Microsoft announced this week that its facial-recognition system is now more accurate in identifying people of color, touting (吹嘘)its progress at tackling one of the technology’s biggest biases (偏见).
But critics, citing Microsoft’s work with Immigration and Customs Enforcement, quickly seized on how that improved technology might be used. The agency contracts with Microsoft for cloud-computing tools that the tech giant says is largely limited to office work but can also include face recognition.
Columbia University professor Alondra Nelson tweeted, “We must stop confusing ‘inclusion’ in more ‘diverse’ surveillance (监管)systems with justice and equality.”
Facial-recognition systems more often misidentify people of color because of a long-running data problem: The massive sets of facial images they train on skew heavily toward white men. A Massachusetts Institute of Technology study this year of the face-recognition systems designed by Microsoft, IBM and the China-based Face++ found that facial-recognition systems consistently giving the wrong gender for famous women of color including Oprah Winfrey, Serena Williams, Michelle Obama and Shirley Chisholm, the first black female member of Congress.
The companies have responded in recent months by pouring many more photos into the mix, hoping to train the systems to better tell the differences among more than just white faces. IBM said Wednesday it used 1 million facial images, taken from the photo-sharing site Flickr, to build the “world’s largest facial data-set” which it will release publicly for other companies to use.
IBM and Microsoft say that allowed its systems to recognize gender and skin tone with much more precision. Microsoft said its improved system reduced the error rates for darker-skinned men and women by “up to 20 times,” and reduced error rates for all women by nine times.
Those improvements were heralded(宣布)by some for taking aim at the prejudices in a rapidly spreading technology, including potentially reducing the kinds of false positives that could lead police officers misidentify a criminal suspect.
But others suggested that the technology's increasing accuracy could also make it more marketable. The system should be accurate, “but that’s just the beginning, not the end, of their ethical obligation,” said David Robinson, managing director of the think tank Upturn.
At the center of that debate is Microsoft, whose multimillion-dollar contracts with ICE came under fire amid the agency’s separation of migrant parents and children at the Mexican border.
In an open letter to Microsoft chief executive Satya Nadella urging the company to cancel that contract, Microsoft workers pointed to a company blog post in January that said Azure Government would help ICE “accelerate recognition and identification.” “We believe that Microsoft must take an ethical stand, and put children and families above profits,” the letter said.
A Microsoft spokesman, pointing to a statement last week from Nadella, said the company’s “current cloud engagement” with ICE supports relatively anodyne(温和的)office work such as “mail, calendar, massaging and document management workloads.” The company said in a statement that its facial-recognition improvements are “part of our going work to address the industry-wide and societal issues on bias.”
Criticism of face recognition will probably expand as the technology finds its way into more arenas, including airports, stores and schools. The Orlando police department said this week that it would not renew its use of Amazon. com’s Rekognition system.
Companies ”have to acknowledge their moral involvement in the downstream use of their technology,”
Robinson said. “The impulse is that they’re going to put a product out there and wash their hands of the consequences. That’s unacceptable.”
1. What is “one of the technology’s biggest biases” in Paragraph 1?| A.Class bias. | B.Regional difference. |
| C.Professional prejudice. | D.Racial discrimination. |
| A.Justice and equality have been truly achieved. |
| B.It is due to the expansion of the photo database. |
| C.It has already solved all the social issues on biases. |
| D.The separation of immigrant parents from their children can be avoided. |
| A.Data problems. | B.The market value. |
| C.The application field. | D.A moral issue |
| A.Skeptical. | B.Approval. |
| C.Optimistic. | D.Neutral. |
| A.companies had better hide from responsibilities |
| B.companies deny problems with its technical process |
| C.companies should not launch new products on impulse |
| D.companies should be responsible for the new product and the consequences |
| A.The wide use of Microsoft system | B.Fears of facial-recognition technology |
| C.The improvement of Microsoft system | D.Failure of recognizing black women |
相似题推荐
【推荐1】Artificial Intelligence (AI) is making it possible for companies to monitor workers’ behavior in great detail and in real time. Start to slack off (懈怠), and AI could talk to your boss.
One company offering such services is London-based start-up Status Today. Its AI platform relies on a regular supply of employee data, including everything from the files you access to when you use a key card. From this, it builds a picture of how employees normally function and signals any unusual performance. The idea is to spot when someone might become a security risk by doing something different from their usual behavioral patterns. “All of this gives us fingerprint of a user, so if we think the fingerprint doesn’t match, we raise a warning”, says Mircea Dumitrescu, the company’s chief technology officer.
The system also aims to catch employee actions that could accidentally cause a security breach (漏洞), like opening malware (恶意软件).“We’re not monitoring if your computer has a virus.” says Dumitrescu. “We’re monitoring human behaviors.”
But catching the security breach means monitoring everyone, and the AI can also be used to track employee productivity. “It seems like they are just using the reputation of AI to give an air of lawfulness to old-fashioned workplace surveillance (监视),” says Javier Ruiz Diaz of digital campaigning organization the Open Rights Group. “You have a right to privacy and you shouldn’t be expected to give that up at work.”
Exactly how companies use the system will be up to them, but it’s hard to shake the picture of an AI constantly looking over employees’ shoulders. “It will bother people, and that could be counterproductive if it affects their behavior,” says Paul Bemal at the University of East Anglia.
Phil Legg at the University of the West of England says it will never catch every security risk. “If people know they’re being monitored, they can change their behavior,” he says.
1. According to the text, AI monitors employees by ________.| A.taking pictures of them | B.getting access to their data |
| C.signaling their usual performance | D.catching their actions |
| A.Doubtful. | B.Supportive. |
| C.Uncaring. | D.Negative. |
| A.Security breach. | B.Employees’ productivity. |
| C.The right to privacy. | D.Workplace surveillance. |
| A.it is too risky to be used at work |
| B.it will affect employees’ emotions |
| C.it may not be so effective as expected |
| D.it will encourage employee, productivity |
【推荐2】Before the age of the smartphone, photographers had to learn how to use high-tech cameras and photographic techniques. Today, with the huge range of camera apps on our smartphones, we’re all good amateur photographers, since the quality of smartphone images now nearly equals that of digital cameras.
The new ease of photography has given us a tremendous appetite for capturing the magical and the ordinary. We are obsessed with documenting everyday moments, whether it’s a shot of our breakfast, our cat or the cat’s breakfast. Even photo journalists are experimenting with mobile phones because their near invisibility makes it easier to capture unguarded moments.
In the past, magazines published unforgettable photos of important people and global events that captured our imaginations. These photos had the power to change public opinion and even the course of history. But if there are fewer memorable images today, it’s not because there are fewer good images. It’s because there are so many, and no one image gets to be special for long.
As people everywhere embrace photography and the media make use of citizen journalists, professional standards appear to be shifting. Before digital images, most people trusted photographs to accurately reflect reality. Today, images can be altered in ways the naked eye might never notice. Photojournalists are trained to accurately represent what they witness. Yet any image can be altered to create an “improved” picture of reality. The average viewer is left with no way to assess the accuracy of an image except through trust in a news organization or photographer.
The question of the accuracy of images gets even trickier when photojournalists start experimenting with camera apps-- like Hipstamatic or Instagram --- which encourage the use of filters (滤镜). Images can be colored, brightened, faded, and scratched to make photographs more artistic, or to give them an antique look. Photographers using camera apps to cover wars and conflicts have created powerful images--- but also controversy. Critics worry that antique-looking photographs romanticize war, while distancing us from those who fight in them.
Yet photography has always been more subjective than we assume. Each picture is a result of a series of decisions-- where to stand, what lens to use, what to leave in and what to leave out of the frame. Does altering photographs with camera app filters make them less true? There’s something powerful and exciting about the experiment the digital age has forced upon us. These new tools make it easier to tell our own stories--- and they give others the power to do the same. Many members of the media get stuck on the same stories, focusing on elections, governments, wars, and disasters, and in the process, miss out on the less dramatic images of daily life that can be as revealing.
Who knows? Our obsession with documentation and constantly being connected could lead to a dramatic change in our way of being. Perhaps we are witnessing the development of a universal visual language, one that could change the way we relate to each other and the world. Of course, as with any language, there will be those who produce poetry and those who make shopping lists.
1. According to the author, there are fewer memorable photographs today because_________.| A.the quality of many images is still poor |
| B.there are so many good images these days |
| C.traditional media refuse to allow amateur photos |
| D.most images are not appealing to a global audience |
| A.indicate it’s a word cited from another source |
| B.stress that the picture of reality is greatly improved |
| C.draw audience attention to a word worth considering |
| D.show it’s arguable whether the picture is truly improved |
| A.The daily life pictures are very expressive themselves. |
| B.Photographs of the digital age are more subjective than before. |
| C.Photos altered by filters of camera apps are too subjective to be true. |
| D.Many members of the media value daily life images over major social events. |
| A.Camera Apps Bury Authenticity |
| B.Photography Redefined: A Visual Language |
| C.Smartphone: Killer of Professional Photography |
| D.The Shifting Standards of Professional Photography |
【推荐3】Both misinformation, which includes honest mistakes, and disinformation, which involves an intention to mislead, have had a growing impact on teenage students over the past 20 years. One tool that schools can use to deal with this problem is called media literacy education. The idea is to teach teenage students how to evaluate and think critically about the messages they receive. Yet there is profound disagreement about what to teach.
Some approaches teach students to distinguish the quality of the information in part by learning how responsible journalism works. Yet some scholars argue that these methods overstate journalism and do little to cultivate critical thinking skills. Other approaches teach students methods for evaluating the credibility of news and information sources, in part by determining the incentive of those sources. They teach students to ask: What encouraged them to create it and why? But even if these approaches teach students specific skills well, some experts argue that determining credibility of the news is just the first step. Once students figure out if it’s true or false, what is the other assessment and the other analysis they need to do?
Worse still, some approaches to media literacy education not only don’t work but might actually backfire by increasing students’ skepticism about the way the media work. Students may begin to read all kinds of immoral motives into everything. It is good to educate students to challenge their assumptions, but it’s very easy for students to go from healthy critical thinking to unhealthy skepticism and the idea that everyone is lying all the time.
To avoid these potential problems, broad approaches that help students develop mindsets in which they become comfortable with uncertainty are in need. According to educational psychologist William Perry of Harvard University, students go through various stages of learning. First, children are black-and-white thinkers—they think there are right answers and wrong answers. Then they develop into relativists, realizing that knowledge can be contextual. This stage is the one where people can come to believe there is no truth. With media literacy education, the aim is to get students to the next level—that place where they can start to see and appreciate the fact that the world is messy, and that’s okay. They have these fundamental approaches to gathering knowledge that they can accept, but they still value uncertainty.
Schools still have a long way to go before they get there, though. Many more studies will be needed for researchers to reach a comprehensive understanding of what works and what doesn’t over the long term. “Education scholars need to take an ambitious step forward,” says Howard Schneider, director of the Center for News Literacy at Stony Brook University.
1. As for media literacy education, what is the author’s major concern?| A.How to achieve its goal. | B.How to measure its progress. |
| C.How to avoid its side effects. | D.How to promote its importance. |
| A.Importance. | B.Variety. | C.Motivation. | D.Benefit. |
| A.compare different types of thinking |
| B.evaluate students’ mind development |
| C.explain a theory of educational psychology |
| D.stress the need to raise students’ thinking levels |
| A.Media Literacy Education: Much Still Remains |
| B.Media Literacy Education: Schools Are to Blame |
| C.Media Literacy Education: A Way to Identify False Information |
| D.Media Literacy Education: A Tool for Testing Critical Thinking |
【推荐1】“Give us back our stolen hour!” Britons demanded as they objected to the introduction of Daylight Saving Time(DST) in 1916. The idea of setting the clocks to move an hour of daylight from the morning to the evening during summer has been controversial throughout its history. People have argued that the practice saves energy, reduces crime, and prevents traffic accidents. Others are not so convinced, and studies conducted over the past decade have shown mixed results.
The idea was first put into operation in Germany during World War I(19141918) in an attempt to reduce coal supply during wartime. Britain soon followed with its own Summer Time but so did confusion and chaos, with some institutions following the changes and some simply ignoring them. One writer felt angry at the laws in a more poetic manner, expressing his dislike for being forced to favor the sun over the moon.
Despite the early controversy, 82 countries currently use DST. The United States moves its clocks forward an hour at 2 a.m. on the second Sunday in March and back an hour on the first Sunday in November. Some states, however, still do not apply DST, and in the past even some areas within individual states refused to observe DST while the rest of the state did.
It was originally thought that DST would reduce energy consumption as people would use less electric lighting in the evening due to the increased hours of daylight. However, recent studies have suggested that this benefit has been canceled out by the increased use of home air conditioners, which people use for longer on long summer evenings.
Brighter evenings have reduced the number of traffic accidents in countries which observe DST, but studies have also noticed a spike(剧增) in the number of accidents during the week after the clocks change, possibly due to the sudden interruption of people's sleeping patterns.
One certain good thing to come out of DST, however, happened in 1999, when a group of West Bank terrorists(on DST) delivered bombs to a cell in Israel(not on DST) but ignored the time difference when setting the timers for their bombs. The bombs went off one hour earlier than planned, killing three terrorists instead of the intended civilians.
1. Which of the following statements about DST is TRUE?| A.It was introduced from Germany to Britain after World War I. |
| B.It can help save energy and reduce traffic accidents. |
| C.It forces people to appreciate the sun more than the moon. |
| D.It probably affects people's sleeping patterns. |
| A.7:00 am | B.7:00 pm |
| C.8:00 pm | D.9:00 pm |
| A.an advertisement | B.an annual report |
| C.an informative essay | D.a persuasive writing |
【推荐2】Lia Thomas, a student at the University of Pennsylvania, is an excellent swimmer. She often beats her rivals by tens of seconds, breaking records. Her success is based on three things. One is natural talent. Another is persistent training. And the third is biology.
For although she identifies as a woman,Ms Thomas was born male.Since humans cannot change their sex (unlike their self-identified gender),she remains that way.On the eve of her biggest competition, Ms Thomas finds herself at the centre of the bad-tempered debate about whether trans women-males who identify as women-should compete in women’s sports.That,in turn,is part of a broader argument: should brute (纯粹的) biological facts sometimes override people’s deeply held feelings about their identities?
This newspaper believes it is almost always unfair to allow transgender women to compete in women’s sports.The advantages bestowed by male puberty (青春期) are so big that no amount of training or talent can enable female athletes to overcome them.Florence Griffith Joyner’s 100-metres world sprinting record has stood for three decades.A male matching it would not even make it to the Olympics, let alone the final.In 2016,at an American event for high-schoolers, four of the eight boys in the 100-metres final ran faster.
Much of the male advantage is granted by testosterone (睾丸素), a potent anabolic steroid whose levels rise sharply in male puberty.For many years,many sporting bodies, following the lead of the International Olympic Committee, hoped to deal with the issue by allowing trans women to compete in women’s events provided they took testosterone-suppressing drugs.But the science suggests this does not level the playing field.Suppressing testosterone in adults, it seems, does little to undo the advantages granted by a male adolescence.
Sports must therefore choose between inclusion and fairness; and they should choose fair play. That does not mean, as is sometimes claimed, that trans women would be barred from all sport.One way to make that clear would be to replace the “men’s” and “women’s” categories with “open” and “female” ones.The first would be open to all comers.The second would be restricted on the basis of biology.
Sport is public, and results can be measured objectively. That means the argument that the material facts of biology should sometimes outrank a person’s subjective sense of identity is easier to make. But bias exists, as a Republican bill in Florida to restrict “instruction” in schools about gender identity or sexual orientation makes plain.
That should be resisted. Most of the time,it costs little or nothing to respect people’s choices about how they wish to present themselves.In the rare cases where rights clash (不相容), society must weigh the balance sensitively and with open eyes.
1. The author mentions Joyner’s 100-metres world sprinting record to show that ________.| A.most female athletes can’t rival trans women athletes |
| B.male puberty is the best time for sports competition |
| C.it is unfair for Ms Thomas to compete in women’s sports |
| D.this record can’t make a male reach the threshold of the Olympics |
| A.bill | B.bias | C.instruction | D.identity |
| A.disagreeable | B.open-minded | C.sympathetic | D.conservative |
| A.Inclusion and Fairness | B.Respect People’s Choices |
| C.“Open” and “Female” in Sports | D.Biology Matters A Great Deal |
【推荐3】Kids nowadays are growing up “connected”, learning to use technology at a surprising speed. Technology is a regular part of school now! Kids as young as Kindergarten are using smartboards, IPads, and computers to complete tasks in the classroom. Older children rely on the Internet for research, getting homework, sending work to teachers, and even accessing( 获得) textbooks. In fact, today’s kids have been given the name “digital(数字)natives” because they are facing technology almost from birth, so new things have never been a greater challenge in the hands of our children. The Internet,Facebook, iPods, pictures and texting on cell phones and all of these are the ways kids communicate today. They have become a central part of their lives. It allows them a private life that most of us know very little about.
Kids just don’t think about the results of the new world of social networking and text messaging. They don’t think that it is dangerous to send a photo of a particular person to a foolish person, who might send it to some friends that may send it to a hundred others and the next thing you know, it’s on many Facebook sites and all over the Internet forever. They don’t think that way because they don’t have the life experience that we do. We have to help them.
The key to knowing how they manage this privacy(隐私) is our “connection” to them. How closely do we connect with our kids and pay attention to what they’re doing? And how often do we talk to our children... and really listen to them? If they believe in us and know that we will be there for them, they are more likely to follow our advice. If we talk openly about what we believe in, what we stand for, those values will become their own before long.
1. What is the author’s opinion about children?| A.They are good at accepting modern things. | B.They are well understood by their parents. |
| C.They almost like to surf on the Facebook. | D.They know the Internet dangers well. |
| A.Kids. | B.Adults. | C.Internet users. | D.Internet teachers. |
| A.They only understand their own private lives. | B.They are badly influenced by new things. |
| C.They do not have life experience. | D.They don’t depend on their parents. |
| A.When they are surfing on the Internet. | B.When they meet some dangerous situations. |
| C.When parents believe in what they are doing. | D.When parents communicate with them deeply. |
【推荐1】Kids nowadays are growing up “connected”, learning to use technology at a surprising speed. Technology is a regular part of school now! Kids as young as Kindergarten are using smartboards, IPads, and computers to complete tasks in the classroom. Older children rely on the Internet for research, getting homework, sending work to teachers, and even accessing( 获得) textbooks. In fact, today’s kids have been given the name “digital(数字)natives” because they are facing technology almost from birth, so new things have never been a greater challenge in the hands of our children. The Internet,Facebook, iPods, pictures and texting on cell phones and all of these are the ways kids communicate today. They have become a central part of their lives. It allows them a private life that most of us know very little about.
Kids just don’t think about the results of the new world of social networking and text messaging. They don’t think that it is dangerous to send a photo of a particular person to a foolish person, who might send it to some friends that may send it to a hundred others and the next thing you know, it’s on many Facebook sites and all over the Internet forever. They don’t think that way because they don’t have the life experience that we do. We have to help them.
The key to knowing how they manage this privacy(隐私) is our “connection” to them. How closely do we connect with our kids and pay attention to what they’re doing? And how often do we talk to our children... and really listen to them? If they believe in us and know that we will be there for them, they are more likely to follow our advice. If we talk openly about what we believe in, what we stand for, those values will become their own before long.
1. What is the author’s opinion about children?| A.They are good at accepting modern things. | B.They are well understood by their parents. |
| C.They almost like to surf on the Facebook. | D.They know the Internet dangers well. |
| A.Kids. | B.Adults. | C.Internet users. | D.Internet teachers. |
| A.They only understand their own private lives. | B.They are badly influenced by new things. |
| C.They do not have life experience. | D.They don’t depend on their parents. |
| A.When they are surfing on the Internet. | B.When they meet some dangerous situations. |
| C.When parents believe in what they are doing. | D.When parents communicate with them deeply. |
【推荐2】Nineteen Eighty-Four, a dystopian novel by George Orwell, was set in a totalitarian state where even the language they use is controlled. Adjectives are forbidden and instead they use phrases such as “ungood”, “plus good” and “double plus good” to express emotions. As I first read this I thought how impossible it would be in our society to have such vocabulary. However, the more I thought about it, the more I realised in its own way it's already happening. I type messages to my friends and alongside each is the obligatory (惯用的) emoji. I often use them to emphasise something, or to not seem too serious, or because this specific GIF conveys my emotions much better than I ever could using just words. And I wonder, with our too much use of emojis, are we losing the beauty and diversity of our vocabulary?
English has the largest vocabulary in the world, with over one million words, but who's to say what it'll be like in the future? Perhaps we will have a shorter language, full of saying “cry face” if something sad happens or using abbreviations like LOL (laugh out loud) or BRB (be right back) instead of saying the full phrase. So does this mean our vocabulary will shrink? Is it the start of an exciting new era? Will they look back on us in the future and say this is where it all began—the new language? Or is this a classic case of the older generations saying, “Things weren't like that when I was younger. We didn't use emoticons to show our emotions?”
Yet when you look back over time, the power of image has always been there. Even in the prehistoric era they used imagery to communicate, and what's even more incredible is that we are able to analyse those drawings and understand the meaning of them thousands of years later. Pictures have the ability to go beyond the usual limits of time and language. Images, be it cave paintings or emojis, allow us to convey a message that's not restrictive but rather universal.
1. Why does the author mention Nineteen Eight Four?| A.To introduce the topic. | B.To show an example. |
| C.To give the reason. | D.To describe a phenomenon |
| A.To reduce the use of words. | B.To save time of typing. |
| C.To express naturally and casually. | D.To make fun of friends. |
| A.Disappear. | B.Lower. |
| C.Reform. | D.Change. |
| A.We can recognise the pictures' time period with technology. |
| B.We have kept the same vocabulary since the prehistoric era. |
| C.Pictures is an only way to record history. |
| D.Pictures can express human feelings accurately and vividly. |
【推荐3】Koko the gorilla knew over 1,000 signs based on American Sign Language, and used them to do everything from asking for food to joking around. Her trainer and long-term companion, Penny Patterson, thought Koko went further still, signing in novel ways and showing complex emotions. According to Ms Patterson, when a cat that Koko loved was killed in an accident, Koko signed: “Cat, cry, have-sorry, Koko-love.” When Koko died last month, some of her obituaries (讣告) mourned the gorilla who had “mastered American sign language.”
Then came the backlash, from linguists and experts in sign languages. Sign languages have complex grammars, equivalent to spoken tongues in expressiveness. Koko’s ability, it was pointed out, fell well short of a fluent human signer. Moreover, Ms Patterson was her interpreter, a role that invited the question of how much she was inferring what Koko “must have meant,” and explaining away random signs. It was hard to be sure: Ms Patterson preferred speaking to journalists over sharing her video and raw data about Koko with fellow researchers.
There is no doubt that animals communicate. Animals from one region can share sounds that differ from groups in another, leading researchers to talk of animal “dialects.” Then there are the remarkable achievements of Koko and her primate predecessors, including a chimp delightfully named Nim Chimpsky. Yet there is an important distinction between communication and language. Take the misleading term “body language.” It is sometimes claimed that words convey just 7% of meaning, and that body language and tone of voice do the rest. This wildly overstretches an old study which found that most emotional messaging — as opposed to the propositional kind — comes from tone and body language, especially when a neutral word such as “maybe” was used. But try conveying a fact like “It will rain on Tuesday” with your eyebrows, and the difference becomes clear. Language allows for clear statements, questions and commands.
Nim Chimpsky’s near-namesake, Noam Chomsky, has argued that people have a kind of “universal grammar”, and that all humankind’s languages are mere variations on a theme. Mr Chomsky has changed his mind repeatedly on what constitutes the core of human language, but one obvious candidate is syntax — rules, not just words, which allow the construction of a huge variety of meaningful utterances (所说的话). This capacity may even be infinite. Any statement in English, for example, can be made longer by adding “He said that …” at the beginning. This property is called recursion: a simple statement (“It’s cold”) is embedded in a more complicated one (“He said that it’s cold”). Human syntax also allows for hypotheticals (“If she hadn’t arrived …”), talking precisely about events distant from the present, and so much more.
That gorillas lack syntax should not blind humans to their magnificence. But the fact that Koko could communicate should not mislead observers into thinking she possessed language.
1. Which statement about KOKO the gorilla is true?| A.Koko’s ability was similar to a fluent human signer. |
| B.Koko could ask for food using sign language. |
| C.Koko was able to show complex feelings using sign language. |
| D.Koko was killed in an accident. |
| A.approval | B.bias | C.opposition | D.evidence |
| A.Koko was not as expressive as a human signer |
| B.Koko seldom needed an interpreter |
| C.Koko was able to communicate with journalists |
| D.Koko failed to speak several animal “dialects” |
| A.Humans can express past events using language while apes cannot. |
| B.Tone and body language play a dominant role in human communication. |
| C.Words enable humans to convey clear meanings. |
| D.Gorillas are still magnificent in terms of their ability to communicate. |
| A.Nim Chimpsky and Noam Chomsky — Who Has the Upper Hand? |
| B.Syntax — What Separates Humans and Apes. |
| C.Koko the Gorilla — A Magnificent Communicator. |
| D.Great Apes — Language and Communication Are Not the Same Thing. |
【推荐1】Many small-business owners watched recent revelations about Facebook with mixed emotions. Like most Americans, they were surprised to discover how much information the social media giant collected on its users. But when it comes to small business, Facebook is a transformative advertising platform for small businesses, not easy to replace.
Let's say you own a small seafood restaurant, and Tuesday nights are $1 oyster (牡蛎)nights. Traditional advertising methods cost a lot and must be planned long in advance, and ifs hit-or-miss as to whether you actually get in front of oyster eaters. With Facebook, on Tuesday morning, with a few clicks, you can target Facebook users in your Zip code who love oysters and eating out (and are over age 21, so they can buy drinks, which is why you have $1 oyster nights). And you can do this for as little as S20.
In my work with small businesses for more than 25 years, I've never seen a more effective method of micro-targeting prospects. Though Facebook is an effective tool for small-business, advertising does not justify (证明合理)the company's collecting vast amounts of data or allowing users' data to be invaded.
"Our primary concern was people's experience on Facebook," said Dan Levy, Facebook's Vice President. "Our teams have also been speaking to small businesses, and they want to make sure we're addressing the situation, and we are."
One concern small businesses want Facebook to address is protecting their uploaded lists. No one wants their customers' information misused or accessed by others, especially competitors.
Small-business owners are rightfully concerned about privacy. They don't want Facebook to know everything about them, and they don't want their customer lists to be let out to others.
But small businesses don't want to lose this effective advertising medium, either. Most Facebook ads are not invasive or offensive. And many receivers may actually benefit from receiving highly targeted ads—after all, those oyster lovers like learning about Tuesday night— $1 oyster night.
1. How does the author explain Facebook's function in Paragraph 2?| A.By performing an experiment. | B.By leading a survey・ |
| C.By analyzing the data・ | D.By giving an example. |
| A.Objective. | B.Supportive. |
| C.Doubtful | D.Respectful. |
| A.What people experience on Facebook. |
| B.That Facebook updates the lists constantly. |
| C.That their competitors benefit more from Facebook. |
| D.That Facebook will give away their customer lists. |
| A.Facebook is benefiting small businesses |
| B.Facebook, a mixed bag for small businesses |
| C.Facebook is protecting customers5 privacy |
| D.Facebook, a powerful advertisement tool |
【推荐2】Imagine looking at a view of mountaintops and wondering about the name of each peak. Suddenly, above each mountaintop, a name appears on the sky. The words are not written in smoke by skywriting planes. The words are actually not in the sky at all. They come from tiny computers in contact lenses (隐形眼镜).
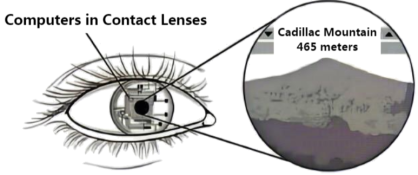
Computers have become smaller and smaller over the decades. The first computers filled houses. Transistors (晶体管) and then chips allowed computers to become small enough to fit on a desktop, then a laptop, and finally a phone. When experimenting with further contraction in size, developers often have to deal with the limits of human eyesight, which control how small the computers can be and still present visible information.
One new solution employs microprojectors (微型投影机) to create a readable display (显示) for tiny computers. These machines project computer information onto any surface. Though an impressive breakthrough, there are potential problems. Such public displays can lead to privacy concerns; most people do not want their information displayed on a wall for everyone to see. Besides, these projectors are extremely expensive, and their screens give users headaches.
Babak Parviz, a researcher at the University of Washington, created another solution: inventing a screen visible only to a person wearing a contact lens. Parviz created a computer in a contact lens that uses the wearer’s field of vision as the display. To create the display, Parviz took ordinary soft contact lenses with a wirelessly controlled system. At some point, Parviz says, it will be possible to connect the lens to a remote personal computer device such as a cellphone or a laptop. By looking in a certain direction, the wearer sends the computer visual information about what he or she sees. The device then uses this information to point out the names of peaks.
These contact lenses are inserted and removed in much the same way as ordinary contact lenses. In addition, the computers in the lenses won’t block the wearer’s sight at all. Although now the computers are not on lenses treating eyesight problems, Parviz hopes that someday the technology will progress to that level.
1. The contact lenses in the text can ________.| A.treat eyesight problems | B.offer beautiful views of nature |
| C.project information on wall surface | D.show information about what wearers see |
| A.expansion | B.spread |
| C.reduction | D.revolution |
| A.put people’s privacy at risk | B.save computer information |
| C.cause serious illnesses | D.support users’ needs |
| A.saving users’ expenses | B.reducing computers’ size |
| C.limiting the field of vision | D.guarding remote computers |
| A.Tiny Computers, Amazing Sights | B.Smaller Lenses, Closer Views |
| C.Progress towards Clearness | D.Road to the Small World |
【推荐3】As Shanghai prepared to introduce mandatory(强制的) garbage sorting on July 1, games and toys that examined fun ways to spread information about the garbage sorting were to encourage younger people to take action.
A 15-second video of a game went on Chinese social media. In the video, players wearing VR(虚拟) headsets saw four different types of trash can in front of them, and had to throw different types of garbage into the right buckets(桶) to get points. Although it was not the only VR game in the place, visitors lined up around the booth to explore it because of the garbage-sorting theme.
“As a Shanghai, I am in great need of this game. Maybe I won’t need to check how to categorize(分类) each piece of garbage on my phone while going through all my garbage every day if I play this game more often, ” said ZhouZhou, a young Shanghai. But some social media users in Shanghai have complained about the difficulty of sorting different types of garbage.
Wu Xia, founder and CEO of VitrellaCore, the company that created the game, said the idea was to provide an interesting way of learning about garbage sorting. “It’s simple and easy to understand. People can practice sorting garbage without actually going through their trash, and it is a more effective method than using paper materials when training volunteers,” Wu said.
1. What is the purpose of the VR game?| A.Just for fun. |
| B.Teach students to sort garbage. |
| C.Do exercise. |
| D.Keep fit. |
| A.It is too hard to sort garbage. |
| B.There are too many people lining up. |
| C.The VR game should be more interesting. |
| D.There are more ways to use paper materials. |
| A.successful | B.interesting | C.traditional | D.disappointing |
| A.Young people like VR games more. |
| B.Shanghai performs mandatory garbage sorting. |
| C.Games were used to help young people sort garbage. |
| D.Learning by playing VR games is practical for the young. |



