented liquid will be captured and used to drive a generator to produce clean power. The officials estimate the test run will produce about 1,500 kWh of energy – enough to run one of Emasesa’s water purification plants. To ensure there is no waste, the orange skins, peels, and flesh will be used as fertiliser.
“It’s not just about saving money. The oranges are a problem for the city, and we’re producing added value from waste,” said Benigno Lopez, head of Emasesa’s environmental department.
If successful, by 2023, the city hopes to recycle all the oranges and add the electricity produced back into its power transmission network. In trial runs, one ton of oranges produced 50 kWh of clean energy – enough to cover the daily electricity needs of five homes. The project team estimates that if all the fruit is recycled, it will produce enough energy to power as many as 73,000 residences.
“This project will help us to reach our targets for reducing emissions, energy self-sufficiency, and the circular economy,” Juan Espadas Cejas, mayor of Seville, said in the press conference announcing the trial scheme.
1. What do we know about oranges in Seville?| A.They are usually picked in spring. |
| B.They are not recommended to be eaten fresh. |
| C.They are mostly used to make jams and juice. |
| D.They make Seville the world’s top orange-producing city. |
| A.Different uses of Seville oranges. |
| B.Ways to produce power from juice. |
| C.An introduction to the trial programme. |
| D.Reasons for launching the trial programme. |
| A.The energy produced will be used to purify water. |
| B.Seville hasn’t carried out the trial programme yet. |
| C.The electricity produced will go to Seville’s power plants. |
| D.14,600 tons of recycled oranges are needed to power 73,000 homes. |
| A.Seville Is Developing New Energy | B.Seville Is Turning Waste into Wealth |
| C.Seville Is Seeking Market for Oranges | D.Seville Is Contributing to Energy Saving |
相似题推荐
【推荐1】Egypt is home to more than 100 pyramids, including the landmark Giza pyramid which is the last-standing ancient wonder of the world. It is an example of the wisdom and skills of ancient development. The Great Pyramid of Giza has stood tall since the 26th Century BC, and took 27years to build, with around 2.3 million blocks of stone weighing 6 million tons.
Giza is actually made up of three pyramids, Khufu, Khafre, and Menkaure—each one is named after a pharaoh (法老). Now, scientists are using High Energy Physics to scan (扫描) the Khufu structure at Giza. The new technology scans deeper into the pyramid than before, and then maps its inside structure.
What we see now is only the central structure of the Great Pyramid. Although the pyramid has been studied closely for centuries, there are two mysterious holes that have kept archaeologists puzzled.
One is around 98 feet long and 20 feet high and could be one large space or several rooms, according to scans of the pyramid, while the other is much smaller, just beyond the north face of the pyramid. Archaeologists are not sure what either space functioned as; the most exciting possibility is that the larger space is the hidden room to keep Khufu, who governed from around 2551BC to 2528BC.
Finding holes in pyramids isn’t unusual, though. Nowadays, though, we have the technology to find out, compared to days gone by when examinations would have to blow up the pyramids to explore.
“Since the instruments that are used are very large, they cannot be placed inside the pyramid, and therefore our approach is to put them outside and meticulously move them along the base. In this way, we can build up the required data set,” the team wrote in the paper. The technology is so precise that scientists may be able to even tell objects within the hole.
1. What can be learned about the Great Pyramid of Giza?| A.It is named after a pharaoh. | B.It is the largest ancient wonder of the world. |
| C.It was built with around 6 million stones. | D.It has a history of more than 4, 000 years. |
| A.The owner of the pyramid. | B.The two mysterious holes. |
| C.The advanced research technology. | D.The central structure of the Giza pyramid. |
| A.They caused damage. | B.They took long to carry out. |
| C.They used no equipment. | D.They explained almost all puzzles. |
| A.Carefully. | B.Quickly. | C.Formally. | D.Secretly. |
【推荐2】Droughts are one of a farmer’s most feared threats. And in our warming climate, the risk of drought has been climbing. Anticipating a drier future, two American teen engineers have been investigating how to help farmers keep their crops from getting dangerously thirsty.
John Benedict, 16, has seen lots of droughts. As a sophomore at Clovis North High School, he wanted to help farmers save their plants from being dried. To measure a plant's drought stress more directly, he built a small robotic arm and used it to measure the light reflecting off of bell peppers. As plants get dry, the way they reflect sunlight changes very slightly. It’s not something that our eyes can see. But it is something a robot could detect. At the same time, his robot measured soil moisture and temperature. With these data, he built a computer model. It predicts which plants will be suffering from thirst faster.
It’s also important to make sure that no irrigation water is wasted. That’s why Arya Tschand, 17, has been launching his drone into the sky. This senior at High Technology High School, aims to help poor farmers like the ones he saw while traveling in India. The teen’s drone hovers over plants and measures their color. Using a computer model, Arya taught the drone to predict how thirsty a plant was based on the color of its leaves. According to that color, the drone then sends a signal to an irrigation system on the ground, which adjusts how much water it sends out to plants.
In areas with drought, where every drop matters, farmers can’t afford to waste any moisture. Just like John, his next step is to scale up his project. In the meantime, he has applied for a patent on his system.
1. What did John focus on in his project?| A.Plants management. | B.Data analyses. | C.Plant-thirst detection. | D.Lights changes. |
| A.Protecting the plants. | B.Helping precise irrigation. |
| C.Forecasting plant colors. | D.Arranging computer models. |
| A.It’s unclear. | B.It’s disappointing | C.It’s controversial. | D.It’s promising. |
| A.A travel brochure. | B.A guidebook. | C.A magazine. | D.A research paper. |
【推荐3】Many years ago, people relied on the sun, the moon and stars to find their way around. Later, the compass was introduced. And now, we have satnav (卫星导航) systems to guide us. A satnav system uses groups of satellites to show the user’s location. They send information to a receiver, such as a smartphone, to show us where we are.
The earliest built satnav system is the Global Positioning Satellite System, which belongs to the US. Then there is Russia’s Global Navigation Satellite system, the European Union’s Galileo and China’s own satellite navigation system, Beidou.
On October 18, 2017, an ARJ21-700 plane, which was the first domestically (国内地) produced jet equipped with the Beidou navigation system, successfully completed a test flight. The results showed the performance of the system developed by China matches that of similar systems produced abroad, according to the Commercial Aircraft Corporation of China.
Since its introduction in 2000, the Beidou navigation system has been increasing numbers of applications linked to everyday life, from shared bikes to farming.
When it comes to shared bikes, smart locks that support Beidou chips offer more accurate positioning than others, making it easier to find a bike.
Farmers can use Beidou-enabled tractors to plow (犁) the soil and use unmanned aircraft with Beidou to sow seeds, which can improve efficiency and make better use of resources. Beidou’s farming applications have spread from Heilongjiang Province to Beijing, Liaoning, Shanxi, Hubei and other regions across China.
With its many uses, the Beidou navigation system is even playing a big role in the Belt and Road Initiative. “To date, the Beidou system has covered most parts of the Asia-Pacific region, as well as countries along the Silk Road Economic Belt and the 21st Century Maritime Silk Road,” said Yang Changfeng, chief designer of the Beidou system.
Today, there are more than 20 Beidou satellites above our heads, and China plans to launch even more this year to expand the Beidou network to better serve the Belt and Road Initiative.
“As Beidou expands its overseas reach, it will be increasingly popular in the logistics (物流) industry,” said Miao Qianjun, Secretary General of the navigation services association. “Ships, for example, can use it to position themselves while sailing across oceans to European countries, no longer limited to Southeast Asian regions in the near future.”
1. What is the purpose of the first two paragraphs?| A.To compare some modern satnav systems. |
| B.To describe the benefits of satnav systems. |
| C.To tell us how satnav systems were created. |
| D.To introduce some satnav systems and their functions. |
| A.It was used successfully in a new jet plane. |
| B.It is more powerful than other satnav systems. |
| C.It was introduced to China on October, 2017. |
| D.It wasn’t used in our everyday life until recently. |
| A.plowing the soil and sowing seeds |
| B.improving the efficiency of network |
| C.producing more smart locks for shared bikes |
| D.navigating ships across oceans to European countries |
| A.Worried. | B.Casual. | C.Positive. | D.Indifferent. |
Here is an expression about bees that is not used much any more, but we like it anyway. We think it was first used in the 1920s. If something was the best of its kind, you might say it was the bee’s knees. Now, we admit that we do not know how this expression developed. In fact, we do not even know if bees have knees!
If your friend cannot stop talking about something because she thinks it is important, you might say she has a bee in her bonnet (女帽). If someone asks you a personal question, you might say “that is none of your beeswax”. This means none of your business.
Speaking of personal questions, there is an expression when their children ask, “Where do babies come from?” Parents who discuss sex and reproduction (生殖) say this is talking about the birds and bees.
Butterflies are beautiful insects, but you would not want to have butterflies in your stomach. That means to be nervous about having to do something, like speaking in front of a crowd. You would also not want to have ants in your trousers. That is, to be unable to sit still.
1. If you make a beeline for something, you _____ .
| A.are as busy as a bee | B.go quickly and directly towards it |
| C.always go to the same place | D.buy something at a certain place |
| A.is not used at all now | B.was first used in the 1820s |
| C.reminds us that bees have knees | D.means “it is very good” |
| A.It is none of your beeswax | B.You have a bee in your bonnet |
| C.It is the bee’s knees | D.You are talking about the birds and bees |
| A.are too sick to sit still | B.have ants in your trousers |
| C.are nervous about something | D.have a stomachache |
【推荐2】Look at the center circles of Diagram A and Diagram B. Which of the center circles looks larger? In Diagram B? In fact, they are exactly the same size.
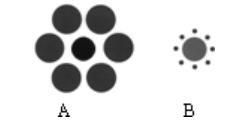
Then look at the picture on the right. What do you see? A vase? Or two faces?Does the picture change quickly from one to the other again and again? Maybe or maybe not, but you can never see them at the same time.

“What’s happening? Is something wrong with my eyes?” You may wonder at what you see.
Don’t worry. Here is how it goes:
When we look at things, our eyes send messages to our brains and then our brains interpret the information. However, sometimes our brains interpret the received information in a wrong way. It seems that our eyes are playing a joke on us. This often happens and we call it “visual illusion (错误)”.
1. Why does the center circle in Diagram A look smaller than that in Diagram B?| A.Something is wrong with our eyes. |
| B.The two circles are not the same size. |
| C.The two pictures change quickly from one to the other. |
| D.Our brains interpret the information in a wrong way. |
a. We look at things with our eyes.
b. Our brains interpret the messages.
c. Our brains tell us what we have seen.
d. Our eyes send messages to our brains.
| A.c a b d |
| B.a d b c |
| C.a c d b |
| D.b c a d |
| A.To make the actors seem different in size. |
| B.To make the actors much braver. |
| C.To help the actors become stronger. |
| D.To help the actors look better. |
【推荐3】The 31,000-year-old skeleton (骨骼) of a young adult found in Indonesia reveals the oldest known evidence of an amputation (截肢), according to a new study.
“We were exploring a cave in Borneo, in a rainforest region, for some of the earliest rock art in the world, when we came across the burial site and the skeleton, which then excited our curiosity,” said Tim Maloney, the study’s lead researcher. Though much of the skeleton was complete, it missed its left foot and the lower part of its left leg, he explained. After examining the remains, the researchers concluded the foot bones weren’t lost in the site or in an accident — they were carefully removed. The remaining leg bone showed a clean cut.
Researchers believed the find presents a remarkable deed. It’s tricky and demanding to prevent infection in amputations, even to this day. Yet more than 30,000 years ago someone was able to handle it. Researchers didn’t know what tool was used to cut the body parts, but they assumed a sharp stone tool may have made the cut. What seems certain is that the patient enjoyed great post-operative care for considerable time, for the person appeared to have lived for around six to nine more years after being disabled.
The operation’s good end result is not pure chance. It implies that the person who performed the operation had some understanding of antimicrobial (抗菌的) medicine. In this respect, their lifestyle and forest environment might have proved to be advantages. “Given these people lived in an area with many medicinal plants, there is a strong case to guess that adapting to this environment may have boosted the development of advanced medical knowledge,” Maloney said.
The surgery rewrites the history of human medical developments. Before this find, the earliest example of amputation had been in a French farmer from almost 7,000 years ago. Researchers had believed advanced medical practice developed around 10,000 years ago, as humans settled down into agricultural societies. But this study adds to evidence that humans started caring for each other’s health long before that.
1. What did Maloney say about the skeleton?| A.It is preserved poorly. | B.It is found by accident. |
| C.It needs further study. | D.It shows ancient wisdom. |
| A.Seeking proper tools. | B.Keeping the cut clean. |
| C.Avoiding the infection. | D.Providing post-operative care. |
| A.Reasons for the surgery’s success. | B.Geographical features of Borneo. |
| C.Knowledge of plants’ medicinal use. | D.Benefits of the forest environment. |
| A.Borneo is the source of surgical amputation. |
| B.Amputation is common for prehistoric people. |
| C.Ancient agriculture promoted medical development. |
| D.Humans made advanced medical practice earlier than thought. |



