1 . Who cares if people think wrongly that the internet has had more important influences than the washing machine? Why does it matter that people are more impressed by the most recent changes?
It would not matter if these misjudgments were just a matter of people’s opinions. However, they have real impacts, as they result in misguided use of scarce resources.
The fascination with the ICT(Information and Communication Technology) revolution, represented by the internet, has made some rich countries wrongly conclude that making things is so “yesterday” that they should try to live on ideas. This belief in “post-industrial society” has led those countries to neglect their manufacturing sector(制造业), with negative consequences for their economies.
Even more worryingly, the fascination with the internet by people in rich countries has moved the international community to worry about the “digital divide” between the rich countries and the poor countries. This has led companies and individuals to donate money to developing countries to buy computer equipment and internet facilities. The question, however, is whether this is what the developing countries need the most. Perhaps giving money for those less fashionable things such as digging wells, extending electricity networks and making more affordable washing machines would have improved people’s lives more than giving every child a laptop computer or setting up internet centres in rural villages, I am not saying that those things are necessarily more important, but many donators have rushed into fancy programmes without carefully assessing the relative long-term costs and benefits of alternative uses of their money.
In yet another example, a fascination with the new has led people to believe that the recent changes in the technologies of communications and transportation are so revolutionary that now we live in a “borderless world”. As a result, in the last twenty years or so, many people have come to believe that whatever change is happening today is the result of great technological progress, going against which will be like trying to turn the clock back. Believing in such a world, many governments have put an end to some of the very necessary regulations on cross-border flows of capital, labour and goods, with poor results.
Understanding technological trends is very important for correctly designing economic policies, both at the national and the international levels, and for making the right career choices at the individual level. However, our fascination with the latest, and our under valuation of what has already become common, can, and has, led us in all sorts of wrong directions.
1. Misjudgments on the influences of new technology can lead to ________.| A.a lack of confidence in technology |
| B.a slow progress in technology |
| C.a conflict of public opinions |
| D.a waste of limited resources |
| A.take people’s essential needs into account |
| B.make their programmes attractive to people |
| C.ensure that each child gets financial support |
| D.provide more affordable internet facilities |
| A.Neglecting the impacts of technological advances. |
| B.Believing that the world has become borderless. |
| C.Ignoring the power of economic development. |
| D.Over-emphasizing the role of international communication. |
| A.People should be encouraged to make more donations. |
| B.Traditional technology still has a place nowadays. |
| C.Making right career choices is crucial to personal success. |
| D.Economic policies should follow technological trends. |
2 . Children as young as ten are becoming dependent on social media for their sense of self-worth, a major study warned.
It found many youngsters(少年)now measure their status by how much public approval they get online, often through “likes”. Some change their behaviour in real life to improve their image on the web.
The report into youngsters aged from 8 to 12 was carried out by Children's Commissioner (专员) Anne Longfield. She said social media firms were exposing children to major emotional risks, with some youngsters starting secondary school ill-equipped to cope with the tremendous pressure they faced online.
Some social apps were popular among the children even though they supposedly require users to be at least 13. The youngsters admitted planning trips around potential photo-opportunities and then messaging friends—and friends of friends — to demand “likes” for their online posts.
The report found that youngsters felt their friendships could be at risk if they did not respond to social media posts quickly, and around the clock.
Children aged 8 to 10 were "starting to feel happy" when others liked their posts. However, those in the 10 to 12 age group were "concerned with how many people like their posts", suggesting a “need” for social recognition that gets stronger the older they become.
Miss Longfield warned that a generation of children risked growing up "worried about their appearance and image as a result of the unrealistic lifestyles they follow on platforms, and increasingly anxious about switching off due to the constant demands of social media.
She said: "Children are using social media with family and friends and to play games when they are in primary school. But what starts as fun usage of apps turns into tremendous pressure in real social media interaction at secondary school."
As their world expanded, she said, children compared themselves to others online in a way that was "hugely damaging in terms of their self-identity, in terms of their confidence, but also in terms of their ability to develop themselves".
Miss Longfield added: "Then there is this push to connect—if you go offline, will you miss something, will you miss out, will you show that you don't care about those people you are following, all of those come together in a huge way at once." "For children it is very, very difficult to cope with emotionally." The Children's Commissioner for England's study—life in Likes—found that children as young as 8 were using social media platforms largely for play.
However, the research—involving eight groups of 32 children aged 8 to 12—suggested that as they headed toward their teens, they became increasingly anxious online.
By the time they started secondary school—at age 11—children were already far more aware of their image online and felt under huge pressure to ensure their posts were popular, the report found.
However, they still did not know how to cope with mean-spirited jokes, or the sense of incompetence they might feel if they compared themselves to celebrities(名人) or more brilliant friends online. The report said they also faced pressure to respond to messages at all hours of the day—especially at secondary school when more youngsters have mobile phones.
The Children’s Commissioner said schools and parents must now do more to prepare children for the emotional minefield(雷区) they faced online. And she said social media companies must also "take more responsibility". They should either monitor their websites better so that children do not sign up too early, or they should adjust their websites to the needs of younger users.
Javed Khan, of children's charity Bamardo's, said: "It's vital that new compulsory age-appropriate relationship and sex education lessons in England should help equip children to deal with the growing demands of social media.”
“It’s also hugely important for parents to know which apps their children are using.”
1. Why did some secondary school students feel too much pressure?| A.They were not provided with adequate equipment. |
| B.They were not well prepared for emotional risks. |
| C.They were required to give quick responses. |
| D.They were prevented from using mobile phones. |
| A.they didn't adequately check their users' registration |
| B.they organized photo trips to attract more youngsters |
| C.they encouraged youngsters to post more photos |
| D.they didn't stop youngsters from staying up late |
| A.less friendliness to each other |
| B.lower self-identity and confidence |
| C.an increase in online cheating |
| D.a stronger desire to stay online |
| A.circulate their posts quickly |
| B.know the qualities of their posts |
| C.use mobile phones for play |
| D.get more public approval |
| A.Communicate more with secondary schools. |
| B.Urge media companies to create safer apps. |
| C.Keep track of children's use of social media. |
| D.Forbid their children from visiting the web. |
| A.The influence of social media on children. |
| B.The importance of social media to children. |
| C.The problem in building a healthy relationship. |
| D.The measure to reduce risks from social media. |
When we read newspapers, we often come across such English words as “AIDS” and “PK.” When we watch TV, we frequently hear words like “NBA” or “PM2.5.” When we speak, we automatically use words like “OUT” or “Bye-bye.” English words and expressions like these are getting popular. They have already become part of our daily language. And 239 English words have been included in the latest Dictionary of Contemporary Chinese.
The inclusion has started a heated discussion. A group of scholars signed a letter of complaint over the inclusion of these English words, which, they think, goes against Chinese language policies. They not only worry that Chinese is borrowing an increasing number of English words but are also concerned that the inclusion may hurt the dignity of the Chinese language. However, others are in favor of the inclusion because it is hard to say whether it will threaten the Chinese language. They believe the selection is mostly a result of their function and use in daily life.
[写作内容]
1. 用约 30 个单词写出上文概要;
2. 用约 120 个单词发表你的观点,内容包括:
(1)支持或反对汉语词典收录英语词汇;
(2)用 2- 3个理由或论据支撑你的观点。
[写作要求]
1. 可以支持文中任一观点,但必须提供理由或论据;
2. 阐述观点或提供论据时,不能直接引用原文语句;
3. 作文中不能出现真实姓名和学校名称;
4. 不必写标题。
[评分标准]
内容完整,语言规范,语篇连贯,词数适当。
___________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
| Saturday Afternoon.In a Shopping Center. Li Jiang: Hi, Su Hua. Which movie shall we see? Su Hua: Whatever. We'er got so many choice, Kung Fu Yoga,Journey to the West…Each sounds great! Li Jiang: Yeah! And some movie stars are fantastic. Su Hua: And the high-tech!… Li Jiang: Perfect! Let's get some food first. We only have 20 minutes left. Su Hua: No hurry. The cinema is on the same floor. |
| One Day in 2016. At Home. Son:Mum, shall we go and see a film tonight? Mother: Why bother?We can stay at home and watch films online. It’s convenient with our new and faster network Son: But it feels good in a cinema. Mother: And the price… We have to pay 50 yuan a ticket. Son: Only 10 yuan more than last year. Mother: But still we cannot get the money’s worth.Some films are just boring… |
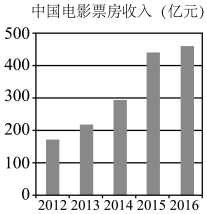
1.用约30个单词概述
2.我国电影票房收入变化的原因有哪些,简要谈谈你的看法(上述对话仅供参考,原因不少于两点);
3.谈谈你对我国电影票房收入走向的看法,并简要说明理由。
【写作要求】
1.写作过程中不能直接引用原文语句;
2.作文中不能出现真实姓名和学校名称;
3.不必写标题。
【评分标准】
内容完整,语言规范,语篇连贯,词数适当。
___________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
5 . 请认真阅读下面短文,并根据所读内容在文章后表格中的空格里填入
注意:请将答案写在答题卡上相应题号的横线上。每个空格只填一个单词。
Population Change
Why is the world’s population growing? The answer is not what you might think. The reason for the explosion is not that people have been reproducing like rabbits, but that people have stopped dropping dead like flies. In 1900, people died at the average age of 30. By 2000 the average age was 65. But while increasing health was a typical feature of the 20th century, declining birth rate could be a defining one of the 21st.
Statistics show that the average number of births per woman has fallen from 4.9 in the early 1960s to 2.5 nowadays. Furthermore, around 50% of the world’s population live in regions where the figure is now below the replacement level (i.e. 2.1 births per woman) and almost all developed nations are experiencing sub-replacement birth rate. You might think that developing nations would make up the loss (especially since 80% of the world’s people now live in such nations), but you’d be wrong. Declining birth rate is a major problem in many developing regions too, which might cause catastrophic global shortages of work force within a few decades.
A great decline in young work force is likely to occur in China, for instance. What does it imply? First, China needs to undergo rapid economic development before a population decline hits the country. Second, if other factors such as technology remain constant, economic growth and material expectations will fall well below recent standards and this could invite trouble.
Russia is another country with population problems that could break its economic promise. Since 1992 the number of people dying has been bigger than that of those being born by a massive 50%. Indeed official figures suggest the country has shrunk by 5% since 1993 and people in Russia live a shorter life now than those in 1961. Why is this occurring? Nobody is quite sure, but poor diet and above all long-time alcoholism have much to do with it. If current trends don’t bend, Russia’s population will be about the size of Yemen’s by the year 2050.
In the north of India, the population is booming due to high birth rates, but in the south, where most economic development is taking place, birth rate is falling rapidly. In a further twist, birth rate is highest in poorly educated rural areas and lowest in highly educated urban areas. In total, 25% of India’s working-age population has no education. In 2030, a sixth of the country’s potential work force could be totally uneducated.
One solution is obviously to import foreign workers via immigration. As for the USA, it is almost unique among developed nations in having a population that is expected to grow by 20% from 2010—2030. Moreover, the USA has a track record of successfully accepting immigrants. As a result it’s likely to see a rise in the size of its working-age population and to witness strong economic growth over the longer term.

71
The expression, “everybody’s doing it,” is very much at the center of the concept of peer pressure. It is a strong influence of a group, especially of children, on members of that group to behave as everybody else does. It can be positive or negative. Most people experience it in some way during their lives.
People are social creatures by nature, and so it is hardly surprising that part of their self-respect comes from the approval of others. This instinct (天性) is why the approval of peers, or the fear of disapproval, is such a powerful force in many people’s lives. It is the same instinct that drives people to dress one way at home and another way at work, or to answer “fine” when a stranger asks “how are you?” even if it is not necessarily true. There is a practical aspect to this: it helps society to function efficiently, and encourages a general level of self-discipline that simplifies day-to-day interaction.
For certain individuals, seeking social acceptance is so important that it becomes like an addiction; in order to satisfy the desire, they may go so far as to abandon their sense of right and wrong. Teens and young adults may feel forced to use drugs, or join gangs that encourage criminal behavior. Mature adults may sometimes feel pressured to cover up illegal activity at the company where they work, or end up in debt because they are unable to hold back the desire to buy a house or car that they can’t afford in an effort to “keep up with the Joneses.”
However, peer pressure is not always negative. A student whose friends are good at academics may be urged to study harder and get good grades. Players on a sports team may feel driven to play harder in order to help the team win. This type of influence can also get a friend off drugs, or to help an adult take up a good habit or drop a bad one. Study groups and class projects are examples of positive peer groups that encourage people to better themselves.
Schools try to teach kids about the dangers of negative peer pressure. They teach kids to stand up and be themselves, and encourage them to politely decline to do things that they believe are wrong. Similarly, it can be helpful to encourage children to greet the beneficial influence of positive peer grou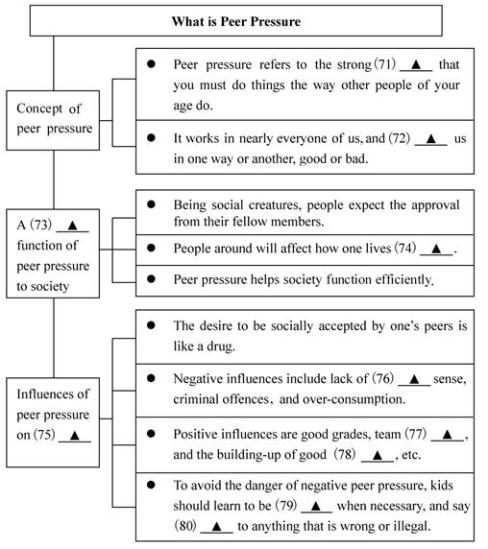
7 . We’ve considered several ways of paying to cut in line: hiring line standers, buying tickets from scalpers (票贩子), or purchasing line-cutting privileges directly from, say, an airline or an amusement park. Each of these deals replaces the morals of the queue (waiting your turn) with the morals of the market (paying a price for faster service).
Markets and queues — paying and waiting — are two different ways of allocating things, and each is appropriate to different activities. The morals of the queue, “First come, first served, have an egalitarian (平等主义的) appeal. They tell us to ignore privilege, power, and deep pockets.
The principle seems right on playgrounds and at bus stops. But the morals of the queue do not govern all occasions. If I put my house up for sale, I have no duty to accept the first offer that comes along, simply because it’s the first. Selling my house and waiting for a bus are different activities, properly governed by different standards.
Sometimes standards change, and it is unclear which principle should apply. Think of the recorded message you hear, played over and over, as you wait on hold when calling your bank: “Your call will be answered in the order in which it was received.” This is essential for the morals of the queue. It’s as if the company is trying to ease our impatience with fairness.
But don’t take the recorded message too seriously. Today, some people’s calls are answered faster than others. Call center technology enables companies to “score” incoming calls and to give faster service to those that come from rich places. You might call this telephonic queue jumping.
Of course, markets and queues are not the only ways of allocating things. Some goods we distribute by merit, others by need, still others by chance. However, the tendency of markets to replace queues, and other non-market ways of allocating goods is so common in modern life that we scarcely notice it anymore. It is striking that most of the paid queue-jumping schemes we’ve considered — at airports and amusement parks, in call centers, doctors’ offices, and national parks—are recent developments, scarcely imaginable three decades ago. The disappearance of the queues in these places may seem an unusual concern, but these are not the only places that markets have entered.
1. According to the author, which of the following seems governed by the principle “First come, first served”?| A.Taking buses. | B.Buying houses. |
| C.Flying with an airline. | D.Visiting amusement parks. |
| A.the necessity of patience in queuing |
| B.the advantage of modern technology |
| C.the uncertainty of allocation principle |
| D.the fairness of telephonic services |
| A.justify paying for faster services |
| B.discuss the morals of allocating things |
| C.analyze the reason for standing in line |
| D.criticize the behavior of queue jumping |
Merrigan, a former college professor, is making stops at universities across the country in hopes of encouraging more students to think about careers in agriculture. Aside from trying to stop the graying of America’s farmers, her work is made tougher by a recent blog posting that put agriculture at No. 1 on a list of “useless” college degrees. Top federal agriculture officials are talking about the posting, and it has the attention of agricultural organizations across the country.
“There couldn’t be anything that’s more incorrect,” Merrigan said. “We know that there aren’t enough qualified graduates to fill the jobs that are out there in American agriculture.”
In addition, a growing world population that some experts predict will require 70% more food production by 2050, she said.
“I truly believe we’re at a golden age of agriculture. Global demand is at an all-time record high, and global supplies are at all-time record lows,” said Matt Rush, director of the Texas Farm Bureau. “Production costs are going to be valuable enough that younger people are going to have the opportunity to be involved in agriculture.”
The Department of Agriculture has programs aimed at developing more farmers and at increasing interest in locally grown food. The National Young Farmers’ Coalition has also been pushing for state and federal policy changes to make it easier for new farmers.
Ryan Best, president of Future Farmers of America, has been living out of a suitcase, traveling the country and visiting with high school students about careers in agriculture. The 21-year-old Best hopes his message—that this is a new time in agriculture—will motivate the next generation to turn around the statistics. “Never before have we had the innovations (创新) in technology which have led to agriculture in this country being the most efficient it has ever been,” he said. “There’s really a place for everybody to fit in.”
1. What is the new challenge to American agriculture?
| A.Fewer and older farmers. | B.Higher fuel prices. |
| C.More natural disasters. | D.Lower agricultural output. |
| A.To draw federal agriculture officials’ attention. |
| B.To select qualified agriculture graduates. |
| C.To clarify a recent blog posting. |
| D.To talk more students into farming careers. |
because__________..
| A.the government will cover production costs |
| B.global food supplies will be even lower |
| C.investment in agriculture will be profitable |
| D.America will increase its food export |
| A.To re-analyze the result of the national census. |
| B.To increase agricultural production. |
| C.To bring down the average age of farmers. |
| D.To invest more in agriculture. |
“Happiness Advantage” Effect
In July 2010 Burt’s Bees, a personal-care products company, was going through enormous change as it began a global expansion into 19 new countries. In this kind of high-pressure situation, many leaders bother their assistants with frequent meetings or flood their in-boxes with urgent demands. In doing so, managers lift everyone’s anxiety level, which activates the part of the brain that processes threats and steals resources from the prefrontal cortex ( 大脑皮层), which is responsible for effective problem solving.
Burt’s Bees’s then-CEO, John Wolfgang, took a different approach. Each day, he’d send out an e-mail praising a team member for work related to global marketing. He’d interrupt his own presentations to remind his managers to talk with their teams about the company’s values. He asked me to further a three-hour session with employees on happiness in the course of the expansion effort. As one member of the senior team told me a year later, Wolfgang’s emphasis on developing positive leadership kept his managers actively involved and loyal as they successfully transformed the company into a global one.
That outcome shouldn’t surprise us. Research shows that when people work with a positive mind-set (思维模式), performance on nearly every level—productivity, creativity, involvement— improves. Yet happiness is perhaps the most misunderstood driver of performance. For one, most people believe that success comes before happiness. “Once I get a promotion, I’ll be happy,” they think. Or, “Once I hit my sales target, I’ll feel great. ”But because success is a moving target—as soon as you hit your target, you raise it again—the happiness that results from success does not last long.
In fact, it works the other way around: People who have a positive mind-set perform better in the face of challenge. I call this the “ happiness advantage”—every business outcome shows improvement when the brain is positive. I’ve observed this effect in my role as a researcher and lecturer in 48 countries on the connection between employee happiness and success. And I’m not alone: In an analysis of 225 academic studies, researchers found strong evidence of cause-and-effect relationship between life satisfaction and successful business outcomes.
Another common misunderstanding is that our genetics, our environment, or a combination of the two determines how happy we are. To be sure, both factors have an impact. But one’s general sense of well-being is surprisingly unstable. The habits you form, the way you interact with colleagues, how you think about stress—all these can be managed to increase your happiness and your chances of success.

Why Difficult?
When we wrong someone we know, even not intentionally, we are generally expected to apologize so as to improve the situation. But when we’re acting as leaders, the circumstances are different. The act of apology is carried out not merely at the level of the individual but also at the level of the institution. It is a performance in which every expression matters and every word becomes part of the public record. Refusing to apologize can be smart, or it can be stupid. So, readiness to apologize can be seen as a sign of strong character or as a sign of weakness. A successful apology can turn hate into personal and organizational harmony—while an apology that is too little, too late, or too obviously strategic can bring on individual and institutional ruin. What, then, is to be done? How can leaders decide if and when to apologize publicly?
Why Now?
The question of whether leaders should apologize publicly has never been more urgent. During the last decade or so, the United States in particular has developed an apology culture—apologies of all kinds and for all sorts of wrongdoings are made far more frequently than before. More newspaper writers have written about the growing importance of public apologies. More articles, cartoons, advice columns, and radio and television programs have similarly dealt with the subject of private apologies.
Why Bother?
Why do we apologize? Why do we ever put ourselves in situations likely to be difficult, embarrassing, and even risky? Leaders who apologize publicly could be an easy target. They are expected to appear strong and capable. And whenever they make public statements of any kind, their individual and institutional reputations are in danger. Clearly, then, leaders should not apologize often or lightly. For a leader to express apology, there needs to be a good, strong reason. Leaders will publicly apologize if and when they think the costs of doing so are lower than the costs of not doing so.
Why Refuse?
Why is it that leaders so often refuse to apologize, even when a public apology seems to be in order? Their reasons can be individual or institutional. Because leaders are public figures, their apologies are likely to be personally uncomfortable and even professionally risky. Leaders may also be afraid that admission of a mistake will damage or destroy the organization for which they are responsible. There can be good reasons for hanging tough in tough situations, as we shall see, but it is a high-risk strategy.




