
Pesticides might just be a bee's worst enemy. They harm their brains, slow down their reproduction, and even kill their buzz. Now it seems they damage their social lives and reduce their ability to care for their young.
While previous studies have shown that commonly used neonicotinoid(新烟碱类)pesticides make bees sick and affect how they search for food and navigate, a new study gives more of an idea of how these chemicals affect the internal workings of a colony(种群). Studying these effects has proved difficult, so the team employed a new technique. They stuck tiny QR codes to the backs of humblebees and tracked their movements using a robotic camera.
The researchers looked at 12 colonies housed in a lab, giving some the same level of imidacloprid—the world's most commonly used pesticide—that they'd be exposed to in the wild while keeping others pesticide-free as controls. They checked on them for a few minutes 12 times a day. The findings are published in the journal Science.
Unfortunately, the researchers found a number of obvious differences between the bees exposed to the pesticide and the controls. The bees given neonicotinoids spent less time interacting with other bees and more time resting. This pause in activity tended to happen more at night, but the researchers aren't sure why.
"Bees actually have a very strong circadian rhythm(生理节奏)," lead author James Crall explained in a statement. "So what we found was that, during the day, there was no statistically observable effect, but at night, we could see that they were crashing. We don't know yet whether the pesticides are destroying circadian gene regulation or if this is just some, maybe physiological feedback…But it suggests that, just from a practical perspective, if we want to understand or study these compounds, looking at effects overnight matters a lot."
1. What does the new study suggest about pesticides' effect on bees?| A.Pesticides lead to their disease. |
| B.Pesticides slow down their brain function |
| C.Pesticides upset their community. |
| D.Pesticides damage bees' internal parts. |
| A.The tools used to observe the bees. |
| B.The data recorded by the robotic camera |
| C.The researchers conducting the experiments. |
| D.The bees kept free from the pesticides. |
| A.The circadian rhythm of bees is stronger during the day. |
| B.It is vital to study the performance of bees at night |
| C.It is certain that pesticides affect bees only at night. |
| D.The pesticides do great harm to circadian gene regulation of bees. |
| A.To inform people of the worrying effects of pesticides. |
| B.To check the best time to observe experimental results. |
| C.To call for the toughest ban on the chemicals. |
| D.To recommend measures to improve the quality of pesticides. |
相似题推荐
【推荐1】Episodic memory (情景记忆) allows humans to revisit past personal experiences in their minds, and it was once thought to be a special skill of humans. Although there are still arguments about the extent of this type of memory in non-human animals, scientists have proved that creatures like rats and dogs can pass tests that are developed to assess episodic memory over the past two decades. “Curiously, there is a lack of research investigating dolphins’ episodic memory,” University of Cambridge cognitive (认知的) scientist James Davies says. Therefore, this surprising fact encourages him to fill this gap.
The team used “where” and “who” questions in their research, each on a different test. Each dolphin was first trained to retrieve a ball from the water, and then trained to get a ball by approaching a person holding it in front of them while ignoring an empty-handed person standing at a different spot. During this training, the locations were randomized (使随机化) and the person holding the ball differed each time, so that those details were irrelevant to learning the retrieving behavior. Then, for the tests, the dolphins were asked to retrieve the ball as they had learned to do, but after 10 minutes, something changed-this time, the ball couldn’t be seen, as it was now behind one of the two people’s backs. In the “where” tests, the ball was hidden in the same spot as in the training, but both people had been changed, while in the “who” tests, the locations of the people changed but the ball remained with the person who’d had it previously.
Eight dolphins went through each of the two tests, separated by at least 48 hours. All the dolphins got it right in choosing the correct spot on the “where” experiments, and seven achieved success on the “who” experiments.
Kelly Jaakkola, a psychologist, says that based on their cognitive skills, dolphins are a good candidate for having episodic-like memory, and this study goes really far in showing that. She also says, “The more we look for such capabilities in non-human animals, the more species we’ll likely find them in.” She adds, “An exciting question is therefore ‘Where do we draw that line? Which animals do have it, which animals don’t, and what sort of cognitive or neurological or social characteristics do those animals share? ’ That’s going to be the fun part of the game.”
1. What does the underlined word “retrieve” in Paragraph 2 probably mean?| A.Fetch. | B.Move. | C.Throw. | D.Play. |
| A.The locations of the people involved in the tests. |
| B.The memory tasks that dolphins need to perform. |
| C.The ability of dolphins to communicate with humans. |
| D.The dolphins’ characteristics related to their memory processing. |
| A.Dolphins pass the tests as a result of training. |
| B.It is very likely that dolphins are affected by people during the tests. |
| C.Scientists will probably find episodic memory in all non-human animals. |
| D.The influence of dolphins’ familiarity with a location or a person is avoided. |
| A.Dolphins Are the Most Intelligent Animals |
| B.Dolphins May Remember Personal Experiences |
| C.Episodic Memory Is Important for Humans and Animals |
| D.A Scientific Method Is Used to Study Dolphins’ Memory |
【推荐2】Wildlife populations around the world are facing dramatic declines, according to new figures that have led environmental campaigners to call for urgent action to rescue the natural world. The 2022 Living Planet Index (LPI), produced by the Zoological Society of London (ZSL), reveals that studied populations of mammals, birds, reptiles (爬行动物) and fish have seen an average decline of 69 per cent since 1970, faster than previous predictions. The LPI tracked global biodiversity between 1970 and 2018, based on the monitoring of 31,821 populations of 5230 vertebrate (脊椎动物) species. Mark Wright of WWF says the degree of decline is destructive and continues to worsen. “We are not seeing any really positive signs that we are beginning to bend the curve of nature,” he says.

Freshwater vertebrates have been among the hardest-hit populations, with monitored populations showing an average decline of 83 per cent since 1970. The Amazon pink river dolphin, for example, has experienced a 65 per cent decline in its population between 1994 and 2016. Meanwhile, some of the most biodiverse regions of the world are seeing the steepest falls in wildlife, with the Caribbean and central and south America seeing average wildlife population declined by 94 per cent since 1970. Habitat loss and reduction is the largest driver of wildlife loss in all regions around the world, followed by species overexploitation by hunting, fishing or poaching (偷猎).
In December, governments from around the world will gather in Montreal, Canada, for the COP15 Biodiversity Framework, a much-delayed summit that aims to agree on a set of new targets intended to prevent the loss of animals, plants and habitats globally by 2030. “This is a once-in-a-decade opportunity that’s coming up,” says Robin Freeman of ZSL. He says it is vital that governments use the summit to agree on “meaningful, well measurable targets and goals”. “We need governments to take action to ensure that those goals deal with the complicated combined threats of climate change and biodiversity, in order for us to see a meaningful action,” says Freeman. But some researchers are critical of the LPI’s use of a headline figure of decline, warning it is easy to be misunderstood.
The findings don’t mean all species or populations worldwide are in decline. In fact, approximately half the populations show a stable or increasing trend, and half show a declining trend. “I think a more appropriate and useful way to look at it is to focus on specific species or populations,” says Hannah Ritchie at Our World in Data. But Wright says the LPI is a useful tool that reflects the findings of other biodiversity indicators. “All of those show they all scream there is something going really very badly wrong,” says Wright.
1. What does the underlined phrase in the first paragraph mean?| A.Loving and protecting nature. | B.Preserving the diversity of nature. |
| C.Underestimating the benefits of nature. | D.Destroying and changing nature. |
| A.the number of Amazon dolphins is on the rise |
| B.freshwater vertebrates are at risk of extinction |
| C.there are no positive measures to protect nature |
| D.some of the world’s wild animals are in decline |
| A.It makes sense to focus on a particular species. |
| B.Preventing the loss of habitats by 2030 is certain to happen. |
| C.New agreement on the prevention of habitat loss will be in vain. |
| D.The Caribbean wildlife has been well protected in recent decades. |
| A.The COP15 Biodiversity Framework |
| B.Wildlife Population Declining Sharply |
| C.Urgent Action to Save the Earth |
| D.Correct Interpretation of LPI |
【推荐3】Dogs may appear to have selective hearing when it comes to commands (指令) but research suggests they are paying attention to human chitchat.
Researchers, who arranged for headphone-wearing dogs to listen to excerpts (节录) from the novel The Little Prince, revealed their brains can tell the difference between speech and non-speech when listening to human voices, and show different responses to speech in an unfamiliar language.
The research involved 18 dogs of various ages and breeds (品种) that were trained to lie in an MRI scanner with headphones on. They were then played recordings either of humans reading excerpts from The Little Prince or those same recordings cut up into small pieces and put back together in a different order so it sounded unnatural.
The results, published in the journal NeuroImage, revealed the dogs’ brains showed a different activity pattern in the primary auditory cortex (听觉皮层) for speech compared with non-speech, with the findings similar regardless of whether the language used — Hungarian or Spanish — was familiar. Curiously, the longer the dog’s head was, the better their brain could distinguish speech from non-speech.
The team also found the activity pattern was stronger for non-speech.In humans, we typically see stronger response to speech.
The research also revealed familiar and unfamiliar languages gave rise to different responses in the secondary auditory cortex —but only for speech. That was important, said Andics, senior author of the study at Eötvös Loránd University in Hungary, as it suggested the ability to distinguish between languages was not simply down to the speakers being different.
Instead, the team said, the differences seen between languages for speech are probably down to exposure to the familiar language and a sensitivity to language-specific regularities.
“This is also supported by the observation that older dogs show the stronger discrimination between the two languages,” said Andics.
1. What did the researchers find?| A.Dogs respond to commands selectively. |
| B.Dogs have a preference for children’s novels. |
| C.Dogs can understand recorded human voices. |
| D.Dogs can distinguish between speech patterns. |
| A.The purpose of the research. |
| B.The process of the research. |
| C.The subject of the research. |
| D.The outcome of the research. |
| A.How old dogs are. |
| B.How long dogs’ heads are. |
| C.How dogs’ brains react to different speeches. |
| D.How dogs get familiar with the languages used. |
| A.They have met more different speakers. |
| B.They have been exposed to stricter training. |
| C.They possess a better sense of commitment. |
| D.They share the speakers’ environment longer. |
【推荐1】Minutes can make a difference when a life is on the line. The American Red Cross has begun offering free training and certification (合格证书) so high school students can act fast in medical emergencies.
Traumatic injuries (创伤性损伤) are the leading cause of death in Americans younger than 45. “What we are trying to do is take lessons that we learned from the battlefield — people with life-threatening injuries might have a much better chance of surviving if they can have immediate treatment,” said Craig Goolsby, a professor of Military Emergency Medicine at the Uniformed Services University. “If people can stop bleeding, particularly bleeding from arms and legs, we have a lot better chance of saving the lives of those people once they reach the hospital,” he said.
First Aid for Severe Trauma (FAST) training is available to teach high school students how to talk to each other effectively during an emergency, how to make sure that the scene is safe so additional people don’t get hurt and how to stop bleeding with a tourniquet (止血带) or direct pressure. “Just some of those really basic things that can be lifesaving before an ambulance arrives,” Goolsby said.
“My team has done a series of research studies over the past several years looking at the public’s ability to apply tourniquets or apply direct pressure. We’ve found that even very brief education, like 15 minutes of education, can have a great effect on how people will react,” Goolsby added. “They start out at a lower level of likelihood of response, get the training, and then all of a sudden, they’re more likely to respond.”
Goolsby noted that in many emergencies, average people on the street jumped in to help people who were injured. “Giving the public these tools and the courage to say ‘I can do this.’ is really important. The FAST program does that. And so we’re excited to be able to empower this next generation of Americans to take those steps,” he said.
1. What did Craig Goolsby learn from the battlefield?| A.The difficulty of surviving. | B.The types of traumatic injuries. |
| C.The importance of immediate treatment. | D.The lifesaving measures taken by medical staff. |
| A.How to move the injured to a safe place. | B.How to help the injured deal with pressure. |
| C.How to communicate effectively in emergencies. | D.How to make tourniquets using materials on hand. |
| A.Most people have little first aid experience. |
| B.Educated people are more likely to offer help. |
| C.Most people find it difficult to apply direct pressure. |
| D.People tend to help others willingly after the training. |
| A.Doubtful. | B.Positive. | C.Worried. | D.Critical. |
When considering the kind of experience that makes life better, most people first think that happiness consists in experiencing pleasure: good food, all the comforts that money can buy. We imagine the satisfaction of traveling to exciting places or being surrounded by expensive devices. If we cannot afford those goals, then we are happy to settle for a quiet evening in front of the television set with a drink close by.
Pleasure is a feeling of contentment that one achieves whenever expectations set by biological programs or by social conditioning have been met. The taste of food when we are hungry is pleasant because it reduces a physiological (生理的) imbalance. Resting in the evening while passively absorbing information from TV, with alcohol or drugs to dull the mind overexcited by the demands of work, is pleasantly relaxing. Traveling to Acapulco is pleasant because the exciting novelty (新奇) restores our sensations (感觉) exhausted by the repetitive routines of everyday life.
When people think further about what makes their lives rewarding, they tend to move beyond pleasant memories and begin to remember other events, other experiences that overlap (重叠) with pleasurable ones but fall into a category that deserves a separate name: enjoyment. Enjoyable events occur when a person has not only met some expectation or satisfied a need or a desire but also gone beyond what he or she has been programmed to do and achieved something unexpected, perhaps something even unimagined before.
Enjoyment is characterized by this forward movement: by a sense of novelty, of accomplishment. Playing a close game of tennis that stretches one’s ability is enjoyable, as is reading a book that reveals things in a new light, as is having a conversation that leads us to express ideas we didn’t know we had. Closing a contested business deal, or any piece of work well done, is enjoyable. None of these experiences may be particularly pleasurable at the time they are taking place, but afterward we think back on them and say, “That really was fun” and wish they would happen again. After an enjoyable event we know that we have changed, that our self has grown: in some respect, we have become more complex as a result of it.
Experiences that give pleasure can also give enjoyment, but the two sensations are quite different. For instance, everybody takes pleasure in eating. To enjoy food, however, is more difficult. A gourmet (美食家) enjoys eating, as does anyone who pays enough attention to a meal so as to discriminate the various sensations provided by it. As this example suggests, we can experience pleasure without any investment of psychic energy, whereas enjoyment happens only as a result of unusual investments of attention. A person can feel pleasure without any effort, but it is impossible to enjoy a tennis game, a book, or a conversation unless attention is fully concentrated on the activity.
Pleasure and Enjoyment
| Main contents | Detailed information |
| Pleasure | • Pleasure is a feeling that one achieves what one has • Things like good food, exciting travelling and a quiet rest can bring one pleasure because they can help restore one’s physiological balance, reduce one’s heavy |
| Enjoyment | • Enjoyment • Enjoyment |
| • Pleasure is often related to the comforts that money can buy, while enjoyment, more linked to one’s inner world, makes one feel rewarded and change for the • While some experiences give both pleasure and enjoyment, some enjoyable ones are not pleasurable when taking place but bring wonderful feelings • Pleasure requires no | |
| Conclusion | Enjoyment is a |
【推荐3】Big data of the human face can make a difference. Technology is rapidly catching up with the human ability to read faces. Apple’s iphone X has already used face recognition to unlock the home screen. Face recognition is becoming increasingly common in China, where it has been equipped at ATM and KFC restaurants. It is also used by shop owners to catch shoplifters.
Some universities are using face recognition technology as a means to keep track of the students’ attendance in the classrooms. Students stand in front of a screen when they walk into lecture halls. Photos taken at the screen are matched with those logged in the university’s database. It’s believed that the system is highly accurate(精确的) because it can identify students even if they change their hair or wear makeup. Students have joked that face recognition is so strict that they don’t dare to skip classes anymore. The traditional way of taking attendance is through a roll call. The new system helps to improve efficiency(效率) .
Face recognition technology has already been used in different fields in China. Police have set up face recognition scanners at busy crossroads to catch jaywalkers, whose photos will be shown on the digital screen as a warning. In the hotels of Wuzhen attractions, face scanner-equipped gates identify tourists staying in its hotels. The data collected will then serve as Entry Pass through the town’s various attractions. Tourists do not have to pay extra entrance fee. Face recognition has also been in business use in Chin A. Alipay, for example, is using its face recognition technology to help customers at a Hangzhou KFC branch order food: The camera in the KFC will check customers’ face against the ID card photos linked to their Alipay accounts.
Face recognition is expected to be used in all sorts of fields. It is going to become part of your life if it isn’t already.
1. New iPhone uses face recognition to _______.| A.catch shoplifters | B.unlock the screen |
| C.keep track of customers | D.take workers’ attendance |
| A.It can take more pictures. |
| B.It never makes any mistake. |
| C.It saves time and reduces workload. |
| D.It can identify students by their hair and makeup. |
| A.Thieves who pickpocket the walkers. |
| B.Walkers listening to music with earphones. |
| C.People who walk across the street hurriedly. |
| D.People walking across street in a dangerous way. |
| A.They can get completely free services. |
| B.They do not need paper tickets any more. |
| C.They can book hotel rooms with Entry Pass. |
| D.They are provided with electronic tour guides. |
| A.How to Prevent Crime | B.Technology Saves Time |
| C.Technology Changes Life | D.Amazing Face Recognition |
【推荐1】Astronauts traveling in space meet forms of radiation(辐射)that are uncommon on Earth. Some of this radiation has been shown to be harmful to human health. It is linked to cancers and heart problems. Yet a new American study suggests the radiation does not shorten astronauts' lives.
Researchers studied nearly 60 years of health records and other data about male astronauts from the United States. They then compared this data with information about a group of men who are in good health, richer than most Americans and receive good health care-professional athletes. The study found that neither group has higher rates of dying at a young age. In fact, both groups generally live longer than other Americans.
Astronauts are usually well-educated, earn more money and are in better physical conditions than the average Americans Some earlier research has linked being an astronaut to a lower risk of early death, the researchers noted. The findings were reported in the medical journal Occupational&Environmental Medicine.
Much of the existing research on mortality rates(死亡率) in astronauts has not yet explored the mental and physical demands of this job. There also has not been a lot of research on whether astronauts show what is known as the "healthy worker effect". This effect leads people with employment of any kind to have fewer medical problems than people who are unable to work, said Robert Reynolds.
Reynolds said, "The challenge has always been to understand if astronauts are as healthy as they would be had they been otherwise comparably employed but had never gone to space at all. To do this, we need to find a group that is comparable on several important factors."
1. How did researchers carry out their study?| A.By doing interviews. | B.By analyzing some factors. |
| C.By comparing different data. | D.By doing experiments in the lab. |
| A.All radiation is harmful to human health. |
| B.Athletes tend to be poorer than most Americans. |
| C.Healthy worker effect makes working people healthier. |
| D.Research has explored the mental and physical demands of being astronauts. |
| A.They are determined to face the challenge. |
| B.The research is almost impossible to conduct. |
| C.Several important factors hold back the research. |
| D.Astronauts are healthier than they haven’t been astronauts. |
| A.Astronauts--Healthy or Otherwise |
| B.Astronauts Are as Healthy as Athletes |
| C.Radiation Affects Astronauts' Health |
| D.Astronauts--- Well-Educated and Well-Paid |
【推荐2】More and more online shopping platforms now offer consumers a detailed look into products’ historical prices. But how does this information influence buying decisions?
To explore this question, we conducted a series of experiments with a total of more than 5,000 business school students and working adults. We measured the impact of different kinds of price shifts on people’s interest in purchasing products and identified several consistent trends:
First, when consumers saw that the price today was lower than it had been in the past, they were more likely to buy now, because the current price seemed like a good deal.
However, the picture gets more complicated when you consider the frequency of historical price shifts: In our studies, we found that if consumers were shown at least three changes in the same direction, they were likely to assume the price would continue to move in the same direction. While if they were only shown one or two changes in the same direction, they expected the price to change in the opposite direction.
So what does this mean for sellers? It may be tempting to slowly lower the price over time. However, our data shows that this can lead consumers to assume that the price will continue to fall, making them hesitant to buy. But if they just see a single price drop, they ‘re more likely to expect a reversal in the near future, pushing them to buy the product now.
Our findings can also help buyers make more informed decisions about whether and when they choose to make a purchase. As with any irrational bias (非理性的偏见), awareness of the natural tendency to expect trends to continue and single large changes to reverse can help consumers question this assumption before acting on it. Instead of letting this arbitrary (武断的) expectation guide buying decisions, consumers may benefit by doing a bit more research around the underlying factors driving price shifts. Buyers may also benefit from learning more about a product’s longer-term price history, fluctuations (波动), and typical industry-wide price ranges, to avoid being disproportionately influenced by near-term price changes. It’s also always a good idea to think about both how urgent your need for a given product is, and your own risk tolerance for a potential price increase, as this can affect whether it’s worth it for you to wait and see if the price falls.
Of course, there are countless factors that influence both consumers’ decisions around whether and when to buy and sellers’ decisions around how to price their products. But it’s important for both sides to recognize the key role that expectations play in influencing these decisions.
1. Which of the following is true about the experiment?| A.It proves that people’s interest in the product drives the purchasing behavior. |
| B.E-commerce platforms turn to it to connect with customers and boost sales. |
| C.It’s designed to figure out the purchasing decision process based on pricing. |
| D.Business school students make up the whole control group for comparison. |
A.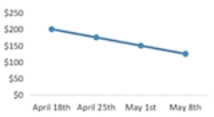 | B.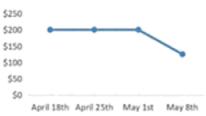 |
C.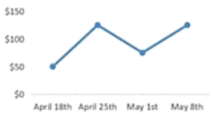 | D.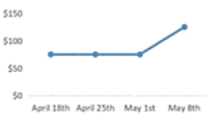 |
| A.decide on the assumptions that long-term price trend will continue |
| B.research longer-term price history, price ranges and hidden factors |
| C.put off the purchase for better deals because of the unsustainable market |
| D.cooperate with sellers while putting aside the personal risk and urgency |
| A.How do price changes influence buying decisions? |
| B.Why should products’ historical prices be shown? |
| C.When is the best time for consumers to purchase? |
| D.What do businesses need to price their products? |
【推荐3】Plans to track Australian magpies (鹊) for a study were ruined when the birds worked together to remove the devices from one another according to new research from scientists at the University of the Sunshine Coast.
The behavior marks the first evidence of cooperative “rescue” observed within the animals, the researchers stated, as, within just ten minutes of fitting the final tracker, a female magpie was seen using her bill to remove a younger bird’s harness (束具). Hours later most of the birds had been freed from their trackers with the assistance of others. Days later, even the most dominant bird had allowed another magpie to assist in removing the device , the researchers said.
“We don’t know if it was the same individual helping each other or if they shared duties, but we had never read about any other bird cooperating in this way to remove tracking devices,’’ Professor Dominique Potvin, who led the study, said.
“The birds needed to solve the problem, possibly testing at pulling and snipping at different sections of the harness with their bill. They also needed to willingly help other individuals, and accept help, ” the study found.
The study had initially been designed to test a new tracker harness that could be released and collected without having to catch the birds again. It was designed with a weak point that would release when magnetized (使磁化), dropping the harness at a feeding station used by the birds. Despite scientists believing it would require a magnet or “really good scissors” to remove the trackers, one bird was seen “snapping another bird’s harness at the only weak point,’’ suggesting it had identified the device’s flaw (缺点).
While studies have previously shown magpies are particularly intelligent and social birds , the team of scientists was surprised by how quickly they discovered a way to team up and get rid of the devices. Despite the study’s initial tracking aim failing, the team hope further research can be conducted to discover if the birds randomly discovered the flaw in the device or systematically worked at it until they found the key weak point.
1. What surprised the scientists about the magpies?| A.They helped each other out of trouble. | B.They fed each other in difficult times. |
| C.They each demonstrated their social status. | D.They each shared their duties in social life. |
| A.To test whether a new tracker harness works. |
| B.To see how the magpies ask for help . |
| C.To test the magpies ‘ level of intelligence. |
| D.To set up feeding stations for the magpies. |
| A.It has some obvious weak points on it. |
| B.It’s very sensitive to the magnetic force . |
| C.It’s inseparable once attached to the magpie. |
| D.It has to be fitted at magpies’ feeding stations. |
| A.Magpies Living in Groups Are Social Birds |
| B.Birds Able to Team Up and Solve Problems |
| C.Magpies Teach Scientists Unexpected Lesson |
| D.Birds Skillful at Discovering Flaws in Devices |
【推荐1】It was in the archives (档案室) of the Archbishop of York that Matthew Collins had a sudden insight: He was surrounded by millions of animal skins.
Another person might say they were surrounded by books and manuscripts written on parchment, which is made from skins, usually of cows and sheep. Collins, however, had been trying to make sense of animal-bone fragments from archaeological digs, and he began to think about the advantages of studying animal skins, already cut into rectangles and arranged neatly on a shelf. Archaeologists consider themselves lucky to get a few dozen samples, and here were millions of skins just sitting there.
In recent years, archaeologists and historians have awakened to the potential of ancient DNA extracted from human bones and teeth. DNA evidence has enriched — and complicated — stories of prehistoric human migrations. It has provided tantalizing clues to epidemics such as the black death. It has identified the remains of King Richard III, found under a parking lot. But Collins isn’t just interested in human remains. He’s interested in the things these humans made; the animals they bred, slaughtered, and ate; and the economies they created.
That’s why he was studying DNA from the bones of livestock — and why his lab is now at the forefront of studying DNA from objects such as parchment and beeswax. These objects can fill in gaps in the written record, revealing new aspects of historical production and trade. How much beeswax came from North Africa, for example?
Collins splits his time between Cambridge and the University of Copenhagen, and it’s hard to nail down exactly what kind of — ologist he is. He has a knack for gathering experts as diverse as parchment specialists, veterinarians, geneticists, archivists, economic historians, and protein scientists (his own background). “All I do is connect people together,” he said. “I’m just the ignorant one in the middle.”
However, it didn’t take long for his group to hit their first culture conflict. In science and archaeology, destructive sampling is at least tolerated, if not encouraged. But book conservators were not going to let people in white coats come in and cut up their books. Instead of giving up or fighting through it, Sarah Fiddyment, a postdoctoral research fellow working with Collins, shadowed conservationists for several weeks. She saw that they used white Staedtler erasers to clean the manuscripts, and wondered whether that rubbed off enough DNA to do the trick. It did; the team found a way to extract DNA and proteins from eraser pieces, a compromise that satisfied the team found a way to extract DNA and proteins from eraser pieces, a compromise that satisfied everyone. The team has since sampled 5,000 animals from parchment this way.
Collins is not the first person to think of getting DNA from parchment, but he’s been the first to do it at scale. Studying the DNA in artifacts is still a relatively new field, with many prospects that remain unexplored. But in our own modern world, we’ve already started to change the biological record, and future archaeologists will not find the same treasure of hidden information in our petroleum-laden material culture. Collins pointed out that we no longer rely as much on natural materials to create the objects we need. What might have once been leather or wood or wool is now all plastic.
1. How is Collin’s study different from the study of other archaeologists?| A.He studies human skins and bones. |
| B.He is the first person to study animal skins. |
| C.He studies objects related to humans and their lives. |
| D.His study can provide clues to previous epidemics. |
| A.his major doesn’t help his research |
| B.he can’t connect experts of different fields |
| C.he finds it hard to identify what kind of — ologist he is |
| D.his study covers a wide range of subjects beyond his knowledge |
| A.Destructive sampling is not allowed in the field of science and archeology. |
| B.Collin made a compromise by only studying copies of books made of animal skins. |
| C.Book protectors were opposed to Collin’s study because his group tracked them for several weeks. |
| D.It is difficult for future archeologists to study what society is like today due to plastic objects. |
| A.A new discovery in archaeology |
| B.A lab discovering DNA in old books |
| C.Archaeology on animals seeing a breakthrough |
| D.Collin’s contributions to the identification of old books |
【推荐2】China is using travel as an important tool to help strengthen its economy.At the recent First World Conference on Tourism a Chinese official spoke about the government’s plan for using tourists and the money they spend. The head of China’s National Tourism Administration, Li Jinzao, said that China plans to send 150million travelers along what he called the “One Belt, One Road”. In the next five years, these tourists are expected to spend $200 billion, he said. This spending estimate(估计) is likely to raise expectations among countries along the ancient Silk Road, which links China to its neighbors.
China has reasons to feel it can use tourism to influence the foreign policy. Governments across the world are changing their immigration rules to welcome the growing numbers of Chinese tourists. Chinese citizens are now going to places where in the past Chinese rarely went. Marketing expert Michel Gutsatz said that among Chinese travelers, South Korea and Thailand are popular destinations. Outside of Asia, he said, Chinese are more likely to visit Europe than North America. These changes, he said, are the result of young Chinese travelers, who spend more and travel independently.
Spending by Chinese tourists has lifted the economies of several Asian countries, including Thailand, Malaysia and Vietnam. It is expected that the number of Chinese traveling overseas to reach 242 million by 2024. In a single year, that number would be equal to the total number of tourists received by Germany, Iran, Indonesia and Egypt combined
China is now the biggest business travel market in the world, The Global Business Travel Association(GBTA) recently announced that China has overtaken the United States in business travel. Chinese spent just over$291 billion on business travel last year. Americans spent just over $290 billion. This year, GBTA predicts that the Chinese business travel market will grow over 10 percent, while the Us business travel market will grow less than 2 percent.
1. We can infer from the passage that foreign countries ________.| A.welcome Chinese immigration to their countries |
| B.take Chinese tourists as their supporting power |
| C.make policies to ban Chinese tourists |
| D.rely entirely on Chinese tourists to increase their economy |
| A.They want to visit the places they rarely visited in the past. |
| B.They spend more money and travel by their own. |
| C.They want to travel to farther places than just nearby countries. |
| D.They think Europe is a more fashionable and poplar destination. |
| A.Chinese tourists make great contribution to their economy. |
| B.Chinese tourists can widen their business travel market. |
| C.The number of Chinese tourists is larger than that of European tourists. |
| D.They have greater expectations from Chinese tourists |
| A.China’s “One Belt, One Road” plan |
| B.Foreign Countries Change Their Policies to Attract Chinese Tourists |
| C.China Has the Biggest Business Travel Market |
| D.Tourism Helps China Strengthen Its Economy |
【推荐3】The animal kingdom is full of beautiful and attractive creatures, and it is inviting to purchase exotic animals and call them pets. But undomesticated(未驯化的) pets may affect the health and safety of both the animals and the people who keep them.
The umbrella cockatoo, for instance, is a type of parrot, which can live up to seventy years. It is often purchased as an exotic pet. It requires a very large living place and a great deal of attention. When its specific needs are unmet, the bird commonly bites itself or becomes aggressive. Similarly, the ball python one of the most popular pet snakes, requires special conditions to survive. Like the umbrella cockatoo, the snake's long lifespan—up to forty years—presents serious practical challenges to any owner, no matter how devoted.
Exotic pet owners are most likely identified as animal lovers who purchased their animals in order to feel a deep connection to the natural world. However, the mere ownership of such an animal means it's probable that the person participated in the illegal trade. This trade—the capture and sale of wild animals——is often cruel to species. Countless animals suffer and die each year.
The problems continue when exotic pets are sold to non-professional owners. When they find they cannot care for them, owners take their exotic pets into the wild and abandon them, as proved by the case of Burmese pythons in Florida. This non-native species multiplied quickly seriously threatening the Florida ecosystem. Also , exotic pets pose a danger to their owners: some emerging infectious diseases, which thousands of people per year are stricken with, and especially occurred in children.
Wild animals are undoubtedly attracting, but they should be admired in their own natural environments. Penning animals as exotic pets harms their quality of life. Pet ownership of any kind is a serious responsibility, and that's why animal lovers should choose domesticated animals that will Boom under the care of humans.
1. What can we infer about exotic pets in paragraph 2?| A.They can live longest in the animal kingdom. |
| B.They need professional care from the owner. |
| C.They require special training from their owner. |
| D.They can’t have a satisfying life under human care. |
| A.To get high income. |
| B.To build a bond with nature, |
| C.To help prevent illegal pet trades. |
| D.To make exotic pets' life comfortable. |
| A.Improving the native ecosystem. |
| B.Increasing the number of rare species. |
| C.Losing control of illegal wildlife trading. |
| D.Putting humans and exotic wildlife at risk. |
| A.Wild animals are more dangerous than ordinary pets. |
| B.It's inappropriate to keep undomesticated exotic pets. |
| C.Exotic pets should be kept in better conditions. |
| D.Rules of the exotic pet trade should be updated. |



