1 . Reducing the workweek to four days could have a climate benefit. In addition to improving the well-being of workers, cutting working hours may reduce carbon emissions. But those benefits would depend on a number of factors, experts emphasize, including how people choose to spend nonworking time.
Commuting and travel
Transportation is the biggest contributor to greenhouse emissions. A November 2021 survey of 2,000 employees and 500 business leaders in the United Kingdom found that if all organizations introduced a four-day week, the reduced trips to work would decrease travel overall by more than 691 million miles a week.
But the climate benefits of less commuting could be eliminated, experts said, if people choose to spend their extra time off traveling, particularly if they do so by car or plane.
Energy usage
Shorter working hours could lead to reductions in energy usage, experts said. According to a 2006 paper, if the United States adopted European work standards, the country would consume about 20 percent less energy.
Energy could also be conserved if fewer resources are needed to heat and cool large office buildings, reducing demands on electricity. For example, if an entire workplace shuts down on the fifth day, that would help lower consumption — less so if the office stays open to accommodate employees taking different days off.
Lifestyle changes
It’s possible that fewer working hours may lead some people to have a larger carbon footprint, but experts say research suggests that most people are likely to shift toward more sustainable lifestyles.
One theory is that people who work more and have less free time tend to do things in more carbon-intensive ways, such as choosing faster modes of transportation or buying prepared foods. Convenience is often carbon-intensive and people tend to choose convenience when they're time-stressed. Meanwhile, some research suggests that those who work less are more likely to engage in traditionally low-carbon activities, such as spending time with family or sleeping.
“When we talk about the four-day workweek and the environment, we focus on the tangible, but actually, in a way, the biggest potential benefit here is in the intangible,” experts said.
1. What is identified as the leading cause of greenhouse emissions according to the passage?| A.The well-being of employees. |
| B.The conservation of energy. |
| C.Commuting and travel. |
| D.The European work standard. |
| A.People will have big potential in achieving intangible benefits while working. |
| B.People are more likely to engage in carbon-intensive activities due to time constraints. |
| C.People may shift toward more sustainable lifestyles and lower carbon footprints. |
| D.People may travel more frequently by car or plane during their extra time off. |
| A.highlight the importance of shortening working time in the context of well-being |
| B.provide an overview of transportation emissions worldwide |
| C.analyze the impact of reduced working hours on mode of business |
| D.illustrate factors affecting the climate benefits of a shorter workweek |
The problem of electronic waste
We have gradually come to realise that in two ways in particular, modern hi-tech can be bad for the planet. The first is its energy use; the worldwide scale of information technology is so enormous that electronics now produce fully two percent of global carbon emissions, which is about the same as the highly controversial emissions of aeroplanes. The other is the hardware, when it comes to the end of its natural life. This, increasingly, is pretty short. We have hardly noticed this important stream of waste, so much so that a Greenpeace report on the untraced and unreported e-waste two years ago referred to it as “the hidden flow”. We need to be aware of it.
The latest United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) report estimates that worldwide, electronic waste is mounting by about 40 million tons a year. So what can we do about it?
The European Union has recognised the problem by adopting a key principle: producer responsibility. In other words, making it the duty of manufacturers of electronic goods to ensure their safe disposal at the end of their lives. In practice, an EU regulation now means that electronics dealers must either take back the equipment they sold you, or help to finance a network of drop-off points, such as public recycling sites. Its main feature is quite ambitious: it aims to deal with “everything with a plug”.
The new UN report suggests that all countries could do something about the problem with a change in design. Groups such as Greenpeace have led the way in putting pressure on major manufacturing companies to find substitutes for the toxic chemicals inside their products. Encouragingly, they have had some success in forcing them to develop non-poisonous alternatives to these. This may be the real way forward.
___________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
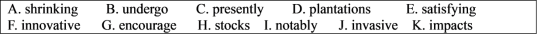
Is climate change consuming your favorite foods?
Coffee: Whether or not you try to limit yourself to one cup of coffee a day, the effects of climate change on the world’s coffee-growing regions may leave you little choice.
Tea: When it comes to tea, warmer climates and erratic precipitation aren't only
Seafood: Climate change is affecting the world's aquaculture as much as its agriculture. As air temperatures rise, oceans and waterways absorb some of the heat and
And that
Is Climate Change Consuming Your Favorite Foods?
Due to climate change, the world’s endangered lists are no longer just for animals. We may not only need to adapt ourselves to living in a warmer world but a
As the increased amount of carbon dioxide in the air linked to global warming
Whether or not you try to limit yourself
Rising temperatures and unpredictable rainfall patterns are reported to have been threatening coffee plantations in South America, Africa, Asia, and Hawaii. The result? Significant cuts in coffee yield.
According to organizations like Australia's Climate Institute, half of the present coffee-producing areas
With temperatures continuously rising, oceans are absorbing some of the heat and undergoing warming of their own,
And how about that satisfying “crack” which you get when you are eating crabs and lobsters? It could be silenced
Even worse is the possibility
| A.The demand of the job market. | B.The location of the hotel. |
| C.The damage to the environment. | D.The solution to the issue. |
| A.Beijing was the most polluted city. |
| B.The air quality index reading for Xi’an reached 500. |
| C.The AQI for Xingtai in Hebei Province was 491. |
| D.Emergency measures against air pollution have not been taken. |
| A.About 100 cities. | B.About 50 cities. |
| C.About 500 cities. | D.About 20 cities. |
| A.Limiting government vehicle use. |
| B.Putting off all construction. |
| C.Asking polluters to apologize for their action. |
| D.Reducing the emissions from power companies. |
7 . The Paris climate agreement finalised in December last year indicated a new era for climate action. For the first time, the world’s nations agreed to keep global warming well below 2℃.
This is vital for climate-vulnerable nations. Fewer than 4% of countries are responsible for more than half of the world’s greenhouse gas emissions. In a study published in Nature Scientific Reports, we reveal just how deep this injustice runs.
Developed nations such as Australia, the United States, Canada, and European countries are essentially climate “free-riders”: causing the majority of the problems through high greenhouse gas emissions, while paying few of the costs such as climate changes impact on food and water. In other words, a few countries are benefiting enormously from the consumption of fossil fuels, while at the same time contributing disproportionately to the global burden of climate change.
On the other hand, there are many “forced riders”, who are suffering from the climate change impacts despite having scarcely contributed to the problem. Many of the world’s most climate-vulnerable countries, the majority of which are African or small island states, produce a very small quantity of emissions. This is much like a non-smoker getting cancer from second-hand smoke, while the heavy smoker is fortunate enough to smoke in good health.
The Paris agreement has been widely considered as a positive step forward in addressing climate change for all, although the details on addressing “climate justice” can be best described as incomplete.
The goal of keeping global temperature rise “well below” 2℃ deserves to be praised but the emissions reduction promises submitted by countries leading up to the Paris talks are very unlikely to deliver on this.
More than $100 billion in funding has been put on the table for supporting developing nations to reduce emissions. However, the agreement specifies that there is no formal distinction between developed and developing nations in their responsibility to cut emissions, effectively ignoring historical emissions. There is also very little detail on who will provide the funds or, importantly, who is responsible for their provision. Securing these funds and establishing who is responsible for raising them will also be vital for the future of climate-vulnerable countries.
The most climate-vulnerable countries in the world have contributed very little to creating the global disease from which they now suffer the most. There must urgently be a meaningful mobilization of the policies outlined in the agreement if we are to achieve national emissions reductions while helping the most vulnerable countries adapt to climate change.
And it is clearly up to the current generation of leaders from high-emitting nations to decide whether they want to be remembered as climate change tyrants (暴君) or pioneers.
1. The author is critical of the Paris climate agreement because ________.| A.it is unfair to those climate-vulnerable nations |
| B.it aims to keep temperature rise below 2℃ only |
| C.it is beneficial to only fewer than 4% of countries |
| D.it burdens developed countries with the full responsibility |
| A.They needn’t worry about the food and water they consume. |
| B.They are better able to cope with the global climate change. |
| C.They hardly pay anything for the problems they have caused. |
| D.They are free from the greenhouse effects affecting “forced riders”. |
| A.It will motivate all nations to reduce carbon emissions. |
| B.There is no final agreement on where it will come from. |
| C.There is no clarification of how the money will be spent. |
| D.It will effectively reduce greenhouse emissions worldwide. |
| A.Encouraging high-emitting nations to take the initiative. |
| B.Calling on all the nations concerned to make joint efforts. |
| C.Pushing the current world leaders to come to a consensus. |
| D.Putting in effect the policies in the agreement at once. |
8 . Keeping The Taps Running in Thirsty Cities
Water covers 71% of Earth’s surface yet only 2% of it is accessible as a source of fresh water.
It is important to recognize that it is not just city residents who
Water stress is not always caused by physical shortages in dry areas.
Every thirsty city operates within its own context,
On February 1, the authorities put in place a strict limit of 50 litres of water per person per day.
In addition, a ban was placed on using
Crises such as the Cape Town drought are in danger of becoming the new norm. The
| A.Impact | B.Pressure | C.Impression | D.Observation |
| A.recycle | B.waste | C.consume | D.apply |
| A.restored | B.abstracted | C.separated | D.preserved |
| A.change | B.source | C.origin | D.volume |
| A.Competition | B.Protection | C.Construction | D.Regulation |
| A.contributing | B.regarding | C.responding | D.referring |
| A.in addition | B.for example | C.on the contrary | D.as a result |
| A.prospect | B.illustration | C.symptom | D.security |
| A.reported | B.presented | C.predicted | D.explained |
| A.respectively | B.increasingly | C.restrictively | D.extensively |
| A.By comparison | B.In other words | C.To our surprise | D.What’s more |
| A.feasible | B.drinkable | C.inevitable | D.influential |
| A.campaign | B.statement | C.presentation | D.advertisement |
| A.invaded | B.liberated | C.suffered | D.proceeded |
| A.change | B.theory | C.record | D.threat |
一家服装店的橱窗外,两只狐狸在对话:
——爸爸快看,妈妈在对我笑呐!
——走吧儿子,有人过来了。
请简要描述这幅图片,并就其传达的信息和意义谈谈你的看法。

.
.
.
.
.
.



