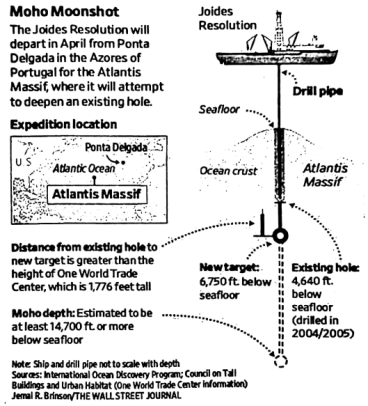
A ship that has spent decades trying to drill nearer to the earth’s mantle (地幔) is preparing for a new voyage to uncover clues to how life began.
With the plan to deepen a hole drilled nearly 20 years ago, two dozen geologists, microbiologists and other scientists will aboard the Joides Resolution to the Atlantis Massif. The hole won’t be the longest in the seafloor but would push closer than ever to the mantle and explore deeper layers of ocean crust (地壳) that haven’t been reached before. Engineers on the ship intend to lower heavy drilling tools through about 5,400 feet of water to find a hole on the seafloor about 15 inches wide. Joides engineers compared the process to standing on a chair and trying to lower a pencil tied to the end of string into the mouth of a soda bottle with a fan blowing.
Samples from the new depths will be taken to investigate whether a special mix of rock and water, Olivine, could have started life on Earth and possibly other planets. This green and magnesium-rich mineral, abundant at such depths, is critical to serpentinization (蛇纹石化), a reaction that occurs when some minerals encounter seawater. Geochemists think the process of serpentinization generates the energy and geochemical conditions favorable to the creation of organic molecules. “These are the building blocks of life,” said Susan Q. Lang, the expedition’s cochief scientist.
The new depth is thought where serpentinization occurs but where temperatures are beyond the limits at which life is known to exist. “If organic molecules are found there, it could help confirm that serpentinization leads to their creation, which contributed to the origin of life.” Dr. Lang said. Finding organic molecules in samples from serpentinization sites could also inform the search for life on other planets. “The geochemistry of fluids in the plumes of Enceladus, a moon of Saturn (土星), have been inferred by astrobiologists to be similar to the makeup of fluids found at the Atlantis Massif.” she added.
| A.14700 feet. | B.12150 feet. | C.11390 feet. | D.10040 feet. |
| A.Deepening the hole will be challenging. |
| B.Engineers will be required to stand high. |
| C.The size of the drill pipe needs to be large. |
| D.The task will be affected by the wind from a fan. |
| A.It may help to find a mineral rich in magnesium. |
| B.It may help to produce the organic molecules. |
| C.It may help to obtain the habitat of life on earth. |
| D.It may help to uncover clues to how life began. |
| A.The Joides Resolution could scale with depth. |
| B.The Wall Street Journal will organize the voyage. |
| C.The new voyage could be named Moho Moonshot. |
| D.The ship will leave for Portugal from Ponta Delgada. |
相似题推荐
【推荐1】In the movie The Wrong Trousers, a pair of futuristic trousers lets people walk on walls and ceilings. Inspired by the movie, researchers in England created “The Right Trousers,” a set of trousers embedded (嵌入) with electrical pumps to force air into tiny tubes (软管) that expand and can help elderly or disabled people with issues like getting up or improving blood flow. Now, material scientists, computer programmers and fabric designers are working to advance robotic clothing.
In June, researchers in Australia created robotic fibers, which can make fabric move automatically. Last year, scientists at MIT built fiber batteries that could be embedded into clothes and power robotic clothing. In recent years, Google partnered with brands like Levi’s and Adidas to put sensors in jackets, backpacks and shoes, letting users access their phones instantly. Researchers said they could soon unlock an era where clothing will act more like a computer, sensing how your body feels and telling your clothes how to help.
At the University of New South Wales in Australia, researchers are creating fabrics that car shape-shift. Thanh Nho Do, a senior lecturer at the school, said his team has created tiny tubes that can weave into sheets of fabric. These tubes can make fabric take various preprogrammed shapes. But challenges still remain for Do’s team, especially around making these robotic tubes smaller so they can weave easily with other fabrics.
Rebecca Kramer-Bottiglio from Yale University agreed that many challenges remain before smart clothing reaches their full potential. “It will be challenging to make these clothes, equipped with fibers and technology, strong enough to go through multiple cycles in the laundry (衣店),” she said. Despite that, she says researchers will figure out a way forward. “Recent breakthroughs,” she said, “point toward a not-so-distant future where smart clothing will be a part of our everyday life. ”
1. What did scientists at MIT do last years?| A.They put sensors in clothes. |
| B.They created movable robotic fibers. |
| C.They made batteries for robotic clothing. |
| D.They released smart clothing connected to cellphones. |
| A.Ensuring the quality of the fabric. |
| B.Finding suitable materials for the fabric. |
| C.Programming the tubes to change shapes. |
| D.Adjusting tubes to weave with other fabrics. |
| A.It struggles to stand repeated washes. |
| B.It will not be a part of everyday life soon. |
| C.It will never overcome laundry-related challenges. |
| D.It has all related challenges solved by researchers. |
| A.The evolution of smart trousers |
| B.The future of laundry innovations |
| C.Smart fabric may shape future wardrobe |
| D.Smart clothing’s impact on everyday life |
【推荐2】For decades, scientists and engineers have been working to develop computer programs that can understand and gen crate natural language. This has been a challenging task, but recent advances in machine learning have allowed us to create powerful language models.
The above paragraph was not written by a human. It was generated by a chatbot called ChatGPT, an artificial intelligence technology designed to mimic human conversation and language while drawing upon a vast wealth of knowledge to answer questions and solve problems. What ChatGPT offers seems more capable―and is potentially even more of a threat to jobs―than existing AI chatbot technology.
AI chatbots have been a routine feature of British life for a few years already. Logging onto many companies’ websites today triggers a popup window saying “Hi, I can answer your questions!” Telephoning restaurant chain Cafe Rouge, for example, puts you through to an audio chatbot that can recognize common questions and plays pre-recorded responses.
While ChatGPT is not infallible, Oxford’s Wooldridge compares its output to well-written undergraduate work. For example, when asked “what is artificial general intelligence” the chatbot responds, “It refers to a type of artificial intelligence that is capable of understanding or learning any intellectual task that a human being can, In other words, AGI is a type of A I that is able to perform any cognitive function that a human being can, rather than being limited to a specific set of tasks.” This level of output poses a threat to those at the lower end of the employment market. According to the Office for National Statistics(ONS), around 1.5 million jobs nationwide can be automated away, with those at greatest risk including restaurant waiters,
Those least likely to sec machines taking over their jobs include legal professionals, doctors and university lecturers. Such occupations are classed as highly skilled. The ONS says, “There is not so much that robots are taking over, but that routine and repetitive tasks which can be carried out more quickly and efficiently by an algorithm written by a human, or a machine designed for one specific function.”
The chairman of Parliament’s Business Committee, Darren Jones, hails Chat GPT as the “start of a new trend” in sophisticated AI tech. He says, “It will become common practice to use tools like this at work with time.”
1. What is the function of Chat GPT?| A.To help humans order food from restaurants. |
| B.To answer questions and solve problems for humans. |
| C.To automate away all human jobs sooner or later. |
| D.To accompany human beings by chatting with them. |
| A.ChatGPT’s output can be compared with undergraduate work. |
| B.ChatGPT could threaten lower-end jobs potentially. |
| C.It explains what artificial general intelligence is. |
| D.It illustrates that Chat GPT is limited to a specific set of tasks. |
| A.Doctors. | B.Lawyers. |
| C.Musicians. | D.Warehouse Keepers. |
| A.ChatGPT, a Powerful Chatbot Posing Threats to Lower-End Jobs |
| B.AGI, a Unique Type of AI Performing Cognitive Function |
| C.AGI, an Outdated AI Technology Taking Over All Jobs |
| D.ChatGPT, a Routine Feature of Our Daily Life for Years |
【推荐3】Scientists have invented a process that can turn non-recyclable glass into everything from tires to toothpaste. Currently, only a small amount of glass is actually recyclable. Because of the effort that is required to sort and separate the smaller parts, they tend to be discarded or sent to the landfill — but researchers from the university of Queensland have come up with a way to turn mountains of non-recyclable glass into useful items.
Researchers said that glass can be broken into silica (二氧化硅) which can be used to make products such as glue, cleaner and coatings. Tom’s of Maine, famous for its natural toothpaste , for instance, uses silicon either as a thickener for its toothpaste or as a whitening agent.
“We’re taking waste glass that is currently going to the landfill because it’s too small to be sorted into the right color, ” said Pirie, one of the researchers. “Glass is about 70 to 75% silica. You need about 1.3 kg of glass to make 1 kg of silica. Most of that goes into the sellable products, so we have very little waste at the end of it.”
Unlike traditional methods of producing liquid silicate, the researchers’ technique requires relatively little energy, which also makes it far cheaper.
“The glass industry has a huge amount it cannot recycle because it is too broken or it is too small, ” said professor Damien Batstone, another researcher who helped to develop the technique. It is currently stockpiled as it cannot be used. We are going to take it through a much simpler process to turn it into a useful resource?
The university’s commercialization company unique quest is now seeking partner companies that are interested in taking the technology to market.
1. What does the underlined word “discarded” in paragraph 1 mean?| A.Sold | B.Divided | C.Broken down | D.Thrown away |
| A.Tom's of Maine is the first to use silica from glass. |
| B.Silica from glass can be used in toothpaste, |
| C.some companies have put silica from glass into use. |
| D.Toothpaste consisting of silica from glass has good quality. |
| A.It has to be sorted first | B.It has a high rate of usage |
| C.It is collected from the landfill. | D.It has to be very small |
| A.It is energy saving | B.It costs lots of money |
| C.It has been taken to market | D.It has a very simple process |
【推荐1】Brewing Up the Best Cup of Coffee
Editor’s note: In the world of coffee, there is a hierarchy (等级) based on brewing (酿制) methods and coffee bean quality. Manual brewing is superior to machine brewing. Italian-style coffee is usually preferred over the American style. At the top of this world, it is specialty coffee (精品咖啡). And becoming a specialty coffee barista (咖啡师) requires specific training. Let’s go to the story of one such barista.
To customers, specialty coffee may be just a simple drink, but for specialty coffee baristas, it is a demanding science. Fei Teng, a 35-year-old barista with 10 years of experience, considers various factors like altitude, climate and grinding (研磨) when making specialty coffee. Fei also has his own principle of developing creative coffee. The Salty Mocha, created by Fei, gained popularity among coffee enthusiasts. “The sea salt neutralizes the sweetness of the mocha, adding layers of flavor to the taste. By introducing innovative changes to classic coffee, it can bring new and wonderful experiences to the taste buds,” Fei told Teens.
Fei majored in fine arts in college but chose to become a coffee apprentice (学徒) after graduation. He began by learning the basics of coffee, including its varieties and roasting levels. Through training and participating in competitions, Fei improved his barista skills, like grinding beans and frothing milk (打奶沫). “Becoming a barista is easy to get started, but difficult to master,” said Fei. To enhance his sensitivity to the quality of coffee beans, Fei tasted a wide variety of coffee, often drinking more than 20 cups a day. That led to diarrhea (腹泻)at times.
“In addition to coffee knowledge, service skills are crucial but often overlooked by baristas,” Fei said. Baristas need to patiently address customer questions and convey the concept behind their coffee in an attractive manner. “Some baristas even create music introductions for their coffee and share them with customers,” added Fei.
“Many view being a barista as a cool job, but actually, it is quite hard and there is a lot of physical labor, like cleaning the cafe,” Fei said. However, despite the challenges, career prospects are promising. A 2023 report reveals that Chinas coffee industry reached 200.7 billion yuan in 2022.
Having dedicated a decade to the coffee industry, Fei plans to continue focusing on specialty coffee and further contribute to the growth of the Chinese coffee sector.
1. What sets the Salty Mocha invented by Fei apart?| A.Its flavor. | B.Its popularity. | C.Its aroma. | D.Its price. |
| A.Why Fei chose to be a barista. | B.What Fei learned about coffee. |
| C.How Fei understood his career. | D.How Fei upgraded his skills. |
| A.They determine a baristas success. | B.They are more important than basic skills. |
| C.They require creativity and talent. | D.They are frequently ignored. |
| A.Promote Chinese coffee overseas. | B.Establish his own unique cafe. |
| C.Continue pursuing his barista career. | D.Teach people how to make coffee. |
【推荐2】You’ve probably followed a few cute dogs and cats on social media. However, are you aware that Ai-generated pets are also gaining popularity nowadays? They are just as adorable as real dogs and cats but also exhibit human-like characteristics.
Chai Dada, 21, runs an AI-generated dog account called “Shizhuangzhuangya” on Xiaohongshu and has already got more than 10,000 followers. Her AI-generated pet Zhuangzhuang is a fluffy Shiba Inu with a big belly who likes to eat and work out. “Zhuangzhuang is actually a reflection of me,” Chai said. “Its life and mood basically reflect my own.”
To personify the character more, the young content maker places Zhuangzhuang in various daily life scenarios. For instance, responding to the recent increase of “hui nan tian”— the super humid (潮湿的) weather in southern China in spring — Chai posted images of Zhuangzhuangmopping a wet floor, with the caption. “It’s wet everywhere at home”; vividly capturing the mood. In the comments section, many have expressed sympathy (同情), for the poor dog.
“Many scenes may seem ordinary, but when a very lifelike and adorable human-like pet appears in these familiar scenes, it looks interesting,” Chai said. Since Zhuangzhuang closely resembles a human in a dog’s body, many followers have come to believe in its real existence. This has provided Chai with opportunities to monetize by partnering with brands for product advertisements. Aiming to expand her reach, Chai expressed a desire to dive deeper into AI to bring her AI pet to life not just in pictures but also in videos.
She also observed that more and more people like her are becoming AI pet bloggers, which has intensified competition in this industry. To attract more fans, bloggers are constantly learning more AI skills and brainstorming to create more interesting storylines. “I want to develop Zhuangzhuang into an intellectual property and create related cultural and creative products such as dolls and stickers,” said Chai.
1. What do we know about the AI pet Zhuangzhuang?| A.It is a digital recreation of Chai’s childhood pet. |
| B.It has gained over one million followers online. |
| C.It is a virtual representation of a real Shiba Inu. |
| D.It mirrors the life and personality of its creator. |
| A.To show the fun Zhuangzhuang brings Chai. |
| B.To illustrate how Chai humanizes Zhuangzhuang. |
| C.To describe Zhuangzhuang’s daily struggles. |
| D.To suggest Zhuangzhuang’s growing fan base. |
| A.Commercialize. | B.Promote. | C.Maximize. | D.Monitor. |
| A.Perfect Zhuangzhuang’s features. | B.Cooperate with other AI pet creators. |
| C.Create lifelike videos of Zhuangzhuang. | D.Write a book featuring Zhuangzhuang. |
【推荐3】In Lulea, a city in northern Sweden, the sun only shines around three hours a day in the winter months. People tend to stay warm at home and that can be very lonely. To help ease winter loneliness, the local authority is asking everyone to just say hello to each other. The new campaign is called Sag hej.
While the world is experiencing an increase in loneliness following the Covid-19 pandemic, in places that do not get a lot of sunlight during the winter months, the issues are exasperating.
“Loneliness and isolation are major problems at any time of the year and almost everywhere in the world right now,” Micael Dahlen, professor of wellbeing and happiness at the Stockholm School of Economics, said. “It comes with the times that we live in, with the lifestyles that we have, where we don’t necessarily encounter each other to the same extent that we used to. This increases in winter when we are outside less and socializing less,” he added.
While most people believe that loneliness is most common amongst seniors who tend to live alone, the opposite is true. It is actually rising in young people. A recent study published in the International Journal of Adolescence and Youth found that loneliness in young people has been increasing and this negatively impacts mental and physical wellbeing. Research about Lulea found that 45 percent of 16-to-29-year-olds were experiencing problems due to being lonely.
Asa Koski, who works for the city, came up with the idea of the Sag hej! campaign. She wants the city, which is undergoing rapid growth due to green industry jobs, to be a friendlier, more welcoming, and less lonely place for newcomers. “We don ’t just want that Lulea is going to grow as a city; we want Lulea to be a pleasant and safe and friendly city as well where there’s culture, leisure activities, and sport,” said Koski.
Many people agree that saying hello should be encouraged and believe that the more international the city becomes, the more people will become friendlier too.
1. Which word can replace the underlined word “exasperating” in Paragraph 2?| A.annoying | B.interesting | C.inspiring | D.surprising |
| A.Loneliness and isolation dominate people’s feeling. |
| B.Saying hello helps people deal with winter loneliness. |
| C.A lack of sunshine in winter contributes to loneliness. |
| D.People ’s lifestyles in winter increase their feeling lonely. |
| A.Seniors suffer more from loneliness. |
| B.There are more young people feeling lonely than seniors. |
| C.The phenomenon of loneliness is common in different age stages. |
| D.45 percent of 16-to-29-year-olds have problems because of loneliness. |
| A.Her job is connected with the city. |
| B.She has confidence in Lulea ’s culture. |
| C.She wishes the city to develop rapidly. |
| D.She expects the city to be a better place for newcomers. |



