1 . As Frans de Waal, a primatologist (灵长动物学家), recognizes, a better way to think about other creatures would be to ask ourselves how different species have developed different kinds of minds to solve different adaptive problems. Surely the important question is not whether animals can do the same things humans can, but how those animals solve the cognitive (认知的) problems they face, like how to imitate the sea floor. Children and some animals are so interesting not because they are smart like us, but because they are smart in ways we haven’t even considered.
Sometimes studying children’s ways of knowing can cast light on adult-human cognition. Children’s pretend play may help us understand our adult taste for fiction. De Waal’s research provides another interesting example. We human beings tend to think that our social relationships are rooted in our perceptions, beliefs, and desires, and our understanding of the perceptions, beliefs, and desires of others — what psychologists call our “theory of mind.” In the 80s and 90s, developmental psychologists showed that pre-schoolers and even infants understand minds apart from their own. But it was hard to show that other animals did the same. “Theory of mind” became a candidate for the special, uniquely human trick.
Yet de Waal’s studies show that chimps (黑猩猩) possess a remarkably developed political intelligence — they are much interested in figuring out social relationships. It turns out, as de Waal describes, that chimps do infer something about what other chimps see. But experimental studies also suggest that this happens only in a competitive political context. The evolutionary anthropologist (人类学家) Brain Hare and his colleagues gave a junior chimp a choice between pieces of food that a dominant chimp had seen hidden and other pieces it had not seen hidden. The junior chimp, who watched all the hiding, stayed away from the food the dominant chimp had seen, but took the food it hadn’t seen.
Anyone who has gone to an academic conference will recognize that we may be in the same situation. We may say that we sign up because we’re eager to find out what other human beings think, but we’re just as interested in who’s on top. Many of the political judgments we make there don’t have much to do with our theory of mind. We may show our respect to a famous professor even if we have no respect for his ideas.
Until recently, however, there wasn’t much research into how humans develop and employ this kind of political knowledge. It may be that we understand the social world in terms of dominance, like chimps, but we’re just not usually as politically motivated as they are. Instead of asking whether we have a better everyday theory of mind, we might wonder whether they have a better everyday theory of politics.
1. According to the first paragraph, which of the following shows that an animal is smart?| A.It can behave like a human kid. |
| B.It can imitate what human beings do. |
| C.It can find a solution to its own problem. |
| D.It can figure out those adaptive problems. |
| A.We talk with infants in a way that they can fully understand. |
| B.We make guesses at what others think while interacting with them. |
| C.We hide our emotions when we try establishing contact with a stranger. |
| D.We try to understand how kids’ pretend play affects our taste for fiction. |
| A.Neither human nor animals display their preference for dominance. |
| B.Animals living in a competitive political context are smarter. |
| C.Both humans and some animals have political intelligence. |
| D.Humans are more interested in who’s on top than animals. |
| A.we know little about how chimps are politically motivated |
| B.our political knowledge doesn’t always determine how we behave |
| C.our theory of mind might enable us to understand our theory of politics |
| D.more research should be conducted to understand animals’ social world |
If you listen to the stream of articles and podcasts telling us how to become a billionaire in 10 easy steps, you might hold the belief that squeezing ourselves dry each second of the day will bring happiness and success.
But this obsession with productivity is costing us. Even a car doesn’t stay in the same gear the whole time. “We are not machines,” says psychologist Professor Drew Dawson. “Performance declines as a function of time, of task and time of day.”
Instead of moments of boredom, where we might let our minds wander and come up with novel solutions to problems and novel ways of thinking, we seek constant stimulation - and have a lowered tolerance for boredom as a result.
“It leads people to a false assumption that the world’s most successful people are literally making good use of every single minute,” Dawson says. “That’s a myth. We’re not hardwired to act that way as humans, and it’s a good recipe for burnout.”
COVID-19, for a variety of reasons, has led people to question and even opt out of this myth. “Who wants to lie on their deathbed going, ‘I wish I’d been more productive’?” Dawson says. “Post-COVID, people are starting to say, ‘what am I losing compared to what am I gaining?’”
So, if not more productivity, what should we be aiming for?
·Get our priorities straight.
A life spent chasing the state of being able to do everything is less meaningful than a life of focusing on a few things that count. We can reflect on five things that matter most to us and lead a life around them. Once clear on them, we also become clear on where to direct our attention and what to say “no” to.
·Enjoy downtime(停工期)for its own sake
Glorifying productivity can blind us to the value of other parts of our lives, including boredom, connection, creativity and play. But activities in our lives don’t need to always be productive or worthwhile-enjoying an activity is reason enough to spend time on it.
We weren’t meant to be productive all the time, so stop constantly struggling, and start chilling.
1. What does “obsession with productivity” refer to in the passage?2. How has COVID-19 changed the situation according to the passage?
3. Please decide which part is false in the following statement, then underline it and explain why.
 It is more meaningful to focus on a few things that count in life, so we can reflect on five things in our life to say “no” to.
It is more meaningful to focus on a few things that count in life, so we can reflect on five things in our life to say “no” to. 4. Do you agree with the statement “enjoying an activity is reason enough to spend time on it”? Why or why not?(In about 40 words)
3 . In general, the society is becoming one of giant enterprises directed by a bureaucratic (官僚主义的) management in which man becomes a small, well-oiled cog in the machinery. The oiling is done with higher wages, well-equipped factories and piped music, and by psychologists and “human-relations” experts; yet all this oiling does not change the fact that man has become powerless, that he does not wholeheartedly participate in his work and he is bored with it. In fact, the blue-collar and the white-collar workers have become economic puppets who dance to the tune of automated machines and bureaucratic management.
The worker and employee are anxious, seemingly because they might find themselves out of a job or they would say that they are unable to acquire any real satisfaction or interest in life. In fact, they feel desperate as they live and die without ever having confronted the fundamental realities of human existence as emotionally and intellectually independent and productive human beings.
Those higher up on the social ladder are no less anxious. Their lives are no less empty than those of their subordinates. They are even more insecure in some respects. They are in a highly competitive race. To be promoted or to fall behind is not a matter of salary but even more a matter of self-respect. When they apply for their first job, they are tested for intelligence as well as for the right mixture of submissiveness and independence. From the moment on they are tested again and again by the psychologists, for whom testing is a big business, and by their superiors, who judge their behavior, sociability, capacity to get along, etc. This constant need to prove that one is as good as or better than one’s fellow-competitor creates constant anxiety and stress, the very causes of unhappiness and illness.
Am I suggesting a return to the pre-industrial mode of production or to nineteenth-century “free enterprise” capitalism? Certainly not. Problems are never solved by returning to a stage which one has already outgrown. I suggest transforming the social system from a bureaucratically managed industrialism in which maximal production and consumption are ends in themselves into a humanist industrialism in which man and full development of his potentialities — those of all love and of reason — are the aims of social arrangements. Production and consumption should serve as means to this end, and should be prevented from ruling man.
1. By “a small, well-oiled cog in the machinery”, the author expresses the idea that man is _________.| A.an essential part of society with irreplaceable functions |
| B.expected to work in reasonable harmony with the rest of society |
| C.an unimportant component of society, though functioning smoothly |
| D.responsible for the smooth running of society and business operations |
| A.they are filled with an overwhelming fear of being unemployed |
| B.they don’t have any genuine satisfaction or interest |
| C.they have to face the fundamental realities of human existence |
| D.they lack a sense of independence and productivity |
| A.caution | B.obedience | C.commitment | D.optimism |
| A.To introduce the production mode of our ancestors. |
| B.To show the problematic situation in society. |
| C.To argue for full development of human potentials. |
| D.To help people escape production and consumption. |
4 . Frozen in time, a 125-million-year-old mammal attacking a dinosaur. A 39-million-year-old whale, the heaviest animal that ever lived. The oldest known jellyfish, from 505 million years ago. Paleontology (古生物学) produces newsworthy discoveries.
Fossils (化石), moreover, provide direct evidence for the long history of life, allowing paleontologists to test hypotheses (假设) about evolution with data only they provide. They allow investigation of present and past life on Earth. Flows of biological diversity, appearances of new life forms and the extinctions of long existing ones, would go undiscovered without these efforts. But the headlines over exciting new fossils greatly underestimate the true importance of paleontology. Its real significance lies in how such discoveries brighten the grand history of life on Earth. From its beginnings, more than three billion years ago, to the present day, fossils record how life adapted or disappeared in the face of major environmental challenges.
Paleontologists provide us with a unique vantage on modern climate change. They play an essential role in interpreting ancient environments, in reconstructing ancient oceans, continents and climates. Fossils provide key limitation on the climate models that are essential for predicting future climate change. And the fossil record gives important insights into how life will respond to predicted future climate conditions, because these have occurred before in Earth’s history.
In addition, paleontology has provided a fundamental contribution to human thought: the reality of species extinction and thus of a world that has dramatically changed over time. In documenting the history of life, paleontologists recognized that many extinction episodes could occur suddenly, such as the event 66 million years ago that ended the dinosaurs. The search for the causes of past mass extinctions started pioneering studies from across the scientific spectrum (科学界), focusing on potential future threats to humanity.
Not only do paleontologists know what happens to life when things go bad, they also know how long it takes for ecosystems and biodiversity to recover from these disasters, which can take far longer than modern humans have existed.
Paleontologists thus provide a unique perspective on the nature and future long-term ecological impact of the current human-produced biodiversity crisis, the so-called Sixth Extinction, and therefore the importance of protecting modern biodiversity. The very concept of a Sixth Extinction would not exist without paleontologists documenting the first five.
Paleontologists know that understanding life’s past is critical to anticipating and adapting to life’s and humanity’s future. Paleontology is important because it brings its unique and critical perspective to current challenges in climate change, biodiversity loss and the environment. Paleontologists can predict the future because they know the past.
1. The first two paragraphs are written to _______.| A.describe an event | B.raise a question |
| C.present an opinion | D.make a comparison |
| A.A positive effect. | B.A valuable suggestion. |
| C.A quick decision. | D.A comprehensive view. |
| A.Ecological recovery takes shorter than imagined. |
| B.Past lessons can help to predict the future threats. |
| C.Paleontologists can handle the biodiversity crisis. |
| D.Fossil studies focus on the causes of mass extinctions. |
| A.Paleontology: A Pioneering Study |
| B.Paleontology: A History Recorder |
| C.Paleontology Tells More About Nature Than Humans |
| D.Paleontology Is Far More Than New Fossil Discoveries |
Do you have trouble finishing your work within a given time? Do you find yourself having to scramble (艰难完成) through your work because time is running out? It is important to manage your time properly.
First, you should write down your tasks on paper. This is to make sure that you do not miss any of them. Having them written down somewhere ensures that you will get the task completed even if you forget about it. Of course, you need to make sure that the task list is always within your sight. Make sure you have a clear view of your tasks. You can write them down in a diary.
After you have written down your tasks, it is time to plan your action. Which tasks need not be completed as urgently How much time are you going to give each task? I suggest that you complete the urgent tasks first, but at the same time, be sure to include some time to take breaks in between. The breaks ensure that you have a moment to run away from stress until you return to continue from where you left off.
Above all, however, don’t procrastinate because it is your number one enemy. Procrastination can also mean that you will not be focused when you do your work. Time is valuable, so do not waste it by procrastinating. Focus on completing the task and get it over once and for all.
1. Where can you write your tasks down?2. Why should we take breaks between tasks?
3. Please decide which part is false in the following statement, then underline it and explain why.
Our biggest enemy when we manage our time properly is that we will not be focused.
4. Do you think it is important to manage your time properly? Why or why not? (About 40 words)
6 . A new artificial intelligence (AI) tool called ChatGPT has excited the Internet community with its superhuman abilities to solve math problems, produce college articles and write research papers. Some educators are warning that such Al systems will change the world of learning, teaching, and research, for better or worse.
Ethan Mollick, a professor at the University of Pennsylvania’s Wharton School of Business, sees its benefits as a learning partner. He has used it as his own teacher’s assistant, for help with preparing a lecture and grading instructions for MBA students. “You can ask it to find a mistake in your writing and correct it and tell you why you got it wrong,” he said. “It’s really amazing.”
But the superhuman assistant has its limitations (局限). ChatGPT was created by humans, after all. OpenAI has trained the tool using a large dataset of real human conversations. It sometimes lies to you, with confidence. There have been situations in which ChatGPT won’t tell you when it doesn’t have the answer.
That’s what Teresa Kubacka, a data scientist based in Zurich, Switzerland, found when she experimented with the language model. “I asked it about something that I thought that I know doesn’t exist (存在) so that I can judge whether it actually also has the idea of what exists and what doesn’t exist.” she said. ChatGPT produced an answer so specific sounding, backed with citations (引文), that Kubacka had to find out whether the made-up thing was actually real. “This is where it becomes kind of dangerous,” she said.
ChatGPT doesn’t produce good science, says Oren Etzioni, the founding CEO of the Allen Institute for AI. But he sees ChatGPT’s appearance as a good thing. He sees this as a moment for review. “ChatGPT is just a few days old, I like to say,” said Etzioni. “It’s giving us a chance to understand what he can and cannot do and to begin the conversation of ‘What are we going to do about it?’”
1. How did Ethan Mollick feel about ChatGPT?| A.It could be used in many different fields. |
| B.It was popular with university students. |
| C.It would replace teachers’ assistants. |
| D.It was advantageous to him. |
| A.The Al tool is not dependable sometimes. |
| B.The Al tool always gives wrong answers. |
| C.The Al tool does not always answer questions. |
| D.The Al tool gives dangerous guidance sometimes. |
| A.It is too early to discuss ChatGPT’s limitations. |
| B.ChatGPT is open for review and suggestions. |
| C.ChatGPT is worth praising for its superhuman abilities. |
| D.It takes time to see whether ChatGPT works well or not. |
A. | B.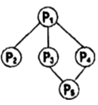 |
C. | D.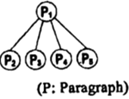 |
7 . Do you listen to quiet music to help you wind down before sleep? However, this practice could be counter-productive, according to a new study by Michael K. Scullin and colleagues at Baylor University. The work, published in Psychological Medicine, found that bedtime music was associated with more sleep disruptions and that instrumental music is even worse than music with lyrics.
In the first study, 199 online participants living in the US reported on their sleep quality and music listening frequency and timing, as well as their beliefs about how this affected their sleep. Almost all—87%—believed that music improves sleep, or at least does not disrupt it. However, the team found that more overall time spent listening to music was associated with poorer sleep and daytime sleepiness. Just over three quarters of the participants also reported experiencing frequent “earworms”—having a song or tune “stuck” and replaying in their minds. A quarter reported experiencing these during the night at least once per week, and these people were six times as likely to report poor sleep quality. The team’s analysis suggested that listening specifically to instrumental music near bedtime was linked to more sleep-related earworms and poorer sleep quality.
The team then ran an experimental study on 48 young adults. After arriving at the sleep lab at 8:45 p. m., participants went to a quiet bedroom, where they completed questionnaires that included measures of stress, sleep quality and daytime sleepiness. They also had electrodes applied, ready for the night-time polysomnography to record their brain wave activity, as well as heart rate and breathing, and reported on how relaxed, nervous, energetic, sleepy and stressed they felt. At 10:00 p. m., they were given some “downtime”, with quiet music playing. Half were randomized to hear three songs while the other half heard instrumental-only versions of these same songs.
Participants reported decreases in stress and nervousness and increased relaxation after listening to either set of songs, and also showed decreases in blood pressure. So-as earlier studies have also suggested- quiet music at bedtime was indeed relaxing at the time. However, a quarter of the participants woke from sleep with an earworm, and the polysomnography data showed that instrumental versions of the songs were more likely to induce these awakenings as well as other sleep disruptions, such as shifts from deeper sleep to lighter sleep. Taken together, the findings represent “causal evidence for bedtime instrumental music affecting sleep quality via triggering earworms” the team writes.
Why instrumental-only songs should have a bigger impact than music with lyrics isn’t clear. The three songs used in this study were chosen because they were likely to be familiar. Hearing them without the lyrics might have prompted the participant’s brains to try to add the words, which might have made earworms more likely. If this is the case, all instrumental music may not have the same effect. However, the data from the first study is consistent with the idea that instrumental music generally is more of a problem.
1. According to the passage, the participants in both studies______.| A.were required to listen to light music | B.felt their sleeping problems resolved |
| C.had their sleeping quality monitored | D.provided feedback on bedtime music |
| A.Lead to. | B.Impact on. | C.Break in. | D.Focus on. |
| A.Earworms are mainly caused by music with lyrics. |
| B.Bedtime music leads to high blood pressure and anxiety. |
| C.Quiet music improves sleeping quality while loud music harms sleep. |
| D.Both familiar and unfamiliar instrumental music can cause sleeping problems. |
| A.how instrumental music disturbs sleep |
| B.the possible negative effect of bedtime music |
| C.how people can improve their sleep quality |
| D.differences between music with and without lyrics |
8 . “When I stopped in at our local tourism office in Montreal to ask where they would recommend visitors to go to smell, taste, and listen to the city, I just received blank stares. They only know about things to see, not about the city’s other sensory attractions, its soundmarks and smellmarks,” says Howes, the director of Sensory Studies, a growing field often referred to as “sensory urbanism”.
Around the world, researchers like Howes are investigating how non-visual information defines the character of a city and affects its livability. Using methods ranging from low-tech sound walks to data collecting, wearables (clothing or glasses that contain computer technology), and virtual reality, they’re fighting what they see as a limiting visual preference in urban planning.
“Just being able to close your eyes for 10 minutes gives you a totally different feeling about a place,” says Oguz Öner, an academic and musician. He has spent years organizing sound walks in Istanbul where participants describe what they hear at different spots with their eyes covered. His research has identified locations where a wave organ could be constructed to strengthen the sounds of the sea, something he was surprised to realize people could hardly hear, even along the waterfront.
Although his findings have not been considered into local urban plans yet, this kind of individual feedback (反馈) about the sensory environment is already being put to use in Berlin, where quiet areas identified by citizens using a free mobile app have been included in the city’s latest noise action plan.
The best way to determine how people react to different sensory environments is a subject of some debate within the field. Howes and his colleagues are using observation and interviews to develop a set of best practices for good sensory design in public spaces. Other researchers are going more high-tech, using wearables to track biological data like heart-rate variability to reveal different sensory experiences.
As data collection about people’s sensory experiences becomes more widespread, many of these experts warn that concerns about privacy and surveillance (监视) need to be taken into account. Issues of fairness and inclusion also come into play when determining whose sensory experiences are factored into planning. “Sensory awareness is not independent or simply biological; whether we find something pleasant or not has been shaped culturally and socially,” says Monica Degen, an urban cultural sociologist at Brunel University London.
Degen cites the example of a London neighborhood where inexpensive restaurants for local youth were replaced by trendy cafes. “It used to smell like fried chicken,” she says, but newer residents found that smell annoying rather than welcoming. “Now it smells like the popular Italian coffee, cappuccinos.”
1. The underlined phrase “blank stares” in Paragraph 1 implies that______.| A.Montreal is lacking in visual appeal |
| B.Montreal’s non-visual information is ignored |
| C.the tourism officers object to sensory urbanism |
| D.there are too many tourist attractions to recommend |
| A.Many methods are used to limit the visual preference. |
| B.Potential concerns about collecting data can be relieved. |
| C.People may fail to notice sound attractions even in better locations. |
| D.Individual feedback restricts the development of sensory environment. |
| A.People’s perceptions of their sensory surroundings are subjective. |
| B.Sensory urbanism needs to focus on developing sensory facilities. |
| C.Sensory experience is dominant in shaping the character of a city. |
| D.Choices of sensory attractions in urban planning depend on tourists. |
9 . “Flying insects don’t fly directly to lights from far away because they’re attracted to them, but appear to change course toward a light if they happen to be passing by due to a strange inborn biological response,” writes Samuel Fabian, a bioengineer, in a research paper.
Until now, the leading scientific hypothesis has been that insects use the moon’s light to direct the way at night and mistake artificial lights for the moon. But this idea doesn’t explain why insects that only fly during the day also gather around lights.
To find out what really happens, Samuel’s team track the precise movements of insects in the wild around lights using a high-speed camera. This revealed two notable behaviours. First, when insects fly above lights, they often invert (转向) themselves and try to fly upside down, causing them to fall very fast. Just after insects pass under a light, they start doing a ring road. As their climb angle becomes too steep, they suddenly stop and start to fall. Second, when insects approach a light from the side, they may circle or “orbit” the light.
The videos show that the inversions sometimes result in insects falling on lights. It can appear to the naked eye as though they are flying at the lights. “Instead, insects turn their dorsum toward the light, generating flight perpendicular(垂直) to the source,” the team write. It is common to the two behaviours that the insects are keeping their backs to the light, known as the dorsal light response (DLR). This DLR is a shortcut for insects to work out which way is up and keep their bodies upright, as the moon or sun is usually more or less directly above them, and this direction allows them to maintain proper flight attitude and control. They also find that the insects fly at right angles to a light source, leading to orbiting and unstable flights as the light’s location relative to them changes as they move.
Samuel’s team suggest that a possible outcome of the research could help the construction industry to avoid the types of light that most attract insects.
1. What does the research focus on?| A.Why insects gather around lights. |
| B.Where artificial lights lead insects to. |
| C.What biological response insects are born with. |
| D.How to design environment friendly artificial lights. |
| A.They fly directly to lights. | B.They circle close to lights. |
| C.Their flying speed is steady. | D.Their inversions can be controlled. |
| A.balance their flying | B.keep their route straight |
| C.decide their body positon | D.shorten their flight distance |
10 . We humans are in trouble. We have let loose a new evolutionary process that we don’t understand and can’t control.
The latest leaps forward in artificial intelligence (AI) are rightly causing anxiety. Yet people are responding as though AI is just one more scary new technology, like electricity or cars once were. We invented it, the argument goes, so we should be able to manage it for our own benefit. Not so. I believe that this situation is new and potentially dangerous.
My thinking starts from the premise that all design anywhere in the universe is created by the evolutionary algorithm (算法). This is the process in which some kind of information is copied many times, the copies vary slightly and only some are selected to be copied again. The information is called the replicator (复制者), and our most familiar example is the gene.
But genes aren’t the only replicator, as Richard Dawkins stressed in The Selfish Gene. People copy habits, stories, words, technologies and songs; we change, recombine and pass them on in ever greater variety. This second replicator, evolving much faster than genes ever could, Dawkins called memes (模仿传递行为) — and they are selfish too.
As we face up to the recent explosion in AI, new questions arise. Could a third replicator take advantage of the first two? And what would happen if it did?
For billions of years, all of the Earth’s organisms were gene machines, until, about 2 million years ago, just one species — our ancestors — started imitating sounds, gestures and ways of processing food. They had let loose a second replicator and turned us into meme machines. Following the same principle, could a third replicator appear if some object we made started copying, varying and selecting a new kind of information?
It could, and I believe it has. Our digital technology can copy, store and spread vast amounts of information with near-perfect accuracy. While we had mostly been the ones selecting what to copy and share, that is changing now. Mindless algorithms choose which ads we see and which news stories they “think” we would like. Once a digital replicator takes off, its products will evolve for its own benefit, not ours.
All is not lost, though. We already cope with fast-evolving parasites such as viruses by using our immune systems, machines and vaccines. Now, we need to build our collective mental immunity, our critical thinking and our ability to protect our attention from all that selfish information. Taking lessons from evolution, we can stop imagining we are the controllers of our accidentally dangerous offspring and start learning how to live with them.
1. As for people’s attitude toward AI, the author is ____________.| A.disapproving | B.unconcerned |
| C.sympathetic | D.tolerant |
| A.memes are composed of selfish genes | B.the speed of evolution is underestimated |
| C.replicators vary with human interference | D.memes and genes share a common feature |
| A.Technologies can be double-edged. |
| B.Collective efforts make a better world. |
| C.We should live in harmony with nature. |
| D.Past experience is relevant to future action. |
| A.The pace of technological progress is unstoppable. |
| B.The initiative of algorithm should be strengthened. |
| C.The new evolution can bring about negative effects. |
| D.The artificial intelligence can satisfy our real desires. |



