When we visit museums, we see cultural artifacts—from everyday household items to precious carvings and statues, which give us a glimpse into the diverse cultures and communities from around the world.
However, controversy surrounds these artifacts and whether or not countries should return these pieces of culture if they were stolen or forcefully taken during colonization (殖民).
On Wednesday, October 7, 2020, the Dutch advisory committee officially released a national report agreeing to the return of cultural artifacts that were stolen from its previous colonies such as Indonesia, Suriname, and islands on the Caribbean. Through these actions, the Dutch government acknowledged the unfair treatment the colonies had previously experienced and demonstrated respect for the culture of these countries.
By the 18th and 19th centuries, European countries such as Britain, France, and the Netherlands had colonized many African and Asian countries. During their rule, they either seized artifacts or took them as spoils of wars, and brought them to their own countries where they are now on display in museums.
Over the years, European museums have received requests for the return of artifacts. The debate regarding this issue took a turn in 2018 when a French report was released that directed that all heritage objects brought to French museums be restored. With the official release of this report, museums all across Europe began reconsidering their previous policies on colonial treasures.
Those who propose returning these objects to their original homes argue that with technology enabling virtual museum tours, returning these artifacts to their homeland does not take away the opportunity to learn about them. Furthermore, the country of origin will receive a significant part of their heritage back, and these artifacts will be given a chance to be truly appreciated in proper historical context.
Those against the restoration claim that culture is shared treasure and the artifacts are in fact “cultural ambassadors” that promote tolerance and understanding. They believe that while stealing them was wrong, history is full of “good” and “bad” actors. Moreover, they feel that keeping the cultural objects in the current museums has kept millions of artifacts safe from disfiguration and damage.
1. What did the Dutch government admit?| A.The colonies were treated unfairly. | B.The colonies had stolen cultural artifacts. |
| C.The colonies had experienced cultural boom. | D.The colonies had been respected for their culture. |
| A.Egypt. | B.France. | C.Britain. | D.The Netherlands. |
| A.These artifacts reflect a culture of shared treasure. |
| B.These artifacts prove that the history is difficult to explain. |
| C.These artifacts will be enjoyed in their historical background. |
| D.These artifacts help people distinguish good history from bad history. |
| A.Are Virtual Museum Tours Meaningful? | B.Do People Appreciate Stolen Treasures? |
| C.Will Stolen Treasures Belong to Colonies? | D.Should Museums Return Stolen Treasures? |
相似题推荐
【推荐1】On average, American kids ages 3 to 12 spent 29 hours a week in school, eight hours more that they did in 1981. They also did more household work and participated in more of such organized activities as soccer and ballet (芭蕾舞). Involvement in sports, in particular, rose almost 50% from 1981 to 1997: boys now spend an average of four hours a week playing sports; girls log half that time. All in all, however, children’s leisure time dropped from 40% of the day in 1981 to 25%
“Children are affected by the same time crunch (危机) that affects their parents,” says Sandra Hofferth, who headed the recent study of children’s timetable. A chief reason, she says, is that more mothers are working outside the home. (Nevertheless, children in both double-income and “male breadwinner” households spent comparable amounts of time interacting with their parents 19 hours and 22 hours respectively. In contrast, children spent only 9 hours with their single mothers.)
All work and no play could make for some very messed-up kids. “Play is the most powerful way a child explores the world and learns about himself,” says T. Berry Brazelton, professor at Harvard Medical School Unstructured(unorganized)play encourages independent thinking and allows the young to handle their relationships with their peers, but kids ages 3 to 12 spent only 12 hours a week engaged in it.
The children sampled spent a quarter of their rapidly decreasing “free time” watching television. But that, believe it or not, was one of the findings parents might regard as good news. If they’re spending less time in front of the TV set, however, kids aren’t replacing it with reading. Despite efforts to get kids more interested in books, the children spent just over an hour a week reading. Let’s face it, who’s got the time?
1. By mentioning “the same time crunch” (Line 1, Para. 2) Sandra Hofferth means ______.| A.children have little time to play with their parents |
| B.both parents and children suffer from lack of leisure time |
| C.children are not taken good care of by their working parents |
| D.both parents and children have trouble managing their time |
| A.he has plenty of time reading and studying |
| B.he has more time participating in school activities |
| C.he is left to play with his peers in his own way |
| D.he is free to interact with his working parents |
| A.extracurricular activities(after-class activities) promote children’s intelligence |
| B.most children will turn to reading with TV sets switched off |
| C.efforts to get kids interested in reading have been fruitful |
| D.most parents believe reading to be beneficial to children |
【推荐2】Labeling can be very helpful when determining certain things about a food item. “USDA (United States Department of Agriculture) Organic” and “raised without antibiotics (抗生素)”, for example, have specific standards, and the product will need to be true to those claims.
Natural claims like “all natural”, “100% natural”, and “made with natural ingredients (成分)” are not defined in USDA. The USDA must approve these special claims prior to food being sold, but the only standard they must meet is that artificial ingredients or colors cannot be added during processing, and the processing method cannot fundamentally alter the product. While that is certainly valuable information to know, the problem is in consumers’ understanding of what “natural” means. The definitions do not address human health, the use of synthetic pesticides (合成杀虫剂), hormones, or antibiotics in crop and livestock production.
Study after study on the topic reveals that people think a product labeled as “natural” delivers benefits far beyond what it does. Most consumers mistakenly assign health and environmental benefits to natural-labeled food.
In a 2017 study, respondents incorrectly believed that natural-labeled foods had 18 percent fewer calories across a variety of foods. In a 2010 study, respondents believed that meat products labeled as “all natural” meant no antibiotics or hormones were used to raise the animals. Some also believed the label meant animals were raised free range.
Consumers aren’t getting what they think they’re getting. But the more serious problem is how this harms food producers who are actually meeting the standards for more strict labels that are actually doing good, like ones around organic practices or animal welfare. Farmers and producers doing the work end up at a competitive disadvantage in the marketplace if consumers treat foods labeled natural as alike. The economic problem raised by natural labels is that consumers could be paying extra for product benefits they are not receiving while producers of products with those benefits lose sales.
1. Which of the following is undefined by authorities?| A.USDA organic. | B.All natural. |
| C.Artificial color free. | D.Raised without antibiotics. |
| A.Being unaware of food safety. |
| B.Paying more on over-processed food. |
| C.Buying food failing to meet the USDA standards. |
| D.Misunderstanding what is claimed on a food label. |
| A.To advocate sensible consumer behavior. |
| B.To suggest a possible solution to a problem. |
| C.To provide evidence for the author’s point of view. |
| D.To demonstrate how far studies on food safety have gone. |
| A.Wasting resources. | B.A market crash. | C.Cheating. | D.Unfairness. |
【推荐3】Recycling in general can be an effective way to reuse natural material resources. The U.S.’s high recycling rate of paper, 68 percent, has proved this point. But although some materials can be effectively recycled and safely made from recycled content, plastics cannot. Plastic recycling does not work and will never work.
The problem with recycling plastic lies not with the concept or process but with the material itself. There are thousands of different plastics, each with its own characteristics. They all include different chemicals that cannot be recycled together, making it impossible to sort the trillions of pieces of plastics into separate types for processing. What’s more, plastic recycling costs more than new plastic because collecting, sorting, transporting, and reprocessing plastic waste is very expensive.
Despite this obvious failure, the plastics industry has begun a decades-long campaign to keep the lie that the material is recyclable, which reminds the public of the tobacco industry’s efforts to tell smokers that filtered (过滤的) cigarettes are healthier than unfiltered cigarettes.
Traditional mechanical recycling, in which plastic waste is ground up and melted (熔化), has been around for many decades. Now the plastics industry is promoting the benefits of so-called chemical recycling, in which plastic waste is broken down using high heat and turned into a low-quality fossil fuel. In 2018, Dow Chemical claimed that the Renewlogy chemical-recycling factory in Salt Lake City was able to reprocess mixed plastic waste through the “Hefty EnergyBag” program and turn it into diesel fuel (柴油). As Reuters showed in a 2021 survey, however, the pyrolysis (高温分解) process was not worth it.
We’re not making a case for hopelessness. Just the opposite(相反的). We need the facts so that individuals and policymakers can take action. Proven solutions to the plastic-waste and pollution problems exist and can be quickly copied across the country. These solutions include placing bans on single-use plastic bags and unrecyclable single-use plastic food-service products, and installing dishwashing equipment in schools.
Consumers can put pressure on companies to stop filling store shelves with single-use plastics by not buying them and instead choosing reusables and products in better packaging. And we should all keep recycling our paper, boxes, cans, and glass, because that actually works.
1. What is the problem with recycled plastic?| A.It costs too much to produce. |
| B.It can hardly be selected out. |
| C.It is generally of poor quality. |
| D.It can’t be stored in large numbers. |
| A.To compete with the tobacco industry. |
| B.To cut down the cost of recycling plastic. |
| C.To uncover the lie of the tobacco industry. |
| D.To prove the possibility of recycling plastic. |
| A.Traditional recycling proves to be safer. |
| B.Chemical recycling turns out to be a failure. |
| C.Chemical recycling can save energy resources. |
| D.Traditional recycling can deal with limited waste. |
| A.To show the difficulty in recycling plastic. |
| B.To introduce a new way of recycling plastic. |
| C.To stress the importance of recycling plastic. |
| D.To call for a ban on single-use plastic products. |
【推荐1】When ice cream maker Adrienne Borlongan first experimented with a White Rabbit flavor, she thought it tasted like “cheap vanilla (香草)”. A few weeks after she added it to her Los Angeles shop, Wanderlust Creamery, visitors showed little interest. But when Borlongan posted a photo of an ice cream cone wrapped in White Rabbit-branded paper, word quickly spread on social media.
The candy, first produced in Shanghai in the 1940s, is known for its red-white-and-blue packaging and is beloved by kids all over China. And when Chinese people began to live in other countries, their love for the white, creamy candy went with them.
Soon after Borlongan posted that photo, people were driving to Wanderlust from all over California. Since then, White Rabbit has been the mainstay of Wanderlust’s ice cream lineup and is regularly sold out in their webshop.
But the story of the ice cream is about way more than taste — it’s about the power of nostalgia (怀旧) and eye-catching branding. White Rabbit’s origins date back to a business called the ABC Company, founded in Shanghai in 1943. It was later sold to the state-owned Guan Sheng Yuan Food Group, which owns it to this day.
The mix of colorful wrappers and the sweet milky taste proved a winner. Kids from Beijing to Hong Kong grew up on the sweets, and it also became a national symbol of the country — most famously, US President Richard Nixon was given some when he made his historic visit to China in 1972.
As for the flavor? The creamy consistency (黏稠度) actually comes from milk, and there’s a piece of rice paper between the candy and the wrapper to prevent melting. Over the years, White Rabbit has tried out other flavors, including red bean and peanut. But it’s the first version that has the most nostalgia connected to it.
1. What can we learn about the White Rabbit ice cream?| A.It used to be popular in China. | B.It is available online. |
| C.It is shaped like a white rabbit. | D.It was first produced in Shanghai. |
| A.Fanciest design. | B.Newest brand. |
| C.Cheapest goods. | D.Bestselling product. |
| A.To look back on the historic visit. |
| B.To show Chinese people’s hospitality. |
| C.To prove White Rabbit’s popularity. |
| D.To indicate Nixon’s interest in White Rabbit. |
| A.The story behind the success of the White Rabbit ice cream. |
| B.Childhood memories carried with White Rabbit. |
| C.The international reputation of the ABC Company. |
| D.The history of the White Rabbit candy. |
【推荐2】We are all busy talking about and using the Internet, but how many of us know the history of the Internet?
Many people are surprised when they find that the Internet was set up in the 1960s. At that time, computers were large and expensive. Computer networks didn’t work well. If one computer in the network broke down, then the whole network stopped. So a new network system had to be set up. It should be good enough to be used by many different computers. If part of the network was not working, information could be sent through another part. In this way, computer network system would keep on working all the time.
At first the Internet was only used by the government, but in the early 1970s, universities, hospitals and banks were allowed to use it, too. However, computers were still very expensive and the Internet was difficult to use. By the start of the 1990s, computers had become cheaper and easier to use. Scientists had also developed software that made “surfing” the Internet more convenient.
Today it is easy to get online and it is said that millions of people use the Internet every day. Sending email is more and more popular among students.
The Internet has now become one of the most important parts of people’s life.
1. The Internet has a history of around ________ years until the year of 2020.| A.ten | B.twenty | C.sixty | D.seventy |
| A.break down the whole network | B.make itself keep on working all the time |
| C.make computers cheaper | D.make computers large and expensive |
| A.Scientists | B.the government |
| C.schools | D.hospitals and banks |
| A.Software | B.Scientists | C.Information | D.Computers |
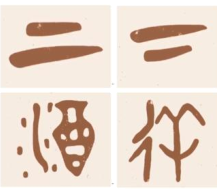
[1] The first Chinese characters date from the late Shang Dynasty, some 3, 000 years ago, originally made for the purposes of divination (占卜). They were written on pieces of tortoiseshell and fragments of bone.
[2] During the Shang Dynasty, divination was very important. To those who knew how to read them, it was belief that exhibits of shell and bone could foretell the future, tell you when to sacrifice, when to harvest, and when illness would strike. So, it was these diviners seeking to unlock the future that accidentally provided us with a key to the past. These oracle bones (甲骨) offer us a precious glimpse of life in China some three thousand years ago.
[3] Of the four thousand characters used in these descriptions, so far 1500 have been deciphered. Through them, we can reconstruct a day in the life of a Shang Dynasty man.
[4] It was that by a combination of careful observation and incredible imagination, the people of the Shang dynasty turned what they saw, did, and felt into symbols that could be written on turtle shells and animal bones — the very first Chinese characters.
[5] In pictograph characters like “Tian”, meaning farm, simple lines were used to outline the shape of something. But more abstract concepts could be described, too. For example, a short horizontal stroke above a long one meant “above”, a short stroke below a long one meant “below”. By combining more than one character into one, even more complex ideas could be expressed. Take Jio, meaning wine, for example, a combination of the character for cup or container and water. Other characters would combine one character indicating a certain sound with another specifying meaning. Yang, for example, meaning wander.
[6] Thanks to the Chinese characters on the oracle bones, Chinese civilization could at last be recorded and passed down the generations. Strange as it may seem, the complex system of writing we use today began life thousands of years ago as scratches on bits of bone. Now they're rooted in hearts and minds of more than a billion people.
1. What were the first Chinese characters initially used for?| A.Serving the rulers. | B.Recording the past. | C.Showing natural power. | D.Unlocking the future. |
| A.Identified. | B.Destroyed. | C.Discovered. | D.Simplified. |
| A.The evolution. | B.The formation. | C.The connection. | D.The meaning. |
| A.To introduce oracle bone script. | B.To stress the value of Chinese characters. |
| C.To highlight the birth of Chinese culture. | D.To offer a glimpse of life in Shang Dynasty. |
【推荐1】“Can’t hold a candle to” is a popular expression. When there was no electricity, someone would have a servant light his way by holding a candle. The expression meant that the person who couldn’t hold a candle for you was not fit even to be your servant. Now, it means such a person cannot compete.
Another expression is“hold your tongue.”It means “to be still and not talk”. “Hold your tongue” is not something you would tell a friend. But a parent or teacher might use the expression to quiet a noisy child.
“Hold out” is an expression one hears often in sports reports and labor news. It means to refuse to play or work. Professional (专业的) football and baseball players “hold out” if their team refuses to pay them what they think they are worth.
The expression “hold up” has several different meanings. One is “to delay (耽误)”. A driver who is held up by heavy traffic might be late for work. Another meaning is “for a story to be thought true after surveys”. A story can hold up if it is proved true.
“Hold on” is another expression, which means “wait or stop”. As you leave for school, your brother may say, “Hold on, and you forgot your book.” It is used to ask a caller to wait und not to hang up his or her telephone.
Our final expression is “hold the line”. This means “to keep a problem or situation from getting worse — to hold steady”. For example, the president may say he will “hold the line on taxes”. He means there will be no increase in taxes.
1. In which of the following sentences can the expression “can’t hold a candle to” be used?| A.Some footballers refuse to play a game. |
| B.Someone else is wanted on the phone. |
| C.Someone is not equal to a job. |
| D.Someone is delayed by heavy traffic. |
| A.interesting | B.polite |
| C.unfriendly | D.joking |
| A.change their attitude | B.refuse to work |
| C.make a promise | D.show their devotion |
| A.Hold is a difficult word for learners to master. |
| B.Expressions made of “hold” have different meanings. |
| C.English has so many words and expressions. |
| D.Hold is one of the most popular words in English. |
【推荐2】Efforts of growing organic vegetables that brings much less damage to the farmland paid off as Yunnan Province in southwest China has been trying to deliver its promise to better protect its natural resources.
In the trail field under the management of Yunling Organic Agriculture Development Co., Ltd , the organic matter in soil has been improved while content of some heavy metals has been reduced ever since the organic planting project started in 2017. The green fertilizer they use has left close to little pollution in the soil, which is of critical significance as the field that covers 240 hectares of land is located right in the middle of Kunming Songhuaba Reservoir Nature Reserve.
Now, more than 50 tons of vegetables of more than 20 varieties from the field are sent to places across China every day. Although the price is three to five times higher than that of ordinary vegetables, it is popular in the middle and high-end retail markets in east, central and south China. In Tonghai County, one of the main producing areas, the organic vegetables have begun to enter Southeast Asian market.
“A revolutionary change should be made to the traditional growing mode or cultivation technology. If the zero emission of chemical remains is realized, our problems of environmental pollution will be solved,” said He Jiangming, researcher at the Institute of Horticulture, Yunnan Academy of Agricultural Sciences.
1. What does the underlined word “deliver” in paragraph 1 probably mean?| A.Send. | B.Address. | C.Keep. | D.Save. |
| A.Yunnan province intends to grow organic vegetables to make more money. |
| B.The soil in the trail field is metal-free. |
| C.The organic vegetables are not popular because of their high prices. |
| D.Organic farming may help solve the problems of environmental pollution. |
| A.Doubtful | B.Critical | C.Optimistic | D.Neutral |
| A.All efforts paid off | B.Clean organic farming brings green future |
| C.How to reduce heavy metals in soil? | D.Traditional or organic ? |
【推荐3】Failure is an unavoidable part of life. Though science has named some life skills that promise success, we're told over and over again that no great success was ever achieved without failure -- or many failed attempts. One of life's most important lessons, therefore, has to be how to handle failure best. But what is the message?
For starters, ignore advice from anyone that tells you, “Don't beat yourself up about it,” no matter how well-meaning they are. According to the new research from the University of Kansas, we absolutely should be beating ourselves up when we fail. Marketing professor Noelle Nelson and her team found that the more emotional a person's response is to failure, the more likely they are to achieve better results the next time they deal with a related task.
The researchers carried out two experiments in which undergraduate students were required to perform specific tasks. In one experiment, they were asked to search online for a squeezer and report the lowest price they could find with the possibility of winning a $50 cash prize. However, the task was controlled, and all participants were told (by a computer) that the lowest price was $3.27 less than their reported price. Consequently, no participant won the cash prize. When the results were announced, some participants were asked to focus on their emotional response, and others on their cognitive (认知的) response. During the next similar task, participants who focused on their emotional response to failure made more effort than those who focused on a cognitive response.
Everybody has their own unique challenges, responsibilities, duties, and projects, but these findings are related to all of us. Your personal failure may be a cake that fails to rise, a presentation that goes wrong, or a deadline that gets missed—it doesn't matter. What matters is how you react to it. Instead of thinking about the failure, let yourself feel bad about it. Then follow this advice on how to bounce back after your failure.
1. What's the relationship between failure and success?| A.Failure promises success. | B.Failure is the key to success. |
| C.Failure does damage to success. | D.Well-handled failure is good for success. |
| A.It's a well-meaning suggestion for failure. |
| B.It's been proved by the study of a university. |
| C.Being emotional is good for his future success. |
| D.It can make people less emotional about failure. |
| A.Personal Failure Is a Cake That Fails to Appear |
| B.The Most Productive Way to Handle Any Failure |
| C.Different Methods to Change Failure into Success |
| D.The Reason Why Failure Is the Mother of Success |



