In the eastern United States, one of the existing types was that commonly know under the Algonkian name of wigwam in which the Iroquois Indians lived. The wigwams were of wagon-top shape with straight sides and ends, made by bending young trees to form the round shape. Over this shape pieces of tree bark were laid to protect the Indians from bad weather. Over the bark dried grass was added. A small hole allowed smoke to escape from the top. Doorways at each end served also as windows. The Iroquois Indians built trunk walls all around their villages. The wall had only one opening. They could quickly close this cpening if their enemies came near.
Interestingly, the Choctaw Indians in Mississippi also lived in a wigwam of a most primitive (原始的) construction, but different from those of the Iroquois Indians. The Choctaw Indians’wigwams, made from mud,cane and straw, were in the form of a bee-hive. The covering was made of a long, tough grass. A post in the centre supported the roof. A hole in the top admitted the light, and allowed the smoke to pass out.
The tipi tent-housing of the upper lake and plains area was put up with poles set lightly in the ground, tied together near the top, and covered with bark and grass in the lake country. It was easily portable, and two women could set it up or take it down within an hour.
The Pawnee, Mandan and other Indian tribes (部落) along the Missouri built solid ring-shaped structhures of trunk, covered with earth and dried grass,housing adozen families.
The Wichita and other tribes of the Texas border built large ring-shaped houses covered with dried grass.
Apart from the regular housing, almost every tribe had some style of housing.
1. Which of the follwing pictures shows the house for the Iroquois Indians?
A.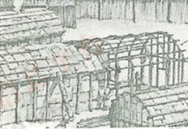 | B. |
C.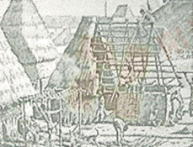 | D. |
| A.with openings in the trunk walls | B.large enough for several families |
| C.in a ring shape with bark and mud | D.by bending young trees to form the shape |
| A.of the same shape | B.covered with grass |
| C.built with a post in the centre | D.built with doorways at each end |
| A.all the native Indians built trunk walls all around their houses |
| B.all the native Indian houses were built with poles tied together |
| C.the Iroquois Indians took safety into account while building their wigwams |
| D.the Choctaw Indians in Mississippi built their wigwams with straight sides and ends |
相似题推荐
【推荐1】For late 19th-century North Americans and Europeans, a display of tableware (餐具)could reveal much about someone’s social position, as the wealthy took great care to get different kinds of forks for everything. Before the 18th century, people of all classes usually ate with a knife and a spoon.
The fork’s path to the table was hard-won and slow. In ancient Egypt, Greece, and Rome, forks were used for slicing food into pieces or lifting meat from a pot or fire.
Following a reduction in size, the fork appeared to have entered dining areas in the courts of the Middle East and Byzantine Empire by the eighth and ninth centuries, and became common among wealthy families there by the tenth century. Early in the 11th century, it appeared in various pieces of European art. In the late 11th century, St.Peter Damian from Ostia wrote about a Byzantine princess who used forks and regarded her dying of a disease as punishment for such “luxury”.
The fork’s slow conquest of Europe was carried out from Italy. Motivated by the same concerns for hygiene(卫生),forks were bought by wealthy Britons,inspired by Queen Victoria, who regarded fork use as a sign of good manners.
The fork’s introduction to North America dates back to 1633, when John Winthrop, a founder of the Massachusetts Bay Colony, was gifted a set of forks. The Industrial Revolution strengthened the fork’s presence on dining room tables as production of flatware became less expensive. Writing in 1896 inSocial Eriquere,Maud C. Cooke declared the fork had finally conquered the knife in America and “any attempt to give the knife importance at table is looked upon as an offense(冒犯)against good taste.”
1. What can we learn about forks from paragraph1?| A.They were used improperly in the 18th century. |
| B.They had many different types in the 19th century. |
| C.They were popular in Europe before the 18th century. |
| D.They led to North American’s rise in social position. |
| A.To eat food. | B.To decorate tables. |
| C.To cut food. | D.To create works of art. |
| A.St.Peter Damian. | B.Thomas Coryate. |
| C.Queen Victoria | D.Maud C.Cooke. |
| A.The appearance of flatware |
| B.The start of the Industrial Revolution. |
| C.John Winthrop receiving forks as presents. |
| D.Maud C.Cooke writing Social Etiquette. |
【推荐2】The Golden Gate Bridge is a well-recognized landmark in the United States. It spans (横跨) the Golden Gate Strait — a mile-wide stretch of water that connects the San Francisco Bay to the Pacific Ocean. The Golden Gate Bridge is one of the most beautiful bridges in the world. It is also one of the tallest.
The idea for a bridge across the strait had been around for many years, because San Francisco suffered from its isolated location. Planning for the Golden Gate Bridge began in 1916, but the design underwent many changes before construction finally started in 1933.
Joseph Strauss was the chief engineer in charge of the bridge project. However, he had little experience with the construction of suspension bridges (吊桥). For this reason, other engineers, architects, and designers made great contributions to the design and construction of the bridge. For example, the bridge owes its art deco (装饰派艺术) style and distinctive orange color to the architects Irving and Gertrude Morrow. Charles Alton Ellis did much of the technical work necessary to build the bridge.
It was not easy to get the project started. Financing had to be found, and there was much opposition to the very idea of a bridge. The US Navy, for example, feared, that a bridge would block ship traffic. The Southern Pacific Railroad, which ran the ferry fleets (轮渡船队), feared competition from the bridge. Many experts did not believe that it would be possible to build such a long bridge under such difficult circumstances. There are strong currents and heavy winds on the bridge site, which made construction dangerous.
The construction of the bridge finally began in 1933. The construction work set new standards for safety — workers were among the first required to wear hard hats, and a safety net saved the lives of nineteen men while the bridge was built. The Golden Gate Bridge was completed in 1937, when the bridge was opened to pedestrians (行人). It was opened to cars one year later. The bridge was finished ahead of schedule and cost much less than originally budgeted.
Because the Golden Gate Bridge is the first sight for many people arriving in the United States by ship, it is sometimes called the “Statue of Liberty” for the West Coast.
1. According to the text, the Golden Gate Bridge .| A.is the best-known symbol of America | B.crosses the Golden Gate Strait |
| C.crosses the San Francisco Bay | D.is about a mile wide. |
| A.To give the West Coast a new tourist attraction. |
| B.To connect San Francisco to the Pacific Ocean. |
| C.To set up a well-known landmark. |
| D.To compete with the ferry fleets. |
| A.was first suggested in 1916 |
| B.was first put forth by Joseph Strauss |
| C.was perfected by Gertrude Morrow in 1933 |
| D.was put forward long before construction started |
| A.It was finished under budget. |
| B.It was delayed for one year. |
| C.It was opened to the vehicles in 1937. |
| D.It was the first to set safety standards. |
【推荐3】A castle was the fortress(堡垒)and home of a king or nobleman.
Most of the castles we think of today were built in Europe. They were constructed from about 1,000 AD to about 1,500 AD, during a period known as the Middle Ages.
Castles played an important role after the fall of the Roman Empire. When a king granted land to nobles, the nobles promised in return to serve the king and provide him with soldiers. Nobles built castles on the lands given to them. But some nobles simply claimed land as their own and built a castle on it. That was asking for trouble. There were many power struggles between nobles and kings, and among the nobles themselves.
A typical stone castle had several main parts. At the centre of the castle was a tall and very strong building called the keep. This is where people in the castle made their last stand if the outer defences failed. The keep was set in a courtyard, where there were workshops, stables, and a kitchen.
High, thick walls surrounded the keep and the courtyard. Strong, round defensive towers stood at the corners of the walls. Guards walked along the tops of the walls and towers.
Many stone castles were surrounded by a wide ditch called a moat. Some moats were filled with water, but many were not. The only way into the castle was across a wooden drawbridge over the moat. If enemies attacked, the defenders raised the bridge. Then they lowered a heavy iron-and-wood barrier called a portcullis to block the entrance to the castle.
A well-built castle was a pretty safe place to be. Attackers had a hard time getting in. But they still had some options. They could go over the walls using ladders. They could smash (撞碎) through the walls or doors. Or they could dig under the walls and try to get part of the wall to fall down. If none of those things worked, they could just camp outside until the defenders ran out of food.
Attackers sometimes brought large machines called siege engines with them to break through castle doors or walls. This was a heavy wooden beam with a metal cap. In the early 1500s, cannons entered wide use in warfare. Cannonballs could dig into the base of stone walls and weaken them. The walls then fell under their own weight. As a result, castles were no longer needed.
1. The underlined word “That” refers to the fact that ________.| A.nobles built castles on the lands given to them |
| B.the nobles promised to serve the king in return |
| C.some nobles simply claimed land as their own |
| D.the nobles provided the king with soldiers |
| A.3 | B.4 | C.5 | D.6 |
| A.Some castles were built to attract more visitors. |
| B.Kings in ancient Europe were more generous. |
| C.Portcullises were used to break through castle doors. |
| D.Warfare must be frequent from 1,000 AD to about 1,500 AD. |
| A.Attacking a castle |
| B.Weakness of a castle |
| C.Pretty safe place |
| D.Siege engines |
【推荐1】There is no doubt that to study abroad gives you an excellent opportunity to learn things which are very helpful in your career building.
Today Canada has earned a good name in providing quality education and safe and healthy environment for its students. That is why more than 130,000 international students enroll (登记入学) every year in famous Canadian universities. It is an ideal education destination and gives students a unique experience of education and its diverse arts and culture. Canada spends a lot on education and is ranked the highest in G-8 countries.
To study in Canada is very cost-effective. These universities are affordable compared to other universities in the world such as in the US, New Zealand and the UK where cost of education and living is very high. According to a survey in 2006, Canada offered the lowest tuition fees (学费) for foreign students compared to the UK and Australia.
The low rate of crimes and the peaceful and safe environment of the country also attracts a lot of international students to Canadian universities. Canada has 92 universities and 175 community colleges and university degrees have three levels ― Bachelor’s, Master’s and Doctoral.
A Bachelor’s degree in Canada is for three or four years’ full-time study depending on the nature of the programme you are doing. On the other hand, a Master’s degree consists of two years of study. For a Doctoral programme in Canadian universities, you require a minimum of three to four or sometimes five years of research and study.
You can also find many diploma and certification (认证) programmes in Canadian universities where the time is generally one year. Some of the Canadian universities are well-regarded worldwide and the degree and diploma gained from these Canadian universities are recognized globally and promise a bright future. After the completion of studies, a person could also find great job offers in Canada itself. International students require a work permit to work on campus.
1. What can we infer from the passage ?| A.Canada has 267 community colleges in all. |
| B.To study in Canada is cheaper than in Australia. |
| C.Canada is the richest one among G-8 countries. |
| D.130,000 Chinese students come to Canada yearly. |
| A.8 years. | B.9 years. | C.10 years. | D.11 years. |
① Quality education. ② Safe environment. ③ Diverse culture.
④ Bright job future. ⑤ High scholarship. ⑥ Low tuition fees.
| A.② | B.③ | C.④ | D.⑤ |
| A.Ignore. | B.Doubt. | C.Support. | D.Oppose. |
【推荐2】The Mysterious World of Deep-Sea Creatures
The deep sea remains one of the least explored and understood environments on our planet. Lying below the sunlit upper layers of the ocean, the deep sea is a region of permanent darkness, freezing temperatures, and massive pressure. Yet, life thrives (茁壮成长) here in some of the most astonishing ways.
* The Black Dragonfish *
Residing at dephs of up to 2,000 meters, the black dragonfish is a predator with a thin and long body and sharp teeth. What makes it unique is its ability to produce its own light, a phenomenon known as bioluminescence. This helps it attract prey (猎物) and communicate with potential mates.
* The Giant Squid *
Long a stuff of legends and tales, the giant squid, which occasionally attacks whales, can reach lengths of up to 43 feet. Its massive eyes, the size of dinner plates, allow it to detect weak light in the deep dark waters. Encounters with this enormous creature are rare, and much of its life remains unknown.
* Tube Worms at Hydrothermal Vents *
In the depths of the ocean, hydrothermal vents (热液喷口) shoot superheated water packed with minerals. Around these vents, communities of tube worms thrive, reaching lengths of up to 2 meters. They possess no mouth or digestive system; instead, bacteria inside them process the minerals from the vents to produce energy.
Modern technology has enabled humans to explore deeper into the ocean than ever before. Using remotely operated vehicles and deep-sea submersibles (潜水器), scientists can now study these creatures in their natural habitats, uncovering secrets that could hold the key to understanding life’s adaptability.
1. What ability is unique to the black dragonfish?| A.Generating light for itself. | B.Attracting and capturing prey. |
| C.Discovering light in the deep water. | D.Communicating with other creatures. |
| A.The black dragonfish | B.The tube worm. | C.The giant squid. | D.The whale. |
| A.An academic article. | B.An experimental report. |
| C.A travel guide. | D.A natural science magazine. |
【推荐3】A new study found evidence that dos developed in physical ways to present “lovely dog eyes” as a way to connect with humans.
The study compared the facial muscles (肌肉) of dogs and wolves, which share ancestral history. Dogs broke off from wolves after being domesticated (驯化) about 33,0000 years ago. During that time dogs changed physically and behaviorally to fit life with humans.
The researchers examined the heads of six dogs and two wolves for comparison. They found the facial structure of both animals was mostly very similar. But one major difference was found above the eyes. The dogs were found to have two well-formed muscles around the eye that were not present in the wolves. These small muscles permit dogs to raise their inner eyebrows, the study found.
Juliane Kaminski, a comparative psychologist from the research suggests this eyebrow-rising movement causes “a warm” feelings in humans because it makes the dogs’ eyes appear larger. This expressions also makes the dog lo more like a human baby. The eye movement is similar to that which humans make when they are sad.
“The evidence is very obvious that dogs developed a muscle to raise the inner eyebrows after they were domesticated from wolves,” Kaminski said.
In a separate part of the study, the researchers observed how 27 dogs and nine wolves interacted with a human. “We also studied dogs’ and wolves’ behavior. And when exposed to a human for two minutes, dogs raised their inner eyebrows more and higher than wolves,” Kaminski said.
The researchers suggest that the eye movements developed over time as a way for dogs to get humans to do things for them, such as giving then food, care or attention.
The only dog species in the study that did not have the muscles was the Siberian husky, which is an ancient kind of dog. The husky could be the best living example of what the link between dogs and wolves looked like.
Kaminski said the main limitation of the study was the small number of dogs and wolves used. This means further study will be required and should include other ancient dog species. The work could also be extended 10 other animals with which humans have developed close relationships, including horses and cats.
1. What is the difference found between dogs and wolves?| A.Dogs have bigger eyes. |
| B.They have different ancestors. |
| C.They have easily distinguishable faces. |
| D.Dogs have additional muscles around the eyes. |
| A.Dogs have developed in order to get along with humans. |
| B.Dogs have learned facial expressions from human babies. |
| C.Dogs are intentionally raising their eyebrows to please humans. |
| D.Dogs have changed their behaviors to get food from humans. |
| A.It has lovelier eyes than the other dogs. |
| B.It seems much more like a wolf than a dog. |
| C.It can raise its eyebrows higher than most dogs do. |
| D.It is better at linking with humans than an ordinary dog. |
| A.The evolution of the wolves. | B.Dogs’ ability to connect with humans. |
| C.The similarities between dogs and wolves. | D.Changes in dogs caused by domestication. |
【推荐1】For thousands of years, buildings have been used to show off power and wealth, to honor leaders or religions, and to stretch the limits of architecture.Since the 19th century,high- rise buildings have sprung up all over the world, showing the modern architecture wonders.
The Empire State Building
The Empire State Building, a 102-story building, was completed in New York in 1931 and was the tallest in the world until 1971.While the Empire State Building was built to be an office building, it still draws millions of tourists each year for overlooking New York.It is currently admired for its green architecture initiatives, in an effort to be a more energy-efficient and eco-friendly green building.
The Jin Mao Building
Completed in 1999 and standing 420.6 meters high,the Jin Mao Building is China's tallest high rise building.Located in Pudong District of Shanghai, the Jin Mao Tower is the 8th super tall 88- floor building, which represents the belief in Chinese culture that the number 8 brings fortune.With both modern and traditional characteristics, the Jin Mao Building is a symbol and landmark of Shanghai and a must-sce for any tourist wishing for a taste of modern Shanghai.
Taipei 101
With a height of 508 meters, Taipei 101 or formerly known as the Taipei World Financial Center became the world's tallest building when it was completed in 2003. Designed by C.Y.Lee &.Partners, the multi-use steel and- glass high rise was intended to prevent typhoons and earthquakes.Taipei 101 has developed into the outstanding landmark of the area, and the ideal shopping and relaxing place for locals.
1. What is the Empire State Building recently recognized for?| A.Its multi-functions. |
| B.Its numerous visitors. |
| C.Its wealth and power. |
| D.Its going- green ideas. |
| A.They are landmark buildings. |
| B.They feature traditional cultures. |
| C.They were built in the 20th century. |
| D.They were designed for natural disasters. |
| A.To promote green buildings. |
| B.To recommend tourist attractions. |
| C.To introduce famous tall buildings. |
| D.To advertise the high- rise buildings. |
【推荐2】Hong Kong has the largest collection of high-rise buildings on Earth, many of which have been designed by world-famous architects.
HSBC Headquarters Building
In 1979, the Hong Kong and Shanghai Banking Corporation(HSBC) launched an international design competition for its new headquarters. Foster +Partners, headed by architect Sir Norman Foster, won the competition with an out-of-the-box idea. With a budget of roughly S667 million in the day’s currency, the British visionary had the modular (模块化的) pieces constructed in the US, Japan and the UK before shipping them to Hong Kong for assembly (组装).
The Henderson
Zaha Hadid Architects(ZHA) has revealed plans to replace a multi-story car park in Hong Kong’s central business district with a new 623-foot tower. Like so many of ZHA’s visionary projects, the office tower, completed in 2023,integrates technology with natural environments. For instance, there is a sky garden which is an outdoor recreational space with a running track and a planting network that acts as an effective biological air-purifying filter by consuming pollutants.
Two International Finance Centre
On a clear day, you can see straight across Hong Kong from the offices in Two International Finance Center(2IFC), completed in 2003. Designed by the late Cesar Pelli, the 1,352-foot tower was the tallest in the city upon its completion. It transformed the skyline when it opened with its breath taking height and tapered (锥形的) shape, symbolizing Hong Kong’s rise.
Bank of China Tower
The 1,205-foot tower, completed in 1990,broke records at the time and became an instant landmark as the first tower over 985 feet outside North America. A vision of urban energy, expansion and geometry, the Bank of China Tower(BOC Tower)was designed to resemble a bamboo shoot, symbolizing strength, vitality and China’s emergence as a significant player in international finance.
1. What is special about the HSBC Headquarters Building?| A.It was designed by several architect teams. | B.It was funded by countries across the world. |
| C.Its style was considered to be the most creative. | D.Its design was a winning work of a competition. |
| A.HSBC Headquarters Building. | B.The Henderson. |
| C.Two International Finance Centre. | D.Bank of China Tower. |
| A.They are known for being eco-friendly. | B.They were completed in the same century. |
| C.They used to be the tallest in Hong Kong. | D.They were designed by the same architect. |
【推荐3】Some libraries use unique architecture to encourage visitors to explore the shelves and settle down with a new book. No matter how they achieve it, these novel libraries are keeping the magic of reading alive.
Stuttgart City Library (Stuttgart, Germany)
Opened in 2011, this 9-story public library is so special because of its wonderful color scheme (lit by blue light at night) and its rare cubic shape. This cultural center for the city, designed to feel open and full of light, can be entered from any of its four sides, and people can borrow artworks as well as books.
Beach Library (Albena, Bulgaria)
Beach Library is the first of its kind in Europe to encourage visitors to read a book on the beach. The white, weather resistant shelves lined up not far from the surf feature 6, 000 books in 15 languages so every visitor can find the perfect book to read while exposed to the sun’s rays.
Seikei University Library (Tokyo, Japan)
This library is the new symbol of Seikei University. Libraries are usually famous for their quiet atmosphere, but this one encourages conversation. Pritzker Prize-winner Shigeru Ban designed the library with free-standing soundproofed(隔音的)equipment to serve as perfect spots for study groups and lively discussions.
Macquarie University Library (Sydney, Australia)
The very library was designed to be a sustainable building. A great combination of high technology and sustainable development, this building was made from recycled materials, features a green roof, and was designed to look like a local unique tree. It is also advanced, using robot tools to bring requested books to the front desk.
1. What can visitors do at Beach Library?| A.Attend a famous festival. | B.Watch wonderful light shows. |
| C.Have discussions with professors. | D.Enjoy reading while taking a sun bath. |
| A.Its cubic shape. | B.Its environmentally friendly building. |
| C.Its peaceful atmosphere. | D.Its weather-resistant shelves. |
| A.Sports. | B.Education. | C.Nature. | D.Economy. |



