1 . For decades, scientists thought of the brain as the most closely guarded organ. Locked safely behind a biological barrier, away from the disorder of the rest of the body, it was broadly free of destruction of germs (病菌) and the battles started by the immune system.
Then, 20-odd years ago, some researchers began to ask a question: is the brain really so separate? The answer, according to a growing body of evidence, is no — and has important effects on both science and health care.
The list of brain conditions that have been associated with changes elsewhere in the body is long and growing. Changes in the make-up of the microorganisms resident in the gut (肠道), for example, have been linked to disorders like Parkinson’s disease. Some researchers think that certain infections could provoke Alzheimer’s disease and some could lead to emotional disorder in babies.
The effect is two-way. There is a lengthening list of symptoms (症状) not typically viewed as disorders of the nervous system in which the brain and the neural processes that connect it to the body play a large part. For example, the development of a fever is influenced by a population of neurons (神经元) that control body temperature and appetite. The effect of brain on body is underlined by the finding that stimulating a particular brain region in mice can ‘remind’ the body of previous inflammation (炎症) — and reproduce them.
These findings and others mark a complete shift in our view of the interconnectedness of brain and body, and could help us both understand and treat illness. If some brain conditions start outside the brain, then perhaps cures for them could also reach in from outside. Treatments that take effect through the digestive system, heart or other organs, for instance, would be much easier and less striking to give than those that must cross the blood-brain barrier, the brain’s first line of defence.
In the opposite direction, the effects of our emotions or mood on our capacity to recover from illness could also be used. There is an opening work under way testing whether stimulating certain areas of the brain that respond to reward and produce feelings of positivity could enhance recovery from conditions such as heart attacks. Perhaps even more exciting is the possibility that making changes to our behaviour — to reduce stress, say — could have similar benefits.
For neuroscientists, it’s time to look beyond the brain. And clinicians treating the body mustn’t assume the brain is above getting involved — its activity could be influencing a wide range of conditions, from mild infections to long-time fatness.
1. The author writes paragraph 1 mainly to ______.| A.evaluate an argument |
| B.present an assumption |
| C.summarize the structure |
| D.provide the background |
| A.Delay. | B.Cure. | C.Cause. | D.Disturb. |
| A.Treatments that cross brain-blood barrier are less used. |
| B.Previous diseases could cause the production of new ones. |
| C.Emotions could affect the capacity to fight against diseases. |
| D.Treatment of the brain takes priority over other treatments. |
I: Introduction P: Point Sp: Sub-point (次要点) C: Conclusion
A.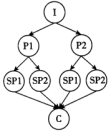 | B.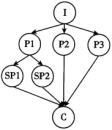 |
C.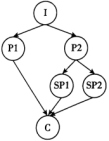 | D.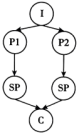 |
Uncertainty is all around us, never more so than today. Whether it concerns your health or relationships, much of what lies ahead in life remains uncertain.
We’re all different in how much uncertainty we can tolerate in life. Some people seem to enjoy taking risks and living unpredictable lives, while others find the randomness of life deeply annoying. But all of us have a limit. If you feel controlled by uncertainty and worry, it’s important to know that you’re not alone; many of us are in the same boat.
To cope with all this uncertainty, many of us use worrying as a tool for trying to predict the future and avoid unpleasant surprises. Worrying can make it seem like you have some control over uncertain circumstances. You may also believe that it will help you find a solution to your problems or prepare you for the worst. Unfortunately, long-term worrying just robs you of enjoyment in the present and weakens your energy. But there are healthier ways to cope with uncertainty.
Identify your uncertainty trigger (诱发因素). A lot of uncertainty tends to be self-generated. However, some can be generated by external sources, such as reading media stories that focus on bad news, or simply communicating with anxious friends. By recognizing your triggers, you can take action to avoid or reduce your exposure to them.
Shift your attention. Focus on solvable worries, taking action on those aspects of a problem that you can control, or simply go back to what you were doing. When the feelings of uncertainty return, refocus your mind on the present moment and your own breathing.
1. How are people different in tolerating uncertainty in life?2. Why do many people use worrying as a tool to deal with uncertainty?
3. Please decide which part is false in the following statement, then underline it and explain why.
▶ Knowing the triggers of your uncertainty, you can learn to expose yourself to them.
4. What are you most uncertain about right now? How will you deal with it? (In about 40 words)
3 . Researchers hope brain implants will one day help people with aphasia(失语症) to get their voice back—and maybe even to sing. Now, for the first time, scientists have demonstrated that the brain’s electrical activity can be decoded and used to reconstruct music.
A new study analyzed data from 29 people monitored for epileptic seizures(癫痫发作), using electrodes(电极) on the surface of their brain. As participants listened to a selected song, electrodes captured brain activity related to musical elements, such as tone, rhythm, and lyrics. Employing machine learning, Robert Knight from UC Berkeley and his colleagues reconstructed what the participants were hearing and published their study results. The paper is the first to suggest that scientists can “listen secretly to” the brain to synthesize(合成) music.
To turn brain activity data into musical sound, researchers trained an artificial intelligence (AI)model to decode data captured from thousands of electrodes that were attached to the participants as they listened to the song while undergoing surgery. Once the brain data were fed through the model, the music returned. The model also revealed some brain parts responding to different musical features of the song.
Although the findings focused on music, the researchers expect their results to be most useful for translating brain waves into human speech. Ludovic Bellier, the study’s lead author, explains that speech, regardless of language, has small melodic differences—tempo, stress, accents, and intonation—known as prosody(韵律). These elements carry meaning that we can’t communicate with words alone. He hopes the model will improve brain-computer interfaces (BCI), assistive devices that record speech-associated brain waves and use algorithms to reconstruct intended messages. This technology, still in its infancy, could help people who have lost the ability to speak because of aphasia.
Future research should investigate whether these models can be expanded from music that participants have heard to imagined internal speech. If a brain-computer interface could recreate someone’s speech with the prosody and emotional weight found in music, it could offer a richer communication experience beyond mere words.
Several barriers remain before we can put this technology in the hands—or brains— of patients. The current model relies on surgical implants. As recording techniques improve, the hope is to gather data non-invasively, possibly using ultrasensitive electrodes. However, under current technologies, this approach might result in a lower speed of decoding into natural speech. The researchers also hope to improve the playback clarity by packing the electrodes closer together on the brain’s surface, enabling an even more detailed look at the electrical symphony the brain produces.

| A.Electrodes can analyze musical elements. |
| B.The decoding of brain data helps recreate music. |
| C.Machine learning greatly enhances brain activity. |
| D.The AI model monitors music-responsive brain regions. |
| A.The prosody of speech. | B.The collection of brain waves. |
| C.The emotional weight of music. | D.The reconstruction of information. |
| A.Unlocking the Secrets of Melodic Mind | B.Brain Symphony: Synthesized Human Speech |
| C.BCI Brings Hope to People with Aphasia | D.Remarkable Journey: Decoding Brain with AI |
4 . Have we reached the peak of the culture war? Looking at my social media feeds, it seems that polarised thinking and misinformation have never been more common. How am I supposed to feel when users I once admired now draw on questionable evidence to support their beliefs?
Perhaps it is time for us all to adopt a little “existential humility”. I came across this idea in a paper by Jeffrey Greenat Virginia from Common Wealth University and his colleagues. They build on a decade of research examining the benefits of “intellectual humility” more generally — our ability to recognise the errors in our judgement and remain aware of the limits of our knowledge.
You can get a flavour of this research by rating your agreement with the following statements, ranging from 1 (not at all like me) to 5 (very like me): I question my own opinions because they could be wrong; I recognise the value in opinions that are different from my own; in the face of conflicting evidence, I am open to changing my opinions.
People who score highly on this assessment are less likely to form knee-jerk reactions on a topic, and they find it easier to consider the strengths or weaknesses of a logical argument. They are less likely to be influenced by misinformation, since they tend to read the article in full, investigate the sources of a news story and compare its reporting to other statements, before coming to a strong conclusion about its truth.
Developing “intellectual humility” would be an excellent idea in all fields, but certain situations may make it particularly difficult to achieve. Greenat points out that some beliefs are so central to our identity that any challenge can activate an existential crisis, as if our whole world view and meaning in life are under threat. As a result, we become more insistent in our opinions and seek any way to protect them. This may reduce some of our feelings of uncertainty, but it comes at the cost of more analytical thinking.
For these reasons, Greenat defines “existential humility” as the capacity to entertain the thought of another world view without becoming so defensive and closed-minded. So how could we achieve it? This will be the subject of future research, but the emotion of awe (a feeling of great respect and admiration) may offer one possibility. One study found that watching awe-inspiring videos about space and the universe led to humbler thinking, including a greater capacity to admit weaknesses.
Perhaps we could all benefit from interrupting our despair with awe-inspiring content. At the very least, we can try to question our preconceptions before offering our views on social media and be a little less ready to criticize when others disagree.
1. Regarding the culture war on social media, the author is _______.| A.embarrassed | B.concerned | C.panicked | D.stressed |
| A.Existential humility reduces the threat to identity. |
| B.People with intellectual humility tend to jump to conclusions. |
| C.Awe could promote existential humility by encouraging modest thinking. |
| D.The higher you score on the assessment, the more you stick to your values. |
| A.Overcome an Existential Crisis | B.Show a Little Humility |
| C.The Path to Screening Information | D.The Approach to Achieving Humility |
5 . When I teach research methods, a major focus is peer review. As a process, peer review evaluates academic papers for their quality, integrity and impact on a field, largely shaping what scientists accept as “knowledge”- By instinct, any academic follows up a new idea with the question, “Was that peer reviewed?”
Although I believe in the importance of peer review and I help do peer reviews for several academic journals-I know how vulnerable the process can be.
I had my first encounter with peer review during my first year as a Ph. D student. One day, my adviser handed me an essay and told me to have my -written review back to him in a week. But at the time, I certainly was not a “peer”-I was too new in my field. Manipulated data (不实的数据) or substandard methods could easily have gone undetected. Knowledge is not self-evident. Only experts would be able to notice them, and even then, experts do not always agree on what they notice.
Let’s say in my life I only see white swans. Maybe I write an essay, concluding that all swans are white. And a “peer” says, “Wait a minute, I’ve seen black swans.” I would have to refine my knowledge.
The peer plays a key role evaluating observations with the overall goal of advancing knowledge. For example, if the above story were reversed, and peer reviewers who all believed that all swans were white came across the first study observing a black swan, the study would receive a lot of attention.
So why was a first-year graduate student getting to stand in for an expert? Why would my review count the same as an expert’s review? One answer: The process relies almost entirely on unpaid labor.
Despite the fact that peers are professionals, peer review is not a profession. As a result, the same over-worked scholars often receive masses of the peer review requests. Besides the labor inequity, a small pool of experts can lead to a narrowed process of what is publishable or what counts as knowledge, directly threatening diversity of perspectives and scholars. Without a large enough reviewer pool, the process can easily fall victim to biases, arising from a small community recognizing each other’s work and compromising conflicts of interest.
Despite these challenges, I still tell my students that peer review offers the best method for evaluating studies aird advancing knowledge. As a process, peer review theoretically works. The question is whether the issues with peer review can be addressed by professionalizing the field.
1. What can we learn about peer review in the first paragraph?| A.It generates knowledge. | B.It is commonly practiced. |
| C.It is a major research method. | D.It is questioned by some scientists. |
| A.Complexity of peer review ensures its reliability. |
| B.Contradictions between scientists may be balanced. |
| C.Individuals can be limited by personal experiences. |
| D.Experts should detect unscientific observation methods. |
| A.Workload for scholars. | B.Toughness of the process. |
| C.Diversification of publications. | D.Financial support to reviewers. |
| A.what fuels peer review | B.why peer review is imperfect |
| C.how new hands advance peer review | D.whether peer reviewers are underrated |
6 . While some allergies (过敏症) disappear over time or with treatment, others last a lifetime. For decades, scientists have been searching for the source of these lifetime allergies.
Recently, researchers found that memory B cells may be involved. These cells produce a different class of antibodies known as IgG, which ward off viral infections. But no one had identified exactly which of those cells were recalling allergens or how they switched to making the IgE antibodies responsible for allergies. To uncover the mysterious cells, two research teams took a deep dive into the immune (免疫的) cells of people with allergies and some without.
Immunologist Joshua Koenig and colleagues examined more than 90, 000 memory B cells from six people with birch allergies, four people allergic to dust mites and five people with no allergies. Using a technique called RNA sequencing, the team identified specific memory B cells, which they named MBC2s that make antibodies and proteins associated with the immune response that causes allergies.
In another experiment, Koenig and colleagues used a peanut protein to go fishing for memory B cells from people with peanut allergies. The team pulled out the same type of cells found in people with birch and dust mite allergies. In people with peanut allergies, those cells increased in number and produced IgE antibodies as the people started treatment to desensitize them to peanut allergens.
Another group led by Maria Curotto de Lafaille, an immunologist at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York City, also found that similar cells were more plentiful in 58 children allergic to peanuts than in 13 kids without allergies. The team found that the cells are ready to switch from making protective IgG antibodies to allergy-causing IgE antibodies. Even before the switch, the cells were making RNA for IgE but didn’t produce the protein. Making that RNA enables the cells to switch the type of antibodies they make when they encounter allergens. The signal to switch partially depends on a protein called JAK, the group discovered. “Stopping JAK from sending the signal could help prevent the memory cells from switching to IgE production,” Lafaille says. She also predicts that allergists may be able to examine aspects of these memory cells to forecast whether a patient's allergy is likely to last or disappear with time or treatment.
“Knowing which population of cells store allergies in long-term memory may eventually help scientists identify other ways to kill the allergy cells,” says Cecilia Berin, an immunologist at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine. “You could potentially get rid of not only your peanut allergy but also all of your allergies.”
1. Why did scientists investigate the immune cells of individuals with and without allergies?| A.To explore the distinctions between IgG and IgE. |
| B.To uncover new antibodies known as IgG and IgE. |
| C.To identify cells responsible for defending against allergies. |
| D.To reveal cells associated with the development of allergies. |
| A.Make. . . less destructive. | B.Make. . . less responsive. |
| C.Make. . . less protective. | D.Make. . . less effective. |
| A.MBC2s make antibodies and proteins that prevent allergies. |
| B.Memory B cells generate both RNA for IgE and the corresponding protein. |
| C.JAK plays a role in controlling antibody production when exposed to allergens. |
| D.Allergists are capable of predicting whether an allergy will last or disappear. |
| A.RNA Sequencing Is Applied in Immunology Research |
| B.Specific Cells Related to Peanut Allergies Are Identified |
| C.Unmasking Cells’ Identities Helps Diagnose and Treat Allergies |
| D.Newfound Immune Cells Are Responsible for Long-lasting Allergies |
7 . We have been defending humanities for many decades now, but the crisis of the humanities only grows. In the face of declining student interest and mounting political scrutiny (审查), universities and colleges are increasingly putting humanities departments on the chopping block.
As a humanist, I am prepared to admit that I do not know what the value of the humanities is. I once asked the best teacher I ever had why she no longer taught her favorite novel, and she said that she stopped teaching a book when she found she was no longer curious about it. The humanistic spirit is, fundamentally, an inquisitive one.
In contrast, defenses of the humanities are not - and cannot be - conducted in an inquisitive spirit, because a defensive spirit is inimical to an inquisitive one. Defensiveness is, it must be admitted, an understandable response when the chopping block is brought out and you need to explain why you shouldn’t be on it, which requires their participants to pretend to know things that they do not actually know.
Nonetheless, we should be alert to the danger of becoming accustomed to putting our worst foot forward. An atmosphere of urgency and calls for immediate action are hostile to fields of study like literature and philosophy that require a reflective mood, and the pretense (假装) of knowing what one doesn’t actually know is hostile to forms of inquiry that demand an open mind.
A defensive mindset also encourages politicization. If the study of literature or philosophy helps to fight sexism or to promote democracy — and everyone agrees that sexism is bad, and democracy is good-then you have your answer as to why we shouldn’t cut funding for the study of literature or philosophy. Politicization is a way of arming the humanities for its political battles, but it comes at an intellectual cost. Why is sexism so bad? Why is democracy so good? Politicization silences these and other questions, whereas the function of the humanities is to raise them.
Humanists are not alone in their ignorance about the purpose of their disciplines. But scientists are under a lot less pressure to explain why they exist because the society at large believes itself to already have the answer to that question. If at some point I am called on to defend the study of Homer or Descartes at some official hearing, I will do my best, but I will not run to battle; the battle will have to come to me.
The task of humanists is to invite, to welcome, to excite, to engage. And when we let ourselves classrooms but also in our public-self presentation, we find we don’t need to defend or prove anything: We are irresistible.
1. What is the main concern regarding the crisis in humanities?| A.Students’ lack of interest in studying humanities courses. |
| B.People’s little knowledge regarding the purpose of humanities. |
| C.The mounting political scrutiny faced by humanities departments. |
| D.The pressure on humanists to argue for the value of their disciplines. |
| A.contrary. | B.relevant. | C.sensitive. | D.immune. |
| A.It is the worst action to take in the face of the crisis. |
| B.It leads to a compromise on human’s intellectual depth. |
| C.It requires a reflective mood on the study of humanities. |
| D.It brings about a lower chance of survival for humanities. |
| A.Humanities may not need any defense. | B.Science is more useful than humanities. |
| C.The future of humanities remains cloudy. | D.The battle of humanities is a hard one to fight. |
8 . Borders, departments, or issue areas all represent what systems analysts call system boundaries. System boundaries divide the big, messy, interconnected world into smaller subsystems. This is useful, even necessary. Our minds and our collective governance systems would be stuck if we had to always consider all the connections of everything to everything else. But dividing systems into subsystems can sometimes break a natural cooperativity. For instance, a decarbonizing country will spend money in its energy and transportation sectors and save money in its health system.
Decarbonization could be a win for the whole, but it might be experienced as a bother for particular subsystems.
Donella Meadows, the early systems modeler, wrote that system boundaries are “lines in the mind, not in the world.” And that is actually good news. If departments, and disciplines are just ideas, then there is nothing immovable about them. We can make these borders less obvious and conduct partnerships across them. We can even redraw them to include more of what matters in a single project or investment. That’s the premise of multisolving — using one investment of time or effort to achieve several goals at once.
For instance, Warm Up New Zealand (WUNZ) upgraded the energy efficiency of residential buildings and provided jobs in the building sector after a financial downturn. The project resulted in better health for residents, as well. That translated into health systems savings. Taken together, a 2011 study estimated that across all these benefits, the project saved $3.90 for every $1 invested.
Multisolving seems possible everywhere and like an obvious choice. Yet, it is very much the exception, not the rule. Why is multisolving still so rare when it has the power to boost progress on some of the most urgent issues we face?
Unfamiliarity stands in the way, as does an often-unexamined assumption that making issues smaller makes them easier to address. We often hear the viewpoint, “I already work on poverty (or climate, etc.) and that’s hard enough. Why should I add biodiversity or pollution to the mix?” Fundraising for crossing borders can be a struggle too. Funders want the “visible results” shown, but they don’t always see crossing borders as an essential part of achieving those results.
It is easy to devalue and underemphasize connection-building. After all, it can be delicate and not always visible. But to realize goals in today’s world, from equitable policies and low-carbon facilities to values like cooperation and fairness, we do need deep shifts, and we need them soon. And facilitating the flow of ideas back and forth across borders is one way to speed change.
1. As for systems boundaries, the author is ______.| A.critical | B.puzzled | C.supportive | D.unconcerned |
| A.Prediction. | B.Precondition. | C.Prevention. | D.Presentation. |
| A.People are familiar with multisolving. |
| B.WUNZ performed multisolving successfully. |
| C.Raising money helps to produce visible results. |
| D.Multisolving is widely used to address problems. |
| A.Multisolving: Hard to achieve soon |
| B.Multisolving: Essential to solve small issues |
| C.Multisolving: Conducting partnership across borders |
| D.Multisolving: Making systems whole, healthy, and sustainable |
9 . Supermarkets have long been suffering as one of the thinnest-margined businesses in existence and one of the least-looked-forward-to places to work or visit. For more than a decade, they have been under attack from e-commerce giants, blamed for making Americans fat, and accused of contributing to climate change.
Supermarkets can technically be defined as giants housing 15,000 to 60,000 different products. The revolutionary idea of a self-service grocery, where people could hunt and gather food from aisles rather than asking a clerk to fetch items from behind a counter, first came about in America. There is some debate about which was the very first, but over the years a consensus has built around King Kullen Supermarket, founded in New York in 1930.
For some 300 years, Americans had fed themselves from small stores and public markets. Shopping for food involved mud, noisy chickens, clouds of flies, nasty smells, bargaining, and getting short-changed. The supermarket imitated the Fordist factory, with its emphasis on efficiency and standardization, and reimagined it as a place to buy food. Supermarkets may not feel cutting-edge now, but they were a revolution in distribution at the time. They were such strange marvels that, on her first official state visit to the United States in 1957, Queen Elizabeth Ⅱ insisted on an impromptu (即兴的) tour of a suburban-Maryland Giant Food.
The typical supermarket layout has barely changed over the past 90 years. Most stores open with flowers, fruit and vegetables at the front as a breath of freshness to arouse our appetite. Meanwhile, they keep the milk, eggs, and other daily basics all the way back so you’ll travel through as much of the store as possible, and be tempted along the way.
In the early days, as the supermarket multiplied, so did our suspicion of it. We have long feared that this “revolution in distribution” uses corporate black magic on our appetite. The book The Hidden Persuaders, published in 1957, warned that supermarkets were putting women in a “hypnoidal trance (催眠恍惚状态),” causing them to wander aisles, bumping into boxes and “picking things off shelves at random.”
1. What problem have supermarkets been facing?| A.They are actually on the way to shutdown. |
| B.They have been losing customers and profits. |
| C.They are forced to use e-commerce strategies. |
| D.They have difficulty adapting to climate change. |
| A.It was put forward by King Kullen. |
| B.It originated in the United States. |
| C.It has been under constant debate. |
| D.It proves revolutionary even today. |
| A.They use tricky strategies to promote their business. |
| B.They are going to replace the local groceries entirely. |
| C.They apply corporate black magic to the goods on display. |
| D.They take advantage of the weaknesses of women shoppers. |
10 . We often think of fingerprints as the tiny arched patterns on the tip of each finger. They are regarded as special markers of human identity, even more individualized than DNA. But new research suggests our brains have “fingerprints” that are equally unchanging and unique to each person.
With modern neuroimaging (神经影像) techniques, scientists can track your brain’s distinct signature composed of tens of thousands of electrical signals that communicate across the brain. The final product is a picture of brain’s electrical activity that is detailed, distinct and difficult to change. According to Zack Y. Shan, head of the neuroimaging platform at the Thompson Institute, “The brain is a symphony orchestra (交响乐团).” Each region plays a unique instrument and adapts to work with nearby tunes at the same time. This cooperation leads to our thoughts and actions. “And no two symphonies sound exactly alike,” Shan adds.
A recent study published in Sleep maps the extent of this neurodiversity through EEG snapshots (脑电图快照), which describe the sleeping brain’s electrical activity as wavy lines. Led by Michael Prerau, a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, the researchers analyzed brainwave data of sleep spindles, one to two seconds evident neural activity associated with our ability to turn short-term memories into long-term memories.
For Dara S. Manoach, a co-author of the Sleep study and professor of psychology at Harvard Medical School, the sleeping brain is a “new frontier” for studying the treatment of memory problems in neurological disorders. She notes that lack of sleep spindle activities has been linked to different mental diseases like epilepsy and Alzheimer’s disease. So, the researchers compared two nights of sleep recordings from healthy participants to those with Alzheimer’s disease. Their analysis revealed that their broadened approach to analyzing sleep spindles also could unearth new biological indicators for Alzheimer’s disease. “It’s a first step to better understanding how the disorder operates and developing targeted treatments,” Manoach says.
Moreover, brain fingerprints may offer inspirations that traditional therapeutic (治疗性的) observation can’t. Patients with different diseases can have similar symptoms. “That’s where neuroimaging comes into play. Brain fingerprints are windows into distinguishing between two patients who seem identical,” explains Dan Hermens, a professor of neurobiology at the Thompson Institute.
In the wake of increasing reports of mental disorders, there is therapeutic promise. Brain fingerprinting could offer a potential way out of the dark chapter and provide new possibilities for the mental health crisis using best evidence-based practices to overcome it.
1. What can we learn about the brain’s “fingerprint”?| A.It can track electrical signals in the brain. |
| B.It refers to the pattern of the surface of the brain. |
| C.It constructs an individualized map of brain structure. |
| D.It shows the unique image of the brain’s electrical activity. |
| A.recording brain fingerprints enhances memory |
| B.brainwave data can identify specific mental illnesses |
| C.EEG can form biological indicators for human identity |
| D.neuroimaging prevents the development of mental disorders |
| A.Sleep Fingerprints Predict Disease Occurrence |
| B.Sleeping Brains: Ideas and Actions Controlled |
| C.Sleep Fingerprints: Brain Identity Revealed |
| D.Sleeping Brains Uncover Memory Codes |



