An experiment published in iScience provides evidence that octopuses (章鱼) feel pain like humans do.
During the experiment, Crook, who comes from San Francisco State University, placed an octopus between two rooms with different lines and spots on the walls, and then observed where she preferred to stay. The next day, in another part of the lab, Crook put acetic acid into one of the octopus’s arms. She says doing so is like pouring lemon juice on a paper cut. When the animal awoke with an aching arm, Crook kept her in the room she had preferred before. The researcher removed the octopus 20 minutes later and used lidocaine to numb (使麻木) her arm. Crook then placed her in the room she had not liked as much at first. After another 20 minutes, Crook returned her to her home container.
Finally, about five hours later, Crook brought the octopus back to the rooms and gave her an alternative: return to the originally preferred room, where she was kept with an aching arm, or go to the one she had not liked as much but where she was numb. Crook ran the experiment with seven octopuses. They all chose to go to the non-preferred room. As a control, Crook put salt water into seven other octopuses. Unlike the experimental group, those octopuses returned to their originally preferred room.
It turned out the octopuses related the room they had once liked better to the ache they felt the last time they were there. Then they compared that experience with their typical pain-free state and decided that how they usually felt was better. Using that information, the octopuses chose to go to the non-preferred room. “There’s a lot of brain processing that has to happen,” Crook says.
Crook’s study suggests that there should be more focus on the welfare of octopuses. Due to people’s ignorance, animals like octopuses are not properly protected in both research and industry in the U.S. Luckily, Crook’s findings, giving us more insights into them, have led to increased protection for octopuses.
1. What effect did lidocaine have on the studied octopus?| A.Keeping her awake. | B.Making her energetic. |
| C.Making her feel less pain. | D.Removing her memory of pain. |
| A.Treat. | B.Choice. | C.Lead. | D.Punishment. |
| A.They tend to work in groups. | B.Their preference changes with time. |
| C.They update their memories regularly. | D.Their painful memories last for hours. |
| A.The significance of the research. | B.The description of the research. |
| C.The reasons for protecting octopuses. | D.The assumption about the octopuses. |
相似题推荐
【推荐1】Young male zebra finches (斑胸草雀) learn to communicate by listening to adults. In the lab, researchers have found that these songbirds can learn from audio recordings. But zebra finches learn better when they listen to live male finches, notes Ralph Simon. He studies how animals make and use sounds at the Nuremberg Zoo in Germany. Simon is part of the team that built RoboFinch, a robotic singing coach for finches.
The researchers recorded videos of adult males to analyze how their beaks (喙) move when they sing. They then programmed their robots to copy those beak movements. Finally, the researchers painted their RoboFinches the same colors as the real birds.
The team divided 45 young finches into four groups. Some only heard recordings of finch songs played by a speaker. Others listened with female birds that weren’t singing. RoboFinches taught the two other groups of chicks. The birdsongs played from a speaker right behind the robots. And the robots’ beaks moved either in or out of syne (协调) with the songs. That allowed the team to investigate whether beak or head movements aid song learning.
The birds housed with RoboFinches eventually spent most of their time near the robot and its speaker. During the first week, finches living with a RoboFinch whose song was in sync with its beak motions spent 27 percent of their time near the robot. Those caged with a robot playing songs out of syne only spent 5 percent of their time near the setup during the first week. Finches that heard only the audio without RoboFinch or female birds spent even less time around the sound source. Young finches partnered with RoboFinches sang less while the songs played. This was especially true when the robots’ beaks moved in sync with the songs. Those paired with a female also sang less while hearing songs. The young finches seemed to pay close attention to the robots’ movements during training sessions.
Simon hopes researchers will adapt this approach to building robots of other species, too.
1. Whose song did the researchers record?| A.Adult male finches’. | B.Adult female finches’. |
| C.Yong finches’. | D.RoboFinches’. |
| A.By how fast they learn. | B.By where they were kept. |
| C.By how they react to the robot. | D.By what they are accompanied with. |
| A.speakers behind them |
| B.female finches keeping silent |
| C.RoboFinches moving their beaks to the songs |
| D.a recorder playing the songs |
| A.RoboFinches Are Used as Singing Coaches |
| B.Machine Learning Are Adapted to Building Robots |
| C.Yong Finches Communicate Through Beak Movements |
| D.Researchers Discovered How Finches Make and Use Sounds |
【推荐2】Anyone who commutes (通勤) by car knows that traffic jams are an unavoidable part of life. But humans are not alone in facing potential jams.
Ants also commute — between their nest and sources of food. The survival of their colonies depends on doing this efficiently.
When humans commute, there’s a point at which cars become dense (稠密) enough to slow down the flow of traffic, causing jams. Motsch, a mathematician in Arizona State University, and his colleagues wanted to know if ants on the move could also get jammed. So they regulated traffic density by constructing bridges of various widths between a colony of Argentine ants and a source of food. Then they waited and watched. “The goal was to try to find out at what point they are going to have a traffic jam.” said Sebastien Motsch.
But it appears that that never happened. They always managed to avoid traffic jams. The flow of ants did increase at the beginning as ants started to fill the bridge and then levelled off at high densities. But it never slowed down or stopped, even when the bridge was nearly filled with ants.
The researchers then took a closer look at how the behaviour of individual ants impacted traffic as a whole. And they found that when ants sense overcrowding, they adjust their speeds and avoid entering high-density areas, which prevents jams. These behaviours may be promoted by pheromones, chemicals that tell other ants where a trail is. The ants also manage to avoid colliding (碰撞) with each other at high densities, which could really slow them down. The study is in the journal eLife.
Can ants help us solve our own traffic problems? Not likely, says Motsch. That’s because when it comes to getting from point A to point B as fast as possible, human drivers put their own goals first. Individual ants have to be more cooperative in order to feed the colony. But the research could be useful in improving traffic flow for self-driving cars, which can be designed to be less like selfish humans—and more like ants.
1. What does the underlined word “this” in para.2 refer to?| A.Surviving. | B.Commuting. |
| C.Finding food. | D.Avoiding jams. |
| A.they follow a special route. |
| B.they level off at high densities. |
| C.they never stop or slow down on the way. |
| D.they depend on their natural chemicals to adjust their speeds. |
| A.Traffic jams. | B.Unavoidable? Not for ants! |
| C.Survival of an ant colony. | D.Difference between humans and ants. |
【推荐3】Just how many truly intelligent species are there living on Earth? While they may not be living “in a pineapple under the sea”, a new study finds there’s at least one species in the ocean that shows the intelligence of human children. Researchers at the Marine Biological Laboratory say cuttlefish (墨鱼) have passed a test designed to measure the advanced skill of delayed gratification (延迟满足) in primates (灵长目动物).
Researchers used an adapted version of the Stanford marshmallow test (棉花糖测试), where children were given a choice of taking an immediate reward (1 marshmallow) or waiting to earn a delayed but better reward (2 marshmallows). “Cuttlefish in the present study were all able to wait for the better reward and tolerated delays for up to 50–130 seconds,” says lead author Alexandra Schnell. This is the first time the link between self-control and intelligence has appeared in a species other than primates.
Why the species is able to delay gratification is a bit of a mystery. For humans, scientists believe the quality strengthens social bonds. An example would be when you see someone wait for a partner to eat. Delayed gratification can also be a function of tool-building animals, who need to make hunting tools before they can eat.
For cuttlefish, however, researchers say they don’t build tools and are not social creatures. For them, Schnell believes delayed gratification is likely the result of having to hide themselves to stay alive. “Cuttlefish spend most of their time hiding,” she explains. “They desist from hiding when they search for food, so they are exposed to every hunter in the ocean that wants to eat them. We assume that delayed gratification may be a byproduct of this, so the cuttlefish can wait to choose better quality food.”
Researchers add that finding a link between self-control and intelligence in an animal other than primates is a good example of convergent evolution (趋同进化). This is the event in which completely separate evolutionary histories still lead to the same signs of intelligence.
1. What can we conclude from the adapted marshmallow test about cuttlefish?| A.They were smarter than children. |
| B.They had little interest in marshmallows. |
| C.They showed a certain amount of self-control. |
| D.They were more likely to take immediate rewards. |
| A.To avoid dangers. |
| B.To maintain relationships. |
| C.Due to their inborn ability. |
| D.Due to the demand from others. |
| A.Enjoy. | B.Consider. | C.Risk. | D.Stop. |
| A.Cuttlefish is a tool-building animal. |
| B.Cuttlefish is a social creature. |
| C.Cuttlefish has its special living habit. |
| D.Cuttlefish has high intelligence. |
| A.A possible reason for the study findings. |
| B.A suggestion for future studies. |
| C.The significance of the study. |
| D.The major limitation of the study. |
【推荐1】Where in the classroom do you prefer to sit,and why? Scientists have discovered that seating preference not only shows students’ personalities,but has a great influence on their school performance.Generally speaking,students show different attitudes depending on where they sit. Based on the research, scientists have developed a funnel-like(像漏斗的) model of “learning zones(区域)” to see the relationship between seating and active learning.
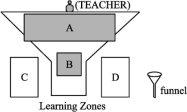
In this model,the mouth of the funnel(A) is the best position for learning. Students in this front area prove to be the most active learners.They show a greater desire(渴求) for learning,which leads them to focus(集中注意力) better and take a more active part than the rest of the class.Those in the neck of the funnel(B) don’t pay the same close attention,but they ask a lot of questions,partly because of the added confidence they feel from being in a safe zone, with others around them. Less desirable is the area “outside the funnel(C,D),” which refers to the side and the back rows,where students take a less active part in classroom activities and find it hard to focus their attention, falling asleep at times.
Studies about learning zones suggest that a change in traditional seating plans can benefit students. In fact, a growing number of teachers have begun less traditional seating plans,such as “U-Type”.There are no side and back areas,so teachers can expect their students to take part in activities more actively and increase student-teacher interaction(互动).
1. According to scientists,students’ learning is greatly influenced by .| A.the number of students | B.the time of class |
| C.seating positions | D.the size of the classroom |
| A.sometimes fall asleep | B.feel safe and confident |
| C.seldom ask their teachers questions | D.try to avoid looking directly at the teacher |
| A.Area A. | B.Area B. | C.Area C. | D.Area D. |
| A.Cause trouble for. | B.Take control of. |
| C.Give a warning to. | D.Do good to. |
【推荐2】The 2017 Noble Prize for Physics was given for the confirmation of a prediction made 101 years earlier. In 1916 Albert Einstein, whose theories of special and general relativity revolutionized scientists’ understanding of the universe, predicted that, in certain circumstances, the fabric of the universe itself should swing and bend.
The cause is gravitational waves In 2015 gravitational waves were directly observed for the first time. LIGO, an American observatory based in Washington State in that country’s northwest, and Louisiana in the southeast, detected waves produced by a pair of crashing black holes, each about 30 times the mass of the sun. That produced ripples (波纹) in space-time with a frequency of about 150 Hz, or cycles per second, and a wavelength of around 2, 000km.
This detection marked the beginning of the era of gravitational wave astronomy, which uses gravity to examine the universe in the same way that conventional astronomy uses electromagnetic radiation, from visible light to radio waves and gamma rays. On June 29th four projects led by researchers in America, Australia, China and Europe claimed to have pushed forward the state of that emerging art. They announced the detection of new, extremely low frequency gravitational waves which could offer insights into some of the hardest-to-study bits of the universe.
Gravitational wave detectors are interferometers (干涉仪). They work by dividing a ray of light into two,and sending each half down one of a pair of long,straight arms. At the end of the arms,the light waves are reflected back towards the source, where they are recombined. If that journey is uninterrupted, the returning rays will cancel each other out when they are put back together. If they do not, then that suggests some disturbance has disturbed them on their journey.
1. Why was Einstein mentioned in Paragraph 1?| A.To make a prediction. | B.To make a comparison. |
| C.To offer more background. | D.To honor this great scientist. |
| A.Expected. | B.Surprising. | C.Accidental. | D.Groundbreaking. |
| A.How they work. | B.What they can do. |
| C.Whether they are accurate. | D.Why they are used. |
| A.Ripples in Space-Time. | B.Theories to Be Confirmed. |
| C.Predictions about the Universe. | D.Ways of Observing the Universe. |
【推荐3】What’s your earliest childhood memory? Can you remember the first time you heard thunder or watched a television program? Adults seldom recall events much earlier than the year or so before entering school, just as children younger than three or four rarely maintain any memory of specific, personal experiences.
A variety of explanations have been proposed by psychologists for this “childhood amnesia”(记忆缺失).One argues that the hippocampus, the region of the brain which is responsible for forming memories, does not mature until about the age of two. But the most popular theory maintains that, since adults do not think like children, they cannot access childhood memories. Adults think in words, and their life memories are like stories. But when they search through their mental files for early childhood memories to add to this verbal life story, they don’t find any that fit the pattern. It’s like trying to find a Chinese word in an English dictionary.
Now psychologist Annette Simms offers a new explanation for childhood amnesia. She argues that there simply aren’t any early childhood memories to recall. According to Dr. Simms, children need to learn to use someone else’s spoken description of their personal experiences in order to turn their own short-term, quickly forgotten impressions of these experiences into long-term memories. In other words, children have to talk about their experiences and hear others talk about them. Mother talking about the afternoon spent looking for crabs at the beach or Dad asking them about their day at Ocean Park. Without this verbal reinforcement(强化), says Dr. Simms, children cannot form permanent memories of their personal experiences.
1. According to the passage, it is widely believed that ________.| A.it is impossible for an adult to recall his (or her) childhood experiences |
| B.adults and children have different brain structures |
| C.adults think in words while children think in images |
| D.adults virtually have no access to their childhood memories |
| A.a research center engaged in the study of human brains |
| B.a psychological research department of a university |
| C.a tiny campus pictured in one’s childhood memory |
| D.a part of the brain in charge of the formation of memories |
| A.adults and children have different memory patterns |
| B.it is unlikely to find a Chinese word in an English dictionary |
| C.Chinese and English are totally different languages |
| D.memories are in some way connected with languages |
| A.verbal reinforcement is necessary for children to have permanent memories |
| B.there does not exist such things as childhood memories |
| C.children’s brains are mature enough to form permanent memories |
| D.children are generally inexperienced and unable to remember things they don’t understand |
【推荐1】It took “great talent or skill to hide ones’ talent or skill,” the French moralist Fran-ois VI once noted. As soon as we’ve reached a certain level of mastery, say in playing chess, it’s hard to act as if we knew little about the game of kings. That’s partly because it’s difficult to imagine what it was like when we were still packed with ignorance, even if that was just five minutes ago. Known as the Curse of Knowledge, this phenomenon speaks to what the tragic burden mastery can be.
The Curse of Knowledge is a cognitive bias that arises from having a greater understanding of a particular topic. It’s a phenomenon where those who possess more knowledge about a given subject find it difficult to relate to those with less familiarity. This can lead to misunderstandings, miscommunication, and even conflict.
The consequences are not far to seek. It’s particularly fateful if it affects those whose job it is to impart their knowledge to others. Imagine a math genius turned school teacher who’s forgotten what it was like not to understand basic algebra, or a highly capable risk analyst who has a hard time enduring journalists failing basic probability. Those with greater knowledge may be so focused on the details of the topic that they’re unable to explain the basics in a way that is accessible to those with less knowledge. This makes even the most skilled expert an ineffective teacher. As a result, the math teacher gets more and more frustrated with her students. The risk analyst lashes out on Twitter.
Sounds gloomy, doesn’t it? The good news is that the Curse of Knowledge is preventable. Those with greater knowledge can take steps to help bridge the gap to those with less knowledge. This can include offering resources and encouraging the ignorant to ask questions. This also requires a combination of intellectual humility and empathy. Avoiding labeling the less knowledgeable ignorant helps, too. Learning to walk a mile in the shoes of the not-yet-cursed becomes a crucial meta-skill. Once we’ve mastered this level of approachability, there’s no need to conceal our talent or skill.
1. What is a problem when we reach a certain level of mastery?| A.Being mistaken as the ignorant. |
| B.Being questioned by ordinary people. |
| C.Being riddled with the miserable burden. |
| D.Being challenged by communicating with the unskilled. |
| A.A pop singer having a concert. |
| B.A mum tutoring her 7-year-old son. |
| C.An artist making a lecture to beginners. |
| D.A foreign student giving a presentation in class. |
| A.Horrible. | B.Overwhelming. | C.Sociable. | D.Avoidable. |
| A.Brave the Curse of Knowledge using your talent. |
| B.Learn new techniques by walking in others’ shoes. |
| C.Get out of your perception and into others’ perspective. |
| D.Fill the knowledge gaps between teachers and students. |
【推荐2】The Walt Disney Company wasn’t about to let COVID-19 stop the company from developing. In the past year, some Disney theme park innovation (革新) have been designed.
For example, Disney had always encouraged face-to-face interactions between cast members and customers. It made perfect sense since Disney spends so much time training its workers in providing good customer service. In fact, Disney is known for pleasing its guests, which explains why it scores so high in customer satisfaction surveys. Well, COVID-19 turned personal interactions into problematic exchanges, as they increased the risk of spreading COVID-19. So, quickly, Disney added cast member virtual chat to its app My Disney Experience. Now, you can rely on a cast member’s knowledge whenever you have a question about Disney visit. It's like having a tour guide on your phone!
There is also the Walk-Up Waitlist. Before 2020, Disney had made strict rules for its Table Service restaurants. Once something sold out, would-be diners had no means of booking a table. COVID-19 has affected park guests, though. Some of them booked tables but then decided not to eat there. This cost Disney money, and it prevented you from dining at your favorite places. So, restaurant managers felt unhappy about the poor business practice, and Disney’s IT department reached a solution. The Walk-Up Waitlist in My Disney Experience allows you to add your name at a restaurant. A previously booked restaurant will find a table for you to dine there. My Disney Experience shows the waiting time. You’ll know whether the wait will fit with your tour. For Disney, the Walk-Up Waitlist improves services and can make it earn more money while increasing customer satisfaction.
In the face of COVID-19, Disney somehow made its parks better and more modern. The company is really worth praising for such great innovations.
1. What can park guests do with the Walk-Up Waitlist?| A.Check whether there's a meal left. | B.Know when to dine in the booked restaurant. |
| C.Dine at any restaurant at any time. | D.Book as many tables as they can. |
| A.It benefits both Disney and its customers. |
| B.It is supposed to be used at a restaurant only. |
| C.It is aimed at more customers during COVID-19. |
| D.It allows Disney to have the most guests at a time. |
| A.How Disney Keeps Its Park Popular. |
| B.How Disney Controls the Flow of Traffic. |
| C.Ways to Tour Around Disney During COVID-19. |
| D.Disney’s Innovations Responding to COVID-19. |
【推荐3】One of China’s greatest resources is no doubt its diverse food. One of the most popular foods to be found is no doubt the street snacks that make up a large part of everyday life. “Compared with A Bite of China, which show eases chefs’ cooking processes and delicious food on air, Chinese Barbecue (烧烤) is more down-to-earth in describing the people,” commented a viewer.
A new documentary series, called Chinese Barbecue, tells the story of this popular food option that sizzles over hot coals on just about every street corner in cities and towns across the country. Barbecued meat shining over hot coal containers, while not as elegant as some of the fine dining options in China, are an essential part of people’s night life. The pleasant smell and atmosphere surrounding the grilled (烤的) street food are “something that could entice a girl to fly downstairs at night wearing her pajamas,” the documentary claims.
In many Chinese’s eyes, barbecue, regarded as the most ordinary and common night street snack, is different from homemade food by mothers as that is a symbol of kinship (亲情). Barbecue is where you go to become connected to people in society. And unlike official business lunches, during which people are rather reserved and polite, barbecue lets people cut loose and relax with old friends and newly made friends, leaving a lasting impression (friendship).
On the other side of the world, in the United States, BBQ, well received by all ages, demonstrates the even more enthusiastic personality of Americans, who grill large steaks on their outdoor stoves at home and enjoy competing to see who has the better cooking skills. It’s safe to say that the world, as a whole, holds deep-rooted good feelings toward barbecue, either for the taste or the warmth generated by fire.
1. What is probably A Bite of China?| A.A popular documentary. | B.A commercial programme. |
| C.A cuisine radio programme. | D.A soap opera of chefs. |
| A.Force. | B.Inform. | C.Remind. | D.Attract. |
| A.Close family bonds. | B.Quality food. |
| C.Unique atmosphere. | D.Beautiful cooking style. |
| A.To indicate the popularity of BBQ. | B.To present special American culture. |
| C.To show friendship between countries. | D.To make a comparison with Chinese BBQ. |



