1 . Walt Disney: A Legacy of Dreams
The name “Disney” evokes a rush of images: from the enchanted kingdom of Disneyland to the heartwarming tales of Bambi and Simba. For almost a century, Disney, initiated by Walt Disney himself, has been synonymous with storytelling, imagination, and dreams-come-true. But what’s the journey behind this global empire of happiness?
Founded in 1923 by Walt and Roy O. Disney, the company started as a small animation studio in the back of a real estate office in Los Angeles.
Disney’s first full-length animated feature film, Snow White and the Seven Dwarfs, premiered in 1937.
Disneyland, opened in 1955, was Walt’s most ambitious venture (经营项目).
With Walt’s death in 1966, there were doubts about the future of the company.
Walt Disney once said, “All our dreams can come true if we have the courage to pursue them.”
| A.The transformation from a humble beginning to a global business came with both achievements and challenges. |
| B.Each turn in the park promises a leap into fantasy, ensuring the magic is felt at every corner. |
| C.This venture greatly changed the landscape of cinematic history. |
| D.Though faced with initial skepticism, the park became an instant success. |
| E.Over the decades, it has redefined entertainment, proving that stories have no boundaries. |
| F.However, despite initial uncertainties in leadership and direction, the enterprise continued to grow. |
| G.It’s a universe of stories, where every character, every song, and every ride have a heart and soul. |
2 . How Do Smartphones Affect Our Sleep
Smart phones can be addictive and may lead to problematic use. This is even more true for teenagers. Smartphone addiction can also negatively affect students’ performance in school. Many studies have also shown the prolonged screen time is bad for our sleep. But is it different if you are actually addicted to your phone? Is that more of a problem for sleep than just spending time on your screen?We asked 1043 UK students aged between 18 to 30 to complete two questionnaires. The first one was about the students’ smartphone use, which includes questions like whether they miss planned work due to smartphone use to see whether they are addicted. The second questionnaire assessed the quality of students’ sleep. We then analyzed the data to find if there is an association between smartphone addiction and some factors like age, ethnicity, or gender.
Around 39% of the students showed several signs of smartphone addiction. It was more prevalent among students under 21. Prolonged use was strongly linked to addiction. About 54% of the students who used their smartphones for more than 5 hours a day suffered from addiction. Only 20% of those who used them for under 2 hours a day were addicted.
Smartphone use before bed is also an important factor. The addiction levels were high among students who used their phones less than 30 minutes before bedtime and low among those who stopped using their phones more than one hour before time.
According to our study, smartphone addiction is also related to using it in late hours. For example, if you use your phone after 1 am, you are three times as likely to have an addiction. So the amount of time spent on your phone is not enough to suggest addiction. But combining that with the latest time you use your phone can be a good indicator.
Our study also shows that smartphone addiction could be harming people’s sleep. And this is not just because of screen time. People could suffer from addiction and poor sleep even when they used their phones for under 2 hours a day. But use in the late hours or right before bedtime tended to harm the students’ sleep.
If you have a smartphone, it could have a bad impact on your health. Students need to take special actions to prevent it from damaging their health before it’s too late.
1. What does the word “prevalent” probably mean?
| A.accepted | B.common | C.controlled | D.understood |
| A.Age of smartphone users. | B.How long smartphones are used per day. |
| C.Latest time on phone. | D.Time and duration of using smartphones. |
| A.Using smartphones right before bedtime harms sleep quality. |
| B.54% of the participants use their phones more than 5 hours a day. |
| C.39% of the participants aged under 21 are addicted to smartphones. |
| D.Using smartphones less than 2 hours a day keeps you away from addiction. |
| A.Stop playing games on the phone. |
| B.Watch relaxing videos before bed. |
| C.Stop using phones 30 minutes before sleep. |
| D.Take a break every 2 hours on his phone. |
3 . When you get in a car, you expect it will have functioning brakes. When you pick up medicine at the drugstore, you expect it won’t be polluted. But it wasn’t always like this. The safety of these products was terrible when they first came to market. It took much research and regulation to figure out how users can enjoy the benefits of these products without getting harmed.
Social media risks are everywhere. The dangers that algorithms designed to maximize attention represent to teens have become impossible to ignore. Other product design elements, often called “dark patterns,” designed to keep people using for longer, also appear to tip young users into social media overuse.
Despite these efforts, two things are clear. First, online safety problems are leading to real, offline suffering. Second, social media companies can’t, or won’t, solve these safety problems on their own.
| A.And those problems aren’t going away. |
| B.The current issues aren’t really about offline suffering. |
| C.Platforms already have systems to remove violent or harmful content. |
| D.Similarly, social media needs product safety standards to keep users safe. |
| E.It’s time we should require social media to take safety seriously, for everyone’s sake. |
| F.Internet platforms, however, have shifted blame on the consumers whenever criticized. |
| G.Some authorities are taking steps to hold social media platforms accountable for the content. |
4 . Self-concept is our personal knowledge of who we are, encompassing all of our thoughts and feelings about ourselves physically, personally, and socially.
By age 2, children begin to differentiate themselves from others.
Between the ages of 7 and 11, children begin to make social comparisons and consider how they’re perceived by others.
| A.Adolescence is a key period for self-concept. |
| B.We all hold numerous, varied ideas about ourselves. |
| C.At this stage, children’s descriptions of themselves become more abstract. |
| D.By the ages of 3 and 4, children understand that they are separate and unique selves. |
| E.However, it is between early childhood and adolescence that self-concept experiences the most growth. |
| F.Self-concept also includes our knowledge of how we behave, our capabilities, and our individual characteristics. |
| G.Success and approval can contribute to greater self-esteem and a stronger self-concept into adulthood. |
5 . As biologist Nicola Foster and her colleagues guided a remote-controlled monitor through the coral reefs (珊瑚礁) of the Indian Ocean’s Chagos Archipelago, they saw corals full of color near the surface. But nearly 300 feet below, in the darker and colder waters of what oceanographers call the “twilight zone,” some corals had turned terrible white, leaving them vulnerable (脆弱的) to disease and death.
“It wasn’t something we were expecting to see,” says Foster, who studies deeperwater coral ecosystems called mesophotic reefs. Mesophotic reefs would seem to be protected from rising sea-surface temperatures that white n higher-up corals. But this team’s 2019 observations show the deepest instance of bleaching (变白) ever recorded — suggesting similar reefs are more vulnerable than previously believed.
Bleaching often happens when warming water boosts corals to remove the colorful algae (水藻) that live in their tissues and help to sustain them. Although surface waters weren’t typically warm when Foster and her team took their measurements, the twilight zone waters neared 84 degrees Fahrenheit (华氏度) — far above the 68-to 75-degree range in which mesophotic corals are used to.
The researchers realized that bleaching is related to the timing of the Indian Ocean Dipole. This phenomenon shifts the region’s surface winds and ocean currents, says study co-author Phil Hosegood. Wind and waves shake the upper ocean, keeping it relatively warm and uniform in temperature. But the 2019 dipole deepened this well-mixed upper layer; the thermocline (the slice of ocean that separates warm upper waters from the cold depths) had become deeper than normal. Then, those corals were exposed to temperatures that are normally found at the surface.
This observation suggests mesophotic reefs elsewhere could also be bleaching. Fortunately, the corals in this study had largely recovered their color by 2022, Foster notes. But each bleaching stresses the corals and, if extended, can starve them. Future Indian Ocean Dipole patterns are likely to be more severe, Hosegood says, noting that data suggest “that these natural cycles are becoming increased with climate change.”
1. What are the first two paragraphs mainly about?| A.Corals in twilight zone become vulnerable because of bleaching. |
| B.Corals normally found at the surface were found in twilight zone. |
| C.Mesophotic reefs are much more vulnerable than higher-up reefs. |
| D.Mesophotic reefs and higher-up reefs need different temperature. |
A.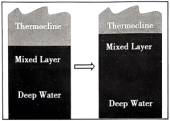 | B.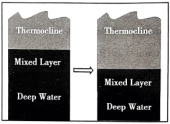 |
C.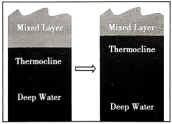 | D.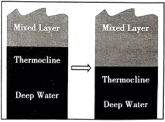 |
| A.excited | B.worried | C.curious | D.hopeful |
6 . At the end of the day, most of us find ourselves on the couch, eyes glued to the television or to our smartphones, doing everything we can to conserve energy.
According to Michael Inzlicht, a social psychologist at the University of Toronto, we’re lazy and also, we’re not.
All humans, given equal options, will take the easy way out. Does it mean we’re lazy? Maybe.
But there are the times when humans are the opposite of lazy and do very difficult things for no apparent reason. Some rewards only come from extensive effort.
So, in that sense, effort is worth the effort. While humans are economically aware of effort most of the time, “in some cases, the effort itself is rewarding,” says Inzlicht.
| A.Think about things like running a marathon. |
| B.It’s not completely clear why humans behave this way. |
| C.It seems that we humans are gifted in the way of laziness. |
| D.We similarly love to space out, our brain tired of focusing. |
| E.But it certainly means that we’re economic with our effort. |
| F.Some people who appear to be lazy are suffering from much more serious problems. |
| G.Likewise, we might get a sense of pleasure or mastery from doing a crossword puzzle. |
7 . Around the world, coral reefs (珊瑚礁) are in danger. Now, let’s check out a few ways conservationists are protecting these habitats.
Seaweed Smackdown
Hot ocean temperatures can supercharge seaweed growth — and that’s not good for a reef. So, in Hawaii, scientists have used an underwater vacuum (真空吸器) to suck up lots of seaweed into the device’s long tube. In Australia, scientists are studying a low-tech solution: pulling seaweed by hand.
21
Some polyps (珊瑚虫) are harmed by heat waves and pollution. Scientists cut parts of coral from a healthy reef. Then these polyps are taken to a nursery, which could be in shallow protected areas underwater. After about a year, the healthy coral parts are attached to damaged reefs. The nursery-grown corals can bring new life to a struggling habitat.
Sound Saver
Healthy reefs are noisy. Fish make different sounds, and thousands of shrimp create and pop bubbles with their claws to create a sound. The biologists play sounds of healthy reefs through underwater speakers. They found that six weeks of broadcasting healthy reef sounds doubled the amount of fish in the area.
Bleaching Killer
One of the biggest threats to coral reefs is bleaching. Here’s how it works.
| Thriving coral Most coral species survive by partnering with tiny algae (藻类), which make food for the coral by changing sunlight into sugar. |
| Under stress But when the ocean water gets too hot, the algae produce too much oxygen, which can hurt the coral. |
| Bleaching So corals kick out the algae. As the algae leave, the color disappears and the coral appears to turn white. This process is called bleaching. |
Biologists have discovered that many corals in the Red Sea have a species of algae in their tissue that’s found nowhere else, so they can survive heat waves. Biologists hope their work will inspire governments and environmental groups to protect these corals.
1. Which of the following might be the subtitle of Paragraph 3?| A.Underwater Nurseries. | B.Fishing Guides. |
| C.Seaweed Cleaners. | D.Colour Designers. |
| A.Breathing in more oxygen. | B.Changing the appearance. |
| C.Absorbing more sound. | D.Partnering with algae. |
| A.To present the serious damages to corals. | B.To explain the reasons for coral habitat loss. |
| C.To introduce the methods of coral protection. | D.To compare the effects of different solutions. |
8 . When fighting sugar dependence, avoiding added sugar in the diet is key, which sounds simple — right? It certainly does, but things become a bit more complicated once we introduce alternative sweeteners into the mix.
Alternative sweeteners are everywhere.
Now that we know some of the common types of alternative sweeteners, let’s take a deeper dive into the problem with them. Research in animals has shown that removing calories from foods that taste sweet can interrupt the ability to control energy intake.
The other interesting thing about alternative sweeteners is that our brains don’t recognize them as “fake (假的)” sugar.
So what do I recommend? In order to fully put a definite end to sugar dependence, reducing your intake of alternative sweeteners should be the goal.
| A.The taste profile of alternative sweeteners varies. |
| B.We can’t forget about the ever-so-popular sugar alcohols. |
| C.There are countless alternative sweeteners on the market. |
| D.Our brain senses something sweet and thinks it is real sugar. |
| E.They may help reduce the calorie content of good-tasting foods and drinks. |
| F.Artificial sweeteners may also cause one’s body to prefer sweeter-tasting foods. |
| G.Alternative sweeteners are referred to as “low-calorie” or “no-calorie” sweeteners. |
9 . A shopkeeper’s son breaks a window, causing a crowd to gather. They tell the shopkeeper not to be angry: actually, the broken window is a reason to celebrate, since it will create work for the glazier (装玻璃的工人). In the story, written by a 19th-century economist, the crowd envisions the work involved in repairing the window, but not that involved in everything else on which the shopkeeper could have spent his money — unseen possibilities that would have brought him greater happiness.
If that window were to be broken these days, people might have a different reaction, especially if they were NIMBYs (Not In My Back Yard) who oppose any local construction that affects their quality of life. Their concern might be with the “embodied carbon”. The production of a piece of glass would carry a sizeable carbon cost. Similarly, the bricks and concrete in a building are relics of past emissions. They are, the logic goes, embodied carbon.
Conserving what already exists, rather than adding to the building stock, will avoid increasing these embodied emissions — or so NIMBYs often suggest. At its worst, this idea is based on a warped logic. Greenhouse gases released by the construction of an existing building will heat the planet whether the building is repaired or knocked down. The emissions have been taken out of the world’s “carbon budget”, so treating them as anew debit means double counting. The right question to ask is whether it is worth using the remaining carbon budget to repair a building or it is better to knock it down.
Choosing between these possibilities requires thinking about the unseen. It used to be said that construction emitted two types of emissions. Besides the embodied sort, there were operational ones from cooling, heating and providing electricity to residents. Around the world, buildings account for 39% of annual emissions, according to the World Green Building Council, of which 28% come from operational carbon.
These two types of emissions might be enough for the architects designing an individual building. But when it comes to broader questions, economists ought also to consider how the placement of buildings affects the manner in which people work, shop and travel. Density (密度) lowers the per-person cost of public transport, and this reduces car use. Research by Green Alliance, a pressure group, suggests that in Britain a policy of “demolish (拆除) and densify” — replacing semi-detached housing near public transport with blocks of flats — would save substantial emissions. Without such demolition, potential residents would typically have to move to the suburbs instead, saving money on rent but consuming more energy.
Targeted subsidies (补贴), especially for research and development into construction materials, could speed up the pace at which the built environment decarbonises. What will never work, however, is allowing the loudest voices to decide how to use land and ignoring the carbon emissions of their would-be neighbours once they are out of sight.
1. The first two paragraphs are written to ________.| A.exemplify an outlook on energy conservation |
| B.present a new way of relieving energy crisis |
| C.explain people’s reaction to a broken window |
| D.introduce an argument on carbon emission |
| A.Unsound. | B.Complicated. | C.Distinctive. | D.Underlying. |
| A.Operational carbon accounts for a larger share of carbon emission. |
| B.Repairing old buildings outweighs demolition in energy conservation. |
| C.Higher residential density near public transport may help reduce emission. |
| D.Stopping residents from living in new buildings is sensible to energy saving. |
| A.Interests of NIMBYs are worthy of consideration. |
| B.A comprehensive insight into emission is essential. |
| C.Upgrading construction materials should be prioritized. |
| D.Every resident should do their bit in reducing carbon emission. |
10 . In the United Arab Emirates (UAE), water is more valuable than oil. To support its citizens, the nation relies on expensive campaigns of cloud seeding from aircraft, which spray particles(喷洒微粒) into passing clouds to make rainfall.
But according to Oliver Branch, a climate scientist, there may be another method to stir up a rainmaker: with city-size solar farms that create their own weather. The heat from dark solar panels can cause updrafts that sometimes lead to rainstorms, providing water for local people. “Maybe it’s not science fiction that we can produce this effect,” says Branch, who led the work.
Few studies have examined how renewable energy might shift weather patterns. In 2020, Branch found that incredibly large solar farms, taking up more than 1 million square kilometers in the Sahara desert, could boost local rainfall. But the reward would come with a cost, the researchers found: By altering wind patterns, the solar farms would push tropical rain bands north. That’s not good news for the Amazon areas.
To find more, researchers turned to a weather model that can account for land surface changes. They modeled the solar farms as nearly black fields that absorbed 95%of the sunlight, surrounded by relatively reflective sand. When the solar farms reached 15 square kilometers, they found, the increased heat they absorbed appreciably increased the updrafts, or convection, that drive cloud formation.
Hacking convection wasn’t enough, however: damp air was also needed. When conditions were ripe, the model also found, a 20-square-kilometer solar field would increase a storm’s total rainfall by nearly 600,000 cubic meters. If such rainstorms occurred 10 times in one summer, they would provide enough water to support more than 30,000 people for a year.
Solar farms in China and elsewhere are nearly big enough, Branch says. If they were built in the right spots, it wouldn’t take much to darken the panels and to plant dark crops between panel rows. Still they’re trying to improve the realism of their solar panel simulations by cross-checking them with field measurements at existing solar farms.
The UAE “is committed to studying the potentially dynamic strategies, such as optimizing convection,” says Alya Al, director of the UAE’s Research Program. For now, she adds, the UAE is deeply committed to its cloud seeding program, carrying out some 300 missions each year.
1. In his study, Branch attempts to produce rainfall ________.| A.by way of updrafts formed on solar farms | B.by spraying particles into passing clouds |
| C.by means of relatively reflective sand | D.by planting dark crops |
| A.the ripe conditions for building a solar farm |
| B.the realistic size of a solar farm for rainfall increase |
| C.the annual amount of water consumption in the UAE |
| D.the heat absorption rate of the solar panels in the black fields |
| A.It is not supported by the director. | B.It needs great investment if applied. |
| C.It remains to be further tested in practice. | D.It has promoted cloud seeding in the UAE. |






