Don't get mad the next time you catch your teenager texting when he promised to be studying. He simply may not be able to resist. A University of lowa(UI) study found teenagers are far more sensitive than adults to the immediate effect or reward of their behaviors. The findings may help explain why the initial rush of texting may be more attractive for adolescents than the long-term pay off of studying.
"For the teenager, 'the rewards are attractive." says Professor Jatin Vaidya,an author of the study. "They draw adolescent. Sometimes, the rewards are a kind of motivation for them. Even when a behavior is no longer in a teenager's best interest to continue, they will, because the effect of the reward is still there and lasts much longer in adolescents than in adults ."
For parents,that means limiting distraction (分心的事情)so teenagers can make better choices. Take the homework and social media dilemma: At 9 p.m., shut off everything except a computer that has no access to Facehook or Twitter, the researchers advise. "I'm not saying they shouldn't be allowed access to technology," Vaidya says. But some help in netting their concentration is necessary for them so they can develop those impulse-control skills.”
In their study,Vaidya and co-author Shaun Vecera note researchers generally believe teenagers are impulsive(冲动的),make bad decisions,and engage in risky behavior because the frontal lobes(额叶)of their trains are not fully developed. But the UI researchers wondered. whether something more fundamental was going on with adolescents to cause behaviors independent of higher-level reasoning.
"We wanted to try to understand the brain's reward system how it change from chillhood to adulthood," Says Vaidya, who adds the reward character in the human brain is easier than decision-making. “We've been trying to understand the reward process in adolescence and whether there is more to adolescence behavior than an under-developed frontal lobe,”he adds.For their study ,the researchers persuaded 40 adolescents, aged 13 and 16,and 40 adults, aged 20 and 35 to participate.
In the future,researchers hope to look into the psychological and neurological(神经学上的)aspects of their results.
1. What does the passage mainly tell us?| A.The initial rush of texting is less attractive for adolescents than the long-term pay off of studying. |
| B.Always, rewards are attractive to teenagers. |
| C.Resistance can be controlled well by adolescents. |
| D.Getting rewards is the greatest motivation for adolescents to study. |
| A.The influence of the reward is weak in adolescents. |
| B.Parents should help children in making decisions. |
| C.Children should have access to the Internet. |
| D.Children need help in refocusing their attention. |
| A.Doing things after some thought. |
| B.Making good decisions. |
| C.Joining in dangerous actions. |
| D.Escaping risky behavior. |
| A.By making a comparison of brain examinations. |
| B.By examining adults’ brain. |
| C.By examining teenage brain. |
| D.By building the train’s reward system. |
相似题推荐
【推荐1】Aspirin has long been believed to help prevent heart attacks and strokes(中风).Some studies have shown that it also has a protective effect against certain types of cancer. As a result, some people religiously pop a low-dose(低剂量的) aspirin after breakfast every day (never take one on an empty stomach). But now its status as a wonder drug has come into question, following a meta-analysis of trial evidence.
A meta-analysis reviews the results of a large number of trials and can therefore come to more certain conclusions. This latest review was published this May in The Journal of the American Medical Association.It focused on the connection between aspirin use and cardiovascular(心血管的) and bleeding events. It found that the well-known risk that aspirin can cause internal bleeding is as great as the benefits of preventing heart attacks and strokes. In some cases, the risk even outweighs the benefits.
Aspirin thins the blood, thus helping to prevent blood clots (血栓). For his reason, it is a good drug for protecting people who have already had a heart attack or stroke from having another. However, the 164,225 people in these trials had no history of cardiovascular disease. They were monitored for an average of six years, during which time they took a daily aspirin or placebo(安慰剂).Among those who took aspirin, there were about 11% fewer heart attacks and strokes but 43% higher likelihood of a major bleeding episode in the stomach, brain or intestine(肠道).
Dr Sean Zheng, a cardiology(心脏病学) researcher at King’s College London, said that taking a daily aspirin couldn’t be recommended for healthy people. But there might still be a case for people with a higher risk of a heart attack or stroke, he added. However, it would be important to consider the bleeding risk.
“Aspirin use requires discussion between the patient and their physician, with the knowledge that any small potential cardiovascular benefits are weighed up against the real risk of severe bleeding." he said.
The findings reflect the average likelihood of bleeds or heart attacks among the patients in all the trials. There will be people among them who would be better off taking aspirin and those who will be worse. It's yet another situation where we need to weigh up our individual risk and benefit--- maybe with the help of an understanding GP.
1. Which of the following is NOT a reason why some people take an aspirin every day?| A.They want to lower their risk of having a heart attack |
| B.They hope to protect themselves against some cancers |
| C.They want to ensure they don't have a sick stomach |
| D.They aim to make sure they won't suffer another stroke |
| A.That aspirin does more harm than good to the human body |
| B.That aspirin frequently causes internal bleeding because it thins the blood |
| C.That previous research into the effects of aspirin on the human body was unreliable. |
| D.That taking aspirin is not worth the risk or those with no history of heart tacks or strokes. |
| A.To have a thorough physical examination |
| B.To ask for others' opinions on the internet. |
| C.To read the findings of new studies on aspirin |
| D.To talk with a doctor familiar with their condition |
| A.the director of a hospital |
| B.a public health journalist |
| C.the CEO of a medical company |
| D.a representative for an insurance company |
【推荐2】We Need to Think about Conservation on a Different Timescale
Time, perceived by humans in days, months, and years, contrasts with nature’s grander scales of centuries and millennia, referred to as “deep time.” While paleontologists (古生物学者) are trained to think in deep time, conservationists are realizing the challenges it poses. Shortsightedness about time limits modern conservation, with efforts often overlooking past healthy conditions of ecosystems in the context of climate and biodiversity crises.
The shifting baseline syndrome (综合症), where standards in a place change gradually, makes conservation more complex. It involves evaluating ecosystems primarily on their recent past, often with negative consequences.
Recent shifts in California’s forest management practices, from stopping fires to embracing Indigenous knowledge of controlled burns, exemplify the importance of understanding historical ecosystem dynamics. To enhance conservation, adopting a deep-time approach is crucial.
Modern mathematical modeling, combined with long-term data, offers a pathway for preserving ecosystems. In California’s kelp (海带、海藻) forest, researchers identified an overlooked keystone species — the extinct Seller’s Sea Cow (大海牛). By examining past kelp forests, a deeper story impacting regeneration was revealed. The sea cow, a massive plant-cater, contributed to a diverse, vital undergrowth by trimming kelp and letting light reach the area.
The researchers put forward a novel approach to kelp forest restoration: selectively harvesting kelp, imitating the sea cow’s impact. This strategy, considering historical dynamics, challenges assumptions about recent ecosystems and offers new conservation methods.
Rather than only focusing on removing urchins (海胆) or reintroducing sea otters, the researchers suggest employing teams of humans to selectively harvest kelp, as the Steller’s sea cow once did, to encourage fresh growth. This sustainable harvest could benefit both the ecosystem and human consumption.
In short, assumptions based on the recent past may impede the understanding and protection of ecosystems. On the other hand, the application of controlled burns, similar modeling studies, and a deep-time perspective (视角) could significantly transform conservation efforts. Recognizing our role in an ongoing narrative spanning millions of years is essential, urging a comprehensive understanding of ecosystems through time. Embracing this role is crucial for shaping the future and establishing vital connections from the past to the future.
1. What is the “shifting baseline syndrome,” mentioned in the passage?| A.A syndrome that affects human beings’ perception of time. |
| B.A phenomenon where ecological standards shift in a place. |
| C.A psychological disorder common among conservationists. |
| D.A condition where ecosystems change gradually over time. |
| A.It promotes the prevention of wildfires. | B.It aids in mathematical modeling efforts. |
| C.It helps reveal historical ecosystem dynamics. | D.It enhances human consumption of ecosystems. |
| A.Reform. | B.Disrupt. | C.Quicken. | D.Deepen. |
| A.Shifting baseline syndrome has positive ecological changes. |
| B.Mathematical modeling with the latest data can be effective. |
| C.Deep-time perspective and historical dynamics are crucial. |
| D.Recent history is more preferred in ecosystem restoration. |
【推荐3】Gone are the days when a mother’s place was in the home: in Britain women with children are now as likely to be in paid work as their unburdened sisters. Many put their little darlings in day care long before they start school. Mindful that a poor start can spoil a person’s chances of success later in life, the state has intervened ever more closely in how babies and toddlers are looked after. Inspectors call not only at nurseries but also at homes where youngsters are minded; three-year-olds follow the national curriculum. Child care has increasingly become a profession.
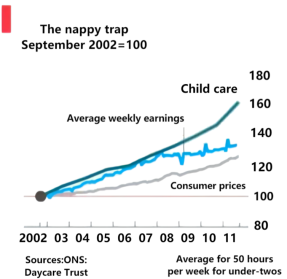
For years after the government first began in 2001 to twist the arms of anyone who looked after an unrelated child to register with the schools, the numbers so doing fell. Kind but clueless neighbours stopped looking after little ones, who were instead herded into formal nurseries or handed over to one of the ever-fewer registered child-minders. The decline in the number of people taking in children now appears to have halted. According to data released by the Office for Standards in Education on October 27th, the number of registered child-minders reached its lowest point in September 2010 and has since recovered slightly.
The new lot are certainly better qualified. In 2010 fully 82% of nursery workers held diplomas notionally equivalent to A-levels, the university-entrance exams taken mostly by 18-year-olds, up from 56% seven years earlier, says Anand Shukla of the Daycare Trust, a charity. Nurseries staffed by university graduates tend to be rated highest by inspectors, increasing their appeal to the pickiest parents. As a result, more graduates are being recruited.
But professionalization has also pushed up the price of child care, defying even the economic depression. A survey by the Daycare Trust finds that a full-time nursery place in England for a child aged under two, who must be intensively supervised, costs £194 ($310) per week, on average. Prices in London and the south-east are far higher. Parents in Britain spend more on child care than anywhere else in the world, according to the OECD, a think-tank. Some 68% of a typical second earner's net income is spent on freeing her to work, compared with an OECD average of 52%.
The price of child care is not only eye-watering, but has also become a barrier to work. Soon after it took power the coalition government pledged to ensure that people are better off in work than on benefits, but a recent survey by Save the Children, a charity, found that the high cost of day care prevented a quarter of low-paid workers from returning to their jobs once they had started a family. The government pays for free part-time nursery places for three-and four-year-olds, and contributes towards day-care costs for younger children from poor areas. Alas, extending such an aid during stressful economic times would appear to be anything but child’s play.
1. Which of the following is true according to the first paragraph?| A.Nursery education plays a leading role in one’s personal growth. |
| B.Pregnant women have to work to lighten families’ economic burden. |
| C.Children in nursery have to take uniform nation courses. |
| D.The supervision of the state makes child care professional. |
| A.the registered child-minders are required to take the university-entrance exams |
| B.the number of registered child-minders has been declining since 2001 |
| C.anyone who looks after children at home must register with the schools |
| D.the growing recognition encourages more graduates to work as child-minders |
| A.prevents mothers from getting employed |
| B.may further depress the national economy |
| C.makes many families live on benefits |
| D.is far more than parents can afford |
| A.Objective. | B.Skeptical. | C.Supportive. | D.Biased. |
| A.The professionalization of child care has pushed up its price. |
| B.The high cost of child nursing makes many mothers give up their jobs. |
| C.The employment of more graduates makes nurseries more popular. |
| D.Parents in Britain pay most for child nursing throughout the world. |
【推荐1】Read the following passage and men answer ne questons.
For a More Creative Brain, Travel
There are plenty of things to be gained from going abroad: new friends, new experiences, new stories. But living in another country may come with a less noticeable benefit, too: Some scientists say it can also make you more creative.
6 Writers and thinkers have long felt the creative benefits of international travel. Ernest Hemingway, for example, drew inspiration for much of his work from his time in Spain and France. Aldous Huxley, the author of Brave New World, moved from the U. K. to the U.S. in his 40s to branch out into screenwriting. Mark Twain, who sailed around the coast of the Mediterranean in 1869, wrote in his travelogue Innocents broad that travel is "fatal to prejudice and narrow-mindedness."
In recent years, psychologists and neuroscientists have begun examining the potential traveling abroad has to affect mental change. In general, creativity is related to how the brain is wired. Neural pathways are influenced by environment and habit, meaning they're also sensitive to change: New sounds,smells, languages, tastes, sensations, and sights spark different synapses(突触)in the brain and may have the potential to refresh the mind.
"Foreign experiences increase cognitive flexibility," says Adam Galinsky, an author of numerous studies on the connection between creativity and international travel. Cognitive flexibility is the mind's ability to jump between different ideas, a key component of creativity. But it's not just about being abroad, Galinsky says: "The key, critical process is multicultural engagement (参与), immersion, and adaptation. Someone who lives abroad and doesn't engage with the local culture will likely get less of a creative boost (促进)than someone who travels abroad and really engages in the local environment.
The researchers also found that the more countries CEOS had lived in, the more creative the products tended to be--but only up to a point. Those who had lived and worked in more than three countries, the study found, still tended to show higher levels of creativity than those who hadn't worked abroad at all. but less creativity than their peers who had worked in a smaller number of foreign countries. The authors assumed that those who had lived in too many countries hadn't been able to properly immerse themselves culturally; they were bouncing around too much. "It gets back to this idea of a deeper level of learning that's necessary for these effects to occur," Galinsky says.
Cultural distance, or how different a foreign culture is from ones own, may also play a role: Surprisingly, Galinsky and his colleagues found that living someplace with a larger cultural distance was often associated with lower creativity than living in a more familiar culture. The reason for that, they hypothesized, was that an especially different culture might come with a bigger intimidation factor, which may discourage people from immersing themselves in it—and no immersion, they explained, could mean none of the cognitive changes associated with living in another country.
Of course, although a new country is an easy way to leave a "social comfort zone," the cultural engagement associated with cognitive change doesn't have to happen abroad. If a plane ticket isn't an option, maybe try taking the subway to a new neighborhood. Sometimes, the research suggests, all that's needed for a creative boost is a fresh cultural scene.
Questions 11 to 15. Judge if the following statements agree with the information given in the passage. Choose A for TRUE if the statements agree with it, choose B for FALSE if the statements don't agree with it, choose C for NOT GIVEN if the information the statements carry is not mentioned anywhere in the passage.
Questions 16 to 19. Match the following words with their meanings in the passage. Note that there are four choices more than you need.

2. The more foreign experiences one has. the more flexible one's mind will be.
3. People who have lived and worked in two countries show the highest level of creativity.
4. A place of completely different culture contributes more to one's creativity than a familiar one.
5. A neighborhood of fresh culture is not necessarily a bad choice to boost creativity.
6. branch
7. fatal
8. wired
9. immersing
10. What is the purpose of the passage?
| A.To show the advantages of traveling. |
| B.To share research findings on traveling. |
| C.To advocate traveling benefits for creativity. |
| D.To suggest an alternative to traveling abroad. |
【推荐2】A survey, by the Australian Council for Educational Research (ACER), which manages the Program for International Student Assessment (PISA) in Australia, found in 2015 a total of 54% of 15-year-old students were aiming for a university degree. Around 3% were aiming for a Technical and Further Education (TAFE) diploma. This was down from 2003, when 63% planned to go to university, and 8% planned to do a TAFE diploma.
A decline in students’ expectations of a university degree may not be cause for alarm. Instead, it may reflect expanding opportunities in other qualification areas, such as apprenticeships(学徒) and other forms of occupational education. The decline in those students expecting to do a TAFE diploma may reflect fewer offerings in the TAFE department. What’s alarming is the noticeable difference that remains between different groups of students. In particular, those related to disadvantage such as low socioeconomic background and rurality.
Having different expectations for future education can impact students’ current experiences of education, influence their motivation, behaviour and achievement at school now. For example, students who know they won’t be able to afford to move out of home to go to their chosen university may decide, consciously or not, to not put so much effort into their schoolwork if they can get into a different course at a local TAFE that requires a lower ATAR(大学入学指数). For young people, expectations for further study can also become a self-fulfilling prophecy(预言). Those expecting to leave school early are more likely to do so. Students who expect to attend university are more likely to do so, and so gain access to improved social and labour markets outcomes. These include increased health and life expectancy, higher incomes and greater levels of wellbeing — the "health, wealth and happiness".
Not only are there differences in their access to and opportunity for further study, the survey highlights the range of their expectations, and what that might represent for their future. Further comparison of the educational expectations of various groups of students show some worrying patterns related to disadvantages.
1. How does the author mainly develop the first paragraph?| A.By giving figures. | B.By presenting facts. |
| C.By arguing and discussing. | D.By comparing and contrasting. |
| A.The employment rate will increase. |
| B.The economics has declined sharply recently. |
| C.Other forms of education will develop better. |
| D.The courses of the TAFE department will increase. |
| A.A student who failed in the last exam. |
| B.A student who has a long-term life goal. |
| C.A student who expects to attend university. |
| D.A student who will require a local TAFE diploma. |
| A.What are the concerning patterns? |
| B.What are the disadvantages of no education? |
| C.What measures the authorities will take to prevent this? |
| D.Why it matters that fewer Australian teenagers are going to university? |
【推荐3】Going to university is supposed to be a mind-broadening experience. That statement is probably made in comparison to training for work straight after school. But is it actually true? Jessika Golle of the University of Tubingen, in Germany reports in Psychological Science this week that those who have been to university indeed seem to leave with broader and more curious minds than those who have spent their immediate post-school years in vocational (职业的) training for work. However, it was not the case that university broadened minds. Rather, vocational training for work seemed to have narrowed them. The result is not quite what might be expected.
Dr. Golle came to this conclusion after she and a team of colleagues studied the early careers of 2,095 German youngsters. The team used two standardized tests to assess their volunteers’ personality traits (特点) including openness, conscientiousness (认真) and so on, and attitudes such as realistic, investigative and enterprising twice, once towards the end of each volunteer’s time at high school, and then again six years later. Of the original group, 382 had to make a choice between the academic and vocational routes, and it was on these that the researchers focused. University beckoned for 212 of them. The remaining 170 chose vocational training and a job.
When it came to the second round of tests, Dr. Golle found that the personalities of both groups had not changed significantly. As for changes in altitude, again, none were noticeable in the university group. However, those who had chosen the vocational route showed marked drops in interest in tasks that are investigative and enterprising in nature. And that might restrict their choice of careers.
The changes in attitude that the researchers recorded were more worrying. Vocational training has always been what Germany prides itself on. If Dr Golle is correct, and changes in attitude brought about by the very training are narrowing people’s choices that is indeed a matter worthy of serious consideration.
1. What does Dr. Colle’s research suggest?| A.Going to university is a mind-broadening experience. |
| B.College students pride themselves on their education. |
| C.Working straight after school narrows people’s minds. |
| D.Attending university has apparent effects on personalities. |
| A.Examined. | B.Attracted. |
| C.Organized. | D.Recognized |
| A.it is essential to scientific research. |
| B.It leads to marked change in personality. |
| C.It helps to broaden the volunteers’ minds. |
| D.It causes less interest in investigative job. |
| A.Skeptical. | B.Optimistic. |
| C.Concerned. | D.Unclear. |



