1 . One of the curious things about social networks is the way that some messages, pictures, or ideas can spread like wildfire while others that seem just as catchy or interesting barely register at all
Before you go deep into the puzzle, consider this: If you measure the height of your male friends, for example, the average is about 170 cm. You are 172 and your friends are all about the same height as you are. Indeed, the mathematical concept of “average” is a good way to capture the nature of this data set.
But imagine that one of your friends was much taller than you. This person would dramatically skew the average, which would make your friends taller than you, on average. In this case, the “average” is a poor way to capture this data set.
Exactly this situation occurs on social networks. On average, your coauthors will be cited more often than you, and the people you follow will post more frequently than you and so on.
Now Lerman from University of Southern Caledonia has discovered a related paradox, which they call the majority illusion (多数错觉). They illustrate this illusion with an example. They take 14 nodes linked up to form a small network. They then color three of these nodes and count how many of the remaining nodes link to them in a single step.
In situation (a), the uncolored nodes see more than half of their neighbors as colored. This is the majority illusion—the local impression that a specific feature is common when the global truth is entirely different. While in situation (b) the majority illusion doesn’t occur.
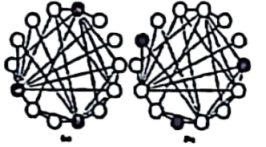
So how popular is it in the real world? It’s found out that the majority illusion occurs in almost all network scenarios. “The effect is largest in the political blogs network, where 60% of nodes will have majority active neigbbours, even when only 20% of the nodes are truly active,” says Lerman.
It immediately explains many interesting phenomena. For a start, it shows how some content can spread globally while other similar content does not—the key is to start with a small number of well-connected early adopters fooling the rest of the network into thinking it is common. The affected nodes then find it natural to follow the trend. A real spread finally comes into being.
But it is not yet a marketer’s charter. For that, marketers must first identify the popular nodes that can create the majority illusion for the merger audience. These influencers must then be persuaded to adopt the desired behavior or product, which is essential to the prospect of the marketing plan.
1. The phrase “skew the average” in the 3rd paragraph most probably refers to the action of __________.| A.hiding the real average to be unrecognizable to others |
| B.producing an average against the general feature of data |
| C.working out the common feature suggested by the average |
| D.ignoring the average because of the frequency by which it is reviewed |
| A.The number of the nodes in the network |
| B.The manner of the connection between the nodes. |
| C.The decision of which nodes to be colored. |
| D.The influence of the network on the nodes. |
| A.Majority illusion rarely bas impacts except in political blogs field. |
| B.The majority illusion on social networks relies on it that people you follow post more than you |
| C.The essence of successful opinion spread is to initiate the trend with well-connected sharers. |
| D.The spread scale of ideas on networks mainly depends on the quality of content. |
| A.thoroughly understand the concept of majority illusion |
| B.accurately figure out who is the powerful person to affect others |
| C.definitely decide who are the target audience for the promotion |
| D.successfully convince the influencers to practice certain action |
| A.The social network vision that tricks your mind. |
| B.Who is stealing your network identity? |
| C.Minority network opinion spread, curse or blessing? |
| D.Have you been misled during the last political voting? |
2 . What is it about kids these days that makes older generations so easily angry? In some way or another, older generations have been disappointed at the youth's decline since the earliest days of civilization. Even Aristotletalked smack abouthow young folks thought they knew everything back in the 4th century BC.
So why do people throw all the shade on the next generation? A study out last month in Science Advances shows that negative opinions about kids aren't always based on their actions; it's more about how adults praise their past and current selves.
In the study, researehers looked at a trio of characteristics in three groups of US adults: respect for elders or authoritarianism(权威主义),intelligence, and enjoyment of reading. The team, led by John Protzko, a cognitive scientist at the University of California, Santa Barbara, asked the participants whether they thought kids in the modern age shared the same qualities. They found that adults who tested especially strong in one of the categories tended to see children today as weak in il. For example, if an adult got tagged or self-identified as intelligent, they were more likely to see "kids these days" as less intelligent than they used to be. This, Protzko thinks, is because they remembered their younger selves to be smarter, whether true or not. What's more, they only reserved their strong opinion for characteristics they related to.
In another stage of the study, the authors assigned random scores to participants to trick them into thinking how well-read they were. Many of the adults changed their opinions on kid's reading ability as a result, Protzko speculates that there are two reasons for the shift: How memories can go wrong and the lack of objective knowledge of what childhood is really like. "People who are high in a trail are imposing(迫使)their current high standing in that trait back in time, thinking 'Oh this must have been what all kids were like,' " he says. Over the years, the same memory bias(偏见)keeps occurring, making it seem like kids are somehow failing more and more. In fact,(he older a participant was, the more heavily this bias came into play, Protzko says.
While there's still a lot to learn about why adults might see younger generations as mediocre, this researeh can hint that an age-old phrase can boil down to one classic human trail:vanity(自负).
―From Popular Science
1. What does the underlined phrase in the first paragraph mean?| A.Expressed his a flection for . | B.Talked positively about. |
| C.Spoke ill of. | D.Thought highly of. |
| A.Negative opinions about kids come from their ill behavior. |
| B.Adults always keeps their previous and present glories in mind. |
| C.Adults hold positive opinions about kids for their actions. |
| D.Kids are always blamed by adults who are more outstanding. |
| A.Because adults got tagged or self-indentified as intelligent. |
| B.Because adults thought they themselves much smarter. |
| C.Because adults hold the view that kids were weaker than them. |
| D.Because adults only remembered their own strengths subjectively. |
| A.Adults hold the bias that kids these days are failing. |
| B.Adults probably forgot all kids have the same characteristics. |
| C.That the same memory bias keeps occurring led to kid's failure. |
| D.The participants ignored the bias as they grew older. |
| A.①②--③④⑤ | B.①--②③④---⑤ |
| C.①②③--④---⑤ | D.①---②---③---④⑤ |
3 . By now you’ve probably heard about the “you’re not special” speech, when English teacher David McCullough told graduating seniors at Wellesley High School: "Do not get the idea you're anything special, because you're not." Mothers and fathers present at the ceremony — and a whole lot of other parents across the internet — took issue with McCullough's ego-puncturing words. But lost in the anger and protest was something we really should be taking to heart: our young people actually have no idea whether they're particularly talented or accomplished or not. In our eagerness to elevate their self-esteem, we forgot to teach them how to realistically assess their own abilities, a crucial requirement for getting better at anything from math to music to sports. In fact, it's not just privileged high-school students: we all tend to view ourselves as above average.
Such inflated (膨胀的) self-judgments have been found in study after study, and it's often exactly when we're least competent at a given task that we rate our performance most generously. In a 2006 study published in the journal Medical Education, for example, medical students who scored the lowest on an essay test were the most charitable in their self-evaluations, while high-scoring students judged themselves much more strictly. Poor students, the authors note, "lack insight" into their own inadequacy. Why should this be? Another study, led by Cornell University psychologist David Dunning, offers an enlightening explanation. People who are incompetent, he writes with co-author Justin Kruger, suffer from a "dual burden": they're not good at what they do, and their wry ineptness (笨拙) prevents them from recognizing how bad they are.
In Dunning and Kruger's study, subjects scoring at the bottom of the heap on tests of logic, grammar and humor "extremely overestimated" their talents. Although their test scores put them in the 12th percentile, they guessed they were in the 62nd. What these individuals lacked (in addition to clear logic, proper grammar and a sense of humor) was "metacognitive skill" (元认知技巧): the capacity to monitor how well they're performing. In the absence of that capacity, the subjects arrived at an overly hopeful view of their own abilities. There's a paradox (悖论) here, the authors note: “The skills that develop competence in a particular domain are often the very same skills necessary to evaluate competence in that domain. "In other words, to get better at judging how well we’re doing at an activity, we have to get better at the activity itself.
There are a couple of ways out of this double bind (两难). First, we can learn to make honest comparisons with others. Train yourself to recognize excellence, even when you yourself don't possess it, and compare what you can do against what truly excellent individuals are able to accomplish. Second, seek out feedback that is frequent, accurate and specific. Find a critic who will tell you not only how poorly you're doing, but just what it is that you're doing wrong. As Dunning and Kruger note, success indicates to us that everything went right, but failure is more ambiguous: any number of things could have gone wrong. Use this external feedback to figure out exactly where and when you screwed up.
If we adopt these strategies — and most importantly, teach them to our children — they won't need parents, or a commencement(毕业典礼) speaker, to tell them that they're special. They'll already know that they are, or have a plan to get that way.
1. The underlined phrase "took issue with" in paragraph 1 most probably means .| A.totally approved of | B.disagreed with |
| C.fully understood | D.held discussion about |
| A.we don’t know whether our young people are talented or not |
| B.young people can't reasonably define themselves |
| C.no requirement is set up for young people to get better |
| D.we always tend to consider ourselves to be privileged |
| A.They lack the capacity to monitor how well they are performing. |
| B.They usually give themselves high scores in self-evaluations. |
| C.They tend to be unable to know exactly how bad they are. |
| D.They are intelligently inadequate in tests and exams. |
| A.are not confident about their logic and grammar |
| B.tend to be very competent in their high-scoring fields |
| C.don't know how well they perform due to their stringent self-judgment |
| D.is very careful about their self-evaluations because they have their own limits |
| A.the best way to recognize excellence is to study past success and failure |
| B.through comparison with others, one will know where and when he fails |
| C.we need internal honesty with ourselves and external honesty from others |
| D.neither parents nor a commencement speaker can tell whether one is special |
| A.Special or Not? Teach Kids To Figure It Out |
| B.Let's Admit That We Are Not That Special |
| C.Tips On Making Ourselves More Special |
| D.Tell The Truth: Kids Overestimate their Talents |
4 . Smartphones are our constant companions. For many of us, their glowing screens are a ubiquitous (十分普遍的) presence, drawing us in with endless distractions. They are in our hands as soon as we wake, and command our attention until the final moments before we fall asleep.

Steve Jobs would not approve.
In 2007, Jobs took the stage and introduced the world to the iPhone. If you watch the full speech, you will be surprised by how he imagined our relationship should be with this iconic invention. This vision is so different from the way most of us use these devices now.
In his remarks, Jobs spent an extended amount of time demonstrating how the device utilized (应用) the touch screen before detailing the many ways Apple engineers had improved the age-old process of making phone calls. It’s the best iPod we’ve ever made,” Jobs exclaimed at one point. “The killer app is making calls,” he later added. Both lines drew thunderous applause.
The presentation confirms that Jobs imagined a simpler iPhone experience than the one we actually have more than a decade later. For example, there was no App Store when the iPhone was first introduced, and this was by design. Jobs was convinced that the phone’s carefully-designed native features were enough. He did not seek to completely change the rhythm of users’ daily lives. He simply wanted to take experiences we had already found important-listening to music, placing calls, generating directions-and make them better.
The minimalist (简约主义者) vision for the iPhone Jobs offered in 2007 is unrecognizable today-and that is a shame.
Under what I call the “constant companion model,” we now see our smartphones as always-on portals (通道) to information. We have become so used to it over the past decade that it is easy to forget the novelty (新奇之处) of the device. It seems increasingly clear to me that Jobs probably got it right from the very beginning: Many of us would be better-off returning to his original minimalist vision for our phones.
Practically speaking, to be a minimalist smartphone user means only using your device for a small number of features that do things of value to you. Otherwise, you simply put it away outside of these activities. This approach dethrones (废黜) this device from the position of a constant companion down to a luxury object, such as a fancy bike, that gives you great pleasure when you use it but does not dominate your entire day.

Early in his 2007 keynote, Jobs said, “Today, Apple is going to reinvent the phone.” What he didn’t add, however, was the follow-up promise: “Tomorrow we’re going to reinvent your life.” The smartphone is fantastic, but it was never meant to be the foundation for a new form of existence.
If you return this innovation to its original role, you will get more out of both your phone and your life.
1. The underlined word “it” in the last but two paragraphs probably refers to .| A.information | B.the smartphone |
| C.the always-on portal | D.the constant companion model |
| A.It allowed the users to have access to the internet. |
| B.It was actually an iPod that could make phone calls. |
| C.It was installed with applications by third-party developers. |
| D.It could fulfill people’s desire to multitask in their daily lives. |
| A.expect to reinvent his life with the device |
| B.buy the latest model of iPhone and see it as a luxury |
| C.remove all the unnecessary applications from the device |
| D.spend more time working than playing with his device |
| A.tell readers why Steve Job created the iPhone |
| B.remind readers not to be addicted to their smartphones |
| C.show readers that smartphones can greatly change our lives |
| D.encourage readers to block internet access on their smartphones |
5 . As the international demand for narrative(叙事的) film/TV content continues to increase with popular streaming services like Netflix and others the two questions then come: will the coming generations receive most of their entertainment through visual means rather than through the written word and will such an increase of narrative film/ TV reduce the importance of reading?
Growing examples of this trend include the diminishment(减少) of fiction in the common core (核心的)curriculum, the ever-rising culture of computer games, the wave of streaming services of wide international reach, and movies filled with special effects made for children and teenagers. Nor must we ignore the economic dangers that lie ahead for the written word. The narrative film industry is a moneymaker that dwarfs(使相形见绌) the publishing industry.
The other underlying question, of course, is “does it really matter if the written word bows to the world of film/TV?” From my point of view, any diminishment of fiction delivered by words is a loss for mankind.
There is no greater human feature than the imagination. It lies at the very soul of the human species. It is the brain’s most powerful engine. It is the essential muscle of life and like all muscles it must be exercised and strengthened.
Writing and reading are the principal tools that inspire, create and empower our imagination. Anything that diminishes that power is the enemy of mankind.
It should be known that I am not opposed to new media and technological advances. Instead, I have always felt it necessary to adapt to advancing technology. In fact, a number of my novels are in various stages of development for film, TV, and live stage productions. My hope is that the written word will only stand to be complemented(补充)by its visual counterparts(对应物), not pushed to the edge of extinction.
Of course, there are those who will present arguments for the superiority of the moving image over the written word. Each has its place. My argument is for finding the right balance between it and the moving image.
1. In what way does narrative film/TV embarrass the written word?| A.Economic benefits | B.International reach |
| C.Cultural influence | D.Educational importance |
| A.It strengthens our muscles. | B.It helps sharpen imagination. |
| C.It distinguishes man from each other. | D.It paves the way for narrative film/TV. |
| A.Cautious | B.Skeptical |
| C.Positive | D.Critical |
| A.The fate of reading. | B.The extinction of fiction. |
| C.The impact of the written word. | D.The future of the moving image. |
6 . British children used to play conkers (板栗游戏) in the autumn when the horse-chestnut trees started to drop their shiny brown nuts. They would select a suitable chestnut, drill a hole in it and thread it onto a string, then swing their conker at that of an opponent until one of them broke. But the game has fallen out of favour. Children spend less time outdoors and rarely have access to chestnut trees. Besides, many schools have banned conkers games, worried that they might cause injuries or nut allergies.
That sort of risk-averseness(规避风险) now spreads through every aspect of childhood. Playgrounds have all the excitement designed out of them to make them safe. Many governments, particularly in societies such as America, have tightened up their rules, requiring parents to supervise(监管) young children far more closely than in the past. Frank Furedi of the University of Kent, a critic on modern parenting, argues that allowing children to play unsupervised or leaving them at home alone is increasingly described as a symptom of irresponsible parenting.
In part, such increased caution is a response to the huge wave of changes. Large-scale urbanization, smaller and more mobile families, the move of women into the labor market and the digitization of many aspects of life have unavoidably changed the way that people bring up their children. There is little chance that any of these trends will be changed, so today's more intensive(精细化的) parenting style is likely to go on.
Such parenting practices now embraced by wealthy parents in many parts of the rich world, particularly in America, go far beyond an adjustment to changes in external conditions. They mean a strong bid to ensure that the advantages enjoyed by the parents’ generation are passed on to their children. Since success in life now turns mainly on education, such parents will do their best to provide their children with the schooling, the character training and the social skills that will secure access to the best universities and later the most attractive jobs.
To some extent that has always been the case. But there are more such parents now, and they are competing with each other for what economists call positional goods. This competition starts even before the children are born. The wealthy classes will take their time to select a suitable spouse and get married, and will start a family only when they feel ready for it.
Children from less advantaged backgrounds, by contrast, often appear before their parents are ready for them. In America 60% of births to single women under 30 are unplanned, and over 40% of children are born outside marriage. The result, certainly in America, has been to widen already massive social inequalities yet further.
All the evidence suggests that children from poorer backgrounds are at a disadvantage almost as soon as they are born. By the age of five or six they are far less “school-ready” than their better-off peers, so any attempts to help them catch up have to start long before they get to school. America has had some success with various schemes involving regular home visits by nurses or social workers to low-income families with new babies. It also has long experience with programmes for young children from poor families that combine support for parents with good-quality child care. Such programmes do seem to make a difference. Without extra effort, children from low-income families in most countries are much less likely than their better-off peers to attend preschool education, even though they are more likely to benefit from it. And data from the OECD’s PISA programme suggest that children need at least two years of preschool education to perform at their best when they are 15.
So the most promising way to ensure greater equality may be to make early-years education and care for more widely available and more affordable, as it is in the Nordics. Some governments are already rethinking their educational priorities, shifting some of their spending to the early years.
Most rich countries decided more than a century ago that free, compulsory education for all children was a worthwhile investment for society. There is now an argument for starting preschool education earlier, as some countries have already done. In the face of crushing new inequalities, a modern version of that approach is worth trying.
1. What can we learn from the first two paragraphs?| A.More attention is placed on children’s safety. |
| B.More and more parents are becoming irresponsible. |
| C.Children are no longer interested in outdoor activities. |
| D.Parents are advised to spend more time with their children. |
| A.Chances are that this style could be changed. |
| B.Financial pressure forces parents to be stricter. |
| C.Rich families adopt such style to keep their advantages. |
| D.Such style is largely influenced by the size of the family. |
| A.Economists offer practical advice to guide parenting. |
| B.A happy marriage secures children’s social positions. |
| C.Unfair division of social resources drives parents mad. |
| D.Parents are struggling for their children’s edge over peers. |
| A.Parents are persuaded to give birth to babies in their later years. |
| B.Funds are provided for poor children after they are admitted to school. |
| C.New babies in low-income families are sent to nurses or social workers. |
| D.Children from low-income families are ensured to receive early education. |
| A.Supportive | B.Disapproving |
| C.Skeptic | D.Unconcerned |
| A.show competition overweighs cooperation |
| B.imply educational inequalities should be broken |
| C.make readers aware of the rules of the game |
| D.indicate the game has lost its appeal to children |



