Gestures refer to the communication where visible bodily actions are used to communicate important messages. They include movement of hands, face, or other parts of the body. Gestures benefit our lives a lot. Take language learning.
In some languages, certain syllables (音节) within words are pronounced with markedly more weight than others, called lexical stress. Languages such as English commonly feature lexical stress. For example, the word “accent” involves more emphasis on the first syllable, “ac”, than the second, “cent”. Native speakers of Chinese, however, don’t use lexical stress and therefore find it difficult to learn languages that feature it.
Making any hand gesture could help learners recognize lexical stress, which has been proved by Xing Tian’s team. They selected 124 native Chinese speakers, who watched videos of people performing hand movements that were synced(同步的) to recordings of the same English words. In addition, they also found when more pronounced gestures matched the stressed syllable, the participants were particularly good at identifying it.
The research involved several experiments, which makes it difficult to combine the results. Nevertheless, Tian estimates that the use of gestures helped identify lexical stress between 10 and 15 percent more accurately compared with no gestures at all, and how much help depends on the nature of gestures.
A follow-up study conducted by another team exposed the same Chinese speakers to Russian words and got similar results. “Our findings highlight the functional role of gestures in enhancing speech learning, suggesting practical strategies for language teaching and learning,” the researchers write in their paper.
The benefits of gestures extend far beyond teaching and learning. Since gestures are deeply integrated into our daily lives, they deserve more of our attention.
1. What do gestures mean?2. What did Xing Tian’s team find in their study?
3. Please decide which part is false in the following statement, then underline it and explain why.
Gestures help learn lexical stress, but the degree to which they help depends on the complexity of the lexical stress.
4. Besides what is mentioned in the passage, how do gestures benefit you in your life? (In about 40words)
2 . In some ways, it is surprising that languages change. After all, they are passed down through the generations reliably enough for parents and children to communicate with each other.
Languages change for a variety of reasons. Large-scale shifts often occur in response to social, economic, and political pressures, as there are many examples of language change fueled by invasions, colonization, and migration.
| A.Changes in sound are somewhat harder to document but just as interesting. |
| B.Yet linguists find that all living languages change over time — at different rates though. |
| C.As long as people are using a language, that language will undergo some change. |
| D.All natural languages change, and language change affects all areas of language use. |
| E.The three main areas of language that change over time are vocabulary, sentence structure, and pronunciation. |
| F.Even without these kinds of influences, a language can change dramatically if enough users adopt a new way of speaking. |
| G.The vocabulary and phrases people use depend on where they live, their age, education level, social status and other factors. |
3 . A Fluent Advantage
When schools go through budget cuts, foreign language classes are often placed on the cutting block. School administrators often do not understand how important foreign language study is for their students’ success in the real world. Far from cutting language classes, schools should be demanding them for all students. Studying a foreign language should be required in middle schools.
Language study strengthens students’ minds. Many studies have indicated that multilingual people—people who speak more than one language—are better at certain tasks. Specifically, multilingual people have better executive function than people who speak only one language. Executive function is the way the brain manages all the information it’s given, such as performing different tasks and deciding what to focus on. In brain scans, multilingual people show increased activity in the areas of the brain that control executive function. Researchers have guessed that this advantage exists because multilingual people must constantly decide which words from which language to use. As a result, multilingual people get lots of practice with executive function. Their brains can then apply those skills to other tasks, like paying attention or multitasking. This effect is especially strong for people who grow up speaking more than one language. The earlier students start language classes, the more benefits they may get from language study.
Moreover, language study helps prepare students for their future careers. Today, language skills are in high demand on the job market and more and more businesses work in many countries across the world. As businesses become global, they need people who can communicate easily across national borders. To prepare for their careers, more students should be learning foreign languages. From 2010 to 2015, the demand in the United States for workers who speak a second language doubled. This trend included workers of all skill levels and backgrounds.
Of course, in order to make better use of the advantages of foreign language study, middle school foreign language classes should not just make students memorize new words and sounds.
They must also teach students about new cultures. Foreign language classes should be required to include lessons about history, literature, customs, and government along with the languages themselves. These subjects will help students become better global citizens and support their studies in other subjects.
Requiring middle schoolers to study a foreign language offers them opportunities to sharpen their brains. It also gives them tools that will help them become productive members of today’s global society.
1. How does the author feel about foreign language study in middle schools?| A.More foreign language classes should be offered in middle schools. |
| B.Taking a foreign language class in middle schools should be a choice. |
| C.Foreign language classes should be cut because of the limited funds. |
| D.Studying a foreign language should be a middle school requirement. |
| A.people who speak more than one language have better executive function |
| B.being able to work in another country doubles people’s job opportunities |
| C.people learn languages better as young people than when they are older |
| D.people’s executive function improves after foreign language classes |
| A.To sum up his argument. | B.To put forward a solution. |
| C.To emphasize his point of view. | D.To introduce an additional suggestion. |
I: Introduction P: Point Sp: Sub-point (次要点) C: Conclusion
A.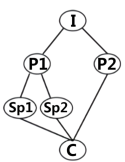 | B.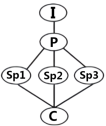 |
C. | D. |
4 . A crucial period for learning the rules and structure of a language lasts up to around age 17 or 18, say psychologist Joshua Hartshorne of MIT and his colleagues.
Previous research had suggested that grammar-learning ability developed in early childhood before hitting a dead end around age 5. However, Hartshorne’s team reports online in Cognition that people who started learning English as a second language in an English-speaking country by age 10 to 12 ultimately mastered the new tongue as well as folks who had learned English and another language at the same time from birth. Both groups, however, fell somewhat short of the grammatical fluency displayed by English-only speakers. After ages 10 to 12, new-to-English learners reached lower levels of fluency than those who started learning English at younger ages because time ran out when their grammar-absorbing ability fell starting around age 17.
Aiming for a sample of tens of thousands of volunteers, Hartshorne began by contacting friends on Facebook to take an online English grammar quiz, which used a person’s responses to guess his or her native language and dialect (方言) of English. Then volunteers filled out a questionnaire asking where they had lived, languages they had spoken from birth, the age at which they began learning English and the number of years they had lived in an English-speaking country.
In the end, the researchers analyzed responses of 669,498 native and nonnative English speakers. Statistical calculations focused on estimating at what ages people with varying amounts of experience peaking English reached peak grammar ability.
Researchers who study language learning regard the new study as fascinating, but exploratory. According to psycholinguist David Barner of the University of California, San Diego, Hartshorne’s team can’t yet say that language skill develops along a single timeline. Different elements of grammar, such as using correct word order or subjects and verbs that agree with one another, might be learned at different rates, Barner says. It’s also unclear whether the responses of volunteers to an online, 132-item grammar test reflect how well of poorly they actually speak English, he says.
What’s more, language learning involves more than a crucial period for acquiring grammar, cautions linguist David Birdsong of the University of Texas at Austin. For instance, growing up speaking two languages at once puts still poorly understood burdens on the ability to grasp grammar, he says.
In the new study, people who were bilinguals from birth fell short of peak English grammar scores achieved by English-only speakers. That’s consistent with evidence that bilinguals cannot easily turn off one language while speaking another, Birdsong says. Interactions between tongues spoken by one person may slightly depress how much can be learned about both languages, even if bilingual communication still reaches high levels, he suggests.
1. Hartshorne and his colleagues found that____ .| A.one reaches a higher level of fluency at age 10 |
| B.one learns a second language fastest at about age 12 |
| C.one gets a good grasp of English grammar before age 5 |
| D.one’s ability to master grammar declines at around age17 |
| A.social media |
| B.experiments in the lab |
| C.literature review |
| D.face-to-face interviews |
| A.language skill develops along a single timeline |
| B.online volunteers do not cover a wide enough range |
| C.different grammar items may be acquired at different paces |
| D.the quiz in the new study does not include enough questions |
| A.They can achieve a perfect grammar score. |
| B.Grammar learning is the biggest burden for them. |
| C.They are able to make a swift shift between languages. |
| D.Speaking two languages affects their language acquisition. |
5 . Languages have been coming and going for thousands of years, but in recent time there has been less coming and a lot more going. When the world was still populated by hunter-gatherers, small, tightly knit (联系) groups developed their own patterns of speech independent of each other. Some language experts believe that 10,000 years ago, when the world had just five to ten million people, they spoke perhaps 12,000 languages between them.
Soon afterwards, many of those people started settling down to become farmers, and their languages too became more settled and fewer in number. In recent centuries, trade, industrialization, the development of the nation-state and the spread of universal compulsory education, especially globalization and better communications in the past few decades, all have caused many languages to disappear, and dominant (占优势的) languages such as English, Spanish and Chinese are increasingly taking over.
At present, the world has about 6,800 languages. The distribution of these languages is hugely uneven. The general rule is that mild zones have relatively few languages, often spoken by many people while hot, wet zones have lots, often spoken by small numbers. Europe has only around 200 languages; the America about 1,000; Africa 2,400; and Asia and the Pacific perhaps 3,200, of which Papua New Cuinea alone accounts for well over 800. The median number (中位数) of speakers is a mere 6,000, which means that half the world’s languages are spoken by fewer people than that.
Already well over 400 of the total of 6,800 languages are close to extinction (消亡), with only a few elderly speakers left. Pick, at random, Busuu in Cameroon (8 remaining speakers), Chiapaneco in Mexico (150), Lipan Apache in the United States (2 or 3) or Wadjigu in Australia (1, with a question-mark); none of these seems to have much chance of survival.
1. What can we learn about language development from the passage?| A.Globalization has brought about more new languages. |
| B.Settling down makes people develop more kinds of languages. |
| C.Education is one of the reasons for some languages’ disappearance. |
| D.Around 1,000 languages only have a few elderly speakers left. |
| A.Not equal. | B.Not narrow. |
| C.Not limited. | D.Not good. |
| A.6,800. | B.2,400. |
| C.3,400. | D.1,200. |
| A.Human being has created a great number of languages. |
| B.Language disappearance leads to the extinction of some cultures. |
| C.Geography is one factor of language evolution. |
| D.Globalized events cause languages to be fewer. |
6 . Learning a second language is tricky at any age and it only gets tougher the longer you wait to open that dusty French book. Now, in a new study, scientists have pinpointed the exact age at which your chances of reaching fluency in a second language seem to plummet: 10.
The study, published in the journal Cognition, found that it’s “nearly impossible” for language learners to reach native-level fluency if they start learning a second tongue after 10. But that doesn’t seem to be because language skills go downhill. “It turns out you’re still learning fast. It’s just that you run out of time, because your ability to learn starts dropping at around 17 or 18 years old,” says study co-author Joshua Hartshorne, an assistant professor of psychology at Boston College.
Kids may be better than adults at learning new languages for many reasons. Children’s brains are more plastic than those of adults, meaning they’re better able to adapt and respond to new information. “All learning involves the brain changing,” Hartshorne says, “and children’s brains seem to be a lot more skilled at changing.”
Kids may also be more willing to try new things (and to potentially look foolish in the process) than adults are. Their comparatively new grasp on their native tongue may also be advantageous. Unlike adults, who tend to default (默认) to the rules and patterns of their first language, kids may be able to approach a new one with a blank slate (石板).
These findings may seem discouraging, but it was heartening for scientists to learn that the critical period for fluent language acquisition might be longer than they previously thought. Some scientists believed that the brief window closes shortly after birth, while others stretched it only to early adolescence. Compared to those estimates, 17 or 18 — when language learning ability starts to drop off — seems relatively old.
“People fared better when they learned by immersion (沉浸), rather than simply in a classroom. And moving to a place where your desired language is spoken is the best way to learn as an adult. If that’s not an option, you can mimic an immersive environment by finding ways to have conversations with native speakers in their own communities,” Hartshorne says. By doing so, it’s possible to become conversationally proficient — even without the advantage of a child’s brain.
1. The underlined word “plummet” in Paragraph 1 is closest in meaning to “__________”.| A.decrease | B.rise |
| C.end | D.vary |
| A.Children are too young to grasp a second language. |
| B.Age 10-18 is the best time to learn a second language. |
| C.Adults go beyond the critical period for learning a second language. |
| D.Communicating with native speakers enables you to master all the language skills. |
| A.Adults are less influenced by their mother tongues. |
| B.Adults spend more time responding to new information. |
| C.Adults are only too willing to experience something awkward in the process. |
| D.Adults prefer an immersive environment to a classroom in learning a second language. |
| A.the best age to learn a second language |
| B.the approaches to learning a second language |
| C.why kids learn a second language more easily than adults |
| D.whether adults can learn a second language like their younger selves |
7 . Hearing Feelings behind Words
Most of us are taught to pay attention to what is said—the words. Words do provide us with some information, but meanings come from so many other sources. So it would be difficult for us to have an effective understanding if we rely too heavily on words alone. Words are used to describe only a small part of the many ideas we associate with any given message. Sometimes we can gain insight into some of those associations if we listen for more than words. We don’t always say what we mean or mean what we say. Sometimes our words don’t mean anything except “I’m letting off some steam. I don’t really want you to pay close attention to what I’m saying. Just pay attention to what I’m feeling.” Mostly we mean several things at once. A person wanting to purchase a house says to the current owner, “This step has to be fixed before I’ll buy.” The owner says, “It’s been like that for years.” Actually, the step hasn’t been like that for years, but the unspoken message is :”I don’t want to fix it. We put up with it. Why can’t you?” The more expansive meaning a message can be obtained by examining who said it, when it occurred, the related conditions or situation, and how it was said.
When a message occurs can also disclose associated meaning. Let us assume two couples do exactly the same amount of kissing and arguing. But one couple always kisses after an argument and the other couple always argues after a kiss. The ordering of the behaviors may mean much more than the frequency of the behavior. How about a friend’s unusually quiet behavior? It may only be understood by nothing what happened previously and the situations that required an abnormal amount of confidence. Some responses may be directly linked to a developing pattern of responses and seem illogic. For example, a person who says “No!” to a serials of charges like “You’re stupid,” “You’re lazy,” and “You’re dishonest,” may also say “No!” and try to justify his or her response if the next statement is “And you’re good looking.”
We would do well to listen for how messages are presented. The words, “It sure has been nice to have you over,” can be said with emphasis and excitement or ritualistically. The phrase can be said once or repeated several times. And the meanings we associate with the phrase will change accordingly. Sometimes if we say something infrequently it assumes more importance; sometimes the more we say something the less importance it assumes.
1. Effective communication is made possible between two conversing partners if .| A.they use proper words to carry their ideas |
| B.they both speak truly of their own feelings |
| C.they try to understand each other’s language |
| D.they are able to associate meaning with their words |
| A.I’m just kidding | B.I’m just saying the opposite |
| C.I’m just calling your attention | D.I’m just giving off some sound |
| A.the step has been like that for years |
| B.he doesn’t think it necessary to fix the step |
| C.the condition of the step is only a minor fault |
| D.the cost involved in the fixing should be shared |
| A.in a way of ceremony | B.without true intention |
| C.with less emphasis | D.light-heartedly |
8 . Language Learning
Learning a new language can be tricky at any age. But in a recent study, scientists have pinpointed the exact age at which your chances of reaching fluency in a new language seem to quickly drop off: 10. Does this mean you should quit your French class if you’re older than 10? Non!
Kids may be better than adults at learning new languages for many reasons. Children’s brains are more adaptable than those of adults.
The findings also offer ideas for adults hoping to pick up a new language.
| A.Now that’s worth talking about! |
| B.But they are unlikely to become fluent. |
| C.The study appeared in the journal Cognition. |
| D.For the study, the researchers created an online quiz. |
| E.This means they’re better able to respond to new information. |
| F.This gave researchers huge amounts of data from English speakers of many ages and backgrounds. |
| G.Researchers found that people did better when they learned by immersion rather than only in a classroom. |
9 . No student of a foreign language needs to be told that grammar is complex. By changing the order of the words and by adding a range of auxiliary verbs (助动词) and suffixes (后缀), we can turn a statement into a question, state whether an action has taken place or is soon to take place, and perform many other word tricks to convey different meanings. However, the question which many language experts can’t understand and explain is — who created grammar?
Some recent languages evolved due to the Atlantic slave trade. Since the slaves didn’t know each other’s languages, they developed a make-shift language called a pidgin. Pidgins are strings of words copied from the language of the landowners. They have little in the way of grammar, and speakers need to use too many words to make their meaning understood. Interestingly, however, all it takes for a pidgin to become a complex language is for a group of children to be exposed to it at the time when they learn their mother tongue. Slave children didn’t simply copy the strings of words used by their elders. They adapted their words to create an expressive language. In this way complex grammar systems which come from pidgins were invented.
Further evidence can be seen in studying sign languages for the deaf. Sign languages are not simply a group of gestures; they use the same grammatical machinery that is found in spoken languages. The creation of one such language was documented quite recently in Nicaragua. Previously, although deaf children were taught speech and lip reading in the classrooms, in the playgrounds they began to invent their own sign system, using the gestures they used at home. It was basically a pidgin and there was no consistent grammar. However, a new system was born when children who joined the school later developed a quite different sign language. It was based on the signs of the older children, but it was shorter and easier to understand, and it had a large range of special use of grammar to clarify the meaning. What’s more, they all used the signs in the same way. So the original pidgin was greatly improved.
Most experts believe that many of the languages were pidgins at first. They were initially used in different groups of people without standardization and gradually evolved into a widely accepted system. The English past tense—“ed” ending — may have evolved from the verb “do”. “It ended” may once have been “It end-did”. It seems that children have grammatical machinery in their brains. Their minds can serve to create logical and complex structures, even when there is no grammar present for them to copy.
1. What can be inferred about the slaves’ pidgin language?| A.It was difficult to understand. |
| B.It came from different languages. |
| C.It was created by the landowners. |
| D.It contained highly complex grammar. |
| A.No consistent signs were used for communication. |
| B.Most of the gestures were made for everyday activities. |
| C.The hand movements were smoother and more attractive. |
| D.The meaning was clearer than the previous sign language. |
| A.English grammar of past tense system is inaccurate. |
| B.Children say English past tense differently from adults. |
| C.The thought that English was once a pidgin is acceptable. |
| D.Experts have proven that English was created by children. |
| A.The Creators of Grammar | B.The History of Languages |
| C.Why Pidgins Came into Being | D.How Grammar Systems Are Used |
10 . Some international languages are widely used for many purposes. Some minority lanuages will die out and some nations tend to keep minority languages. I reckon that most common used international languages ease our life quality and communication with different nationalities. On the other hand, we need to help improve minority languages.
There are many languages in the entire world but two or three minority languages die out each year. Some countries try to save dying languages. For instance, Australian Government created a project to save the language and culture of Maori who are Australian aborigines. And there are other projects to keep minority languages such as American Indian language.
However, the worldwide job market usually requires candidates who can speak English or other international languages. People who cannot speak lingua franca (共通语) could hardly be promoted at work. For example, some companies need an employee who can deal with foreign companies. So most people tend to learn at least one international language that helps them to find a better job.
Therefore, world needs one common lingua franca that should be spoken in any country. Consequently, one common language should be a required subject in every school. So anyone speaking one common language can travel without worries to any point of the world and trade their products. People will not be forced to learn many languages.
In conclusion, we should help minority nations to keep their languages for the cultural diversity. To ease the worldwide communication among nations, we should create a common language and provide courses of it. As a result, no one will face a language issue.
1. What does the underlined word “reckon” in Paragraph 1 mean?| A.Deny. | B.Fear. |
| C.Ignore. | D.Think. |
| A.Not all minority languages are useful. |
| B.Some minority languages have died out. |
| C.Maori is attractive to Australian tourists. |
| D.American Indian language is well preserved. |
| A.It benefits their journey. |
| B.They can earn more money. |
| C.It does good to find a good job. |
| D.They are eager to get promoted. |
| A.By learning a common language. |
| B.By wiping out minority languages. |
| C.By studying more languages at college. |
| D.By communicating more with foreigners. |



