1 . The Japanese government said it planned to begin the discharge (排放) of slightly radioactive wastewater from the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear plant on Thursday, rejecting calls for a delay from some people in neighboring countries.
An earthquake and tsunami knocked out power at the Fukushima nuclear plant on March 11, 2011, causing meltdowns at three reactors. Tritium (氚) and carbon-14 are, respectively, radioactive forms of hydrogen (氢) and carbon, and are difficult to separate from water. They are widely present in the natural environment, water and even in humans, as they are formed in the Earth’s atmosphere and can enter the water cycle. Both emit very low levels of radiation but can pose a risk if absorbed in large quantities. Water which was used to cool reactor cores as well as rainwater and groundwater that flowed into or near the plant have been contaminated with radioactive substances. Plant operator Tokyo Electric Power, or Tepco, has stored the water in more than 1,000 tanks at the facility but says it is running out of room.
Tepco says it will reduce the concentration (浓度) of nearly all radioactive substances in the wastewater to a safe level with the exception of tritium, an isotope (同位素) of hydrogen. The water will then get diluted (稀释) with seawater so the concentration of tritium is reduced to a safe level before the discharge, according to Tepco. As the water is diluted further in the ocean, the concentration of tritium will almost equal the natural level by 6 miles from the discharge point, which is at the end of an undersea tunnel about six-tenths of a mile from the shoreline, a Tepco official said.
But that hasn’t reassured many of Japan’s neighbors, with officials from China and the Pacific Islands voicing alarm and opposition to the plan. Beijing will take “necessary measures” to safeguard food safety and its people’s health, said Chinese foreign ministry spokesperson Wang Wenbin on Tuesday, adding they “strongly urge the Japanese side to correct its wrongful decision”. Meanwhile, fishing communities in Japan and South Korea worry the wastewater release could mean the end of their livelihoods — with consumers across the region already beginning to quit seafood from Japan and its nearby waters, and some governments even banning imported food from parts of Japan, including Fukushima.
1. The meltdowns at three reactors were caused by ________.| A.the greenhouse effect | B.human behaviour |
| C.climate change | D.natural disasters |
| A.purified | B.reduced | C.polluted | D.operated |
| A.More than 1,000 tanks at the facility can store all the radioactive wastewater. |
| B.The concentration of all radioactive substances will be reduced to a safe level. |
| C.The discharge won’t affect the coastal residents since the discharge point is about 0.6 miles offshore. |
| D.The concentration of tritium will be nearly at the natural level after being diluted further in the ocean. |
| A.people in these areas couldn’t make a profit in the future |
| B.it would threaten people’s physical health and livelihoods |
| C.it would be more difficult to import food from parts of Japan |
| D.the local seafood would be unaffordable for people in these areas |
2 . Plastic is everywhere, from the Arctic ice to vital organs in the human body. In fact, previous estimates suggest that the average person swallows a credit card-worth of microscopic plastic particles(颗粒) every week. But new research shows that this could actually be an understatement.
Microplastics are plastics smaller than 5 millimeters, found in industrial waste, beauty products, and formed during the degradation of larger plastic pieces. Over time, they break down into even smaller nanoplastics. These tiny particles can pass through our intestines and lungs into our bloodstreams, reaching vital organs like the heart and brain.
While the idea of eating plastic is unsettling in itself, the major concern here is that these plastic particles contain chemicals that can interrupt our body’s natural release of hormones, potentially increasing our risk of reproductive disorders and certain cancers. They can also carry toxins(毒素) on their surface like heavy metals.
In the past, researchers have shown bottled water can contain tens of thousands of identifiable plastic fragments in a single container. However, until recently, only the larger microplastics were detectable with available measuring tools, leaving the area of nanoplastics largely a mystery.
Using Raman microscopy (显微镜学), capable of detecting particles down to the size of a flu virus, the team measured an average of 240, 000 particles of plastic per liter of bottled water, 90 percent of which were nanoplastics, a revelation 10 to 100 times larger than previous estimates.
These plastics likely originate from the bottle material, filters used to “purify” the water, and the source water itself. “It is not totally unexpected to find so much of this stuff, ” the study’s lead author, Columbia graduate student Naixin Qian, said in a statement. His team hopes to expand their research into tap water and other water sources to better inform our exposure to these potentially dangerous particles. “The idea is that the smaller things get, the more of them I reveal, ” he added.
1. What is the primary focus of the new research?| A.The presence of plastic particles. | B.The use of plastic in everyday products. |
| C.The detection methods for microplastics. | D.The potential risks of nanoplastics to human. |
| A.Finding the source of plastic particles. | B.Helping to cure the deadly flu virus. |
| C.Detecting the smaller plastic particles. | D.Improving the quality of bottled water. |
| A.To focus on areas with higher plastic pollution. |
| B.To be aware of the dangerous particles in daily life. |
| C.To further measure the types of particles in tap water. |
| D.To detect the smaller plastic particles in industrial areas. |
| A.Skeptical. | B.Objective. | C.Conservative. | D.Positive. |
E-waste, the world’s largest and fastest growing type of waste, doesn’t only come from computers but other electronics as well.  |
In 2019, the world produced 53. 6 million tons of e-waste.  |
The world’s e-waste will reach 74.7 million tons by 2030. That’s almost a doubling of e-waste in just 16 years. 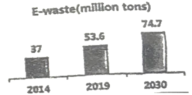 Today, only 15-20 percent of all e-waste is collected and recycled. |
Why should we recycle e-waste? E-waste has many valuable things in it, such as gold, silver and copper(铜). One smart phone battery can pollute 600,000 liters(升)of water. |
What can we do? ●Try to repair your electronics instead of buying new ones. ●Check for recycling organizations and give away your broken electronics. ●Remove any batteries (电池) because they need to be recycled separately. ●Tell others to recycle e-waste. |
1. In___________, the amount of e-waste reached about 37.3 million tons.
| A.2014. | B.2019. | C.2022. | D.2030. |
| A.E-waste only comes from computers. |
| B.In 2019, 53.6 million tons of e-waste was recycled. |
| C.We need to recycle batteries with other electronics. |
| D.We should consider repairing rather than buying new electronics. |
| A.instruction | B.novel | C.newspaper | D.comic book |
4 . Recycling is a great way of doing your bit for the environment and helping to protect the earth’s precious resources. However, a new study has revealed that our desire to be sustainable maybe doing more harm than good. According to waste company Biffa, this is because of “wish-cycling” — assuming that items such as disposable coffee cup sand pizza boxes will be recycled if put in the recycling bin. In fact, pollution from those items or other non-recyclables can result in recyclable items that have been put in the correct bin going to landfill. David Heaton, a business director at Biffa, said: “Pollution happens when items are disposed of in the wrong bins or haven’t been cleaned before being recycled.”
Experts at Biffa analyzed the amounts of non-target and non-recyclable materials that entered UK material recycling facilities between 2016 and 2020. It was found that, in 2016, the average pollution rate of recycling waste was 13.4 percent, rising over four years to 17 percent by the end of 2020. This shows that, even as people are becoming more eco-conscious, wish-cycling is increasing both in households and businesses.
The Biffa experts say that one of the best ways to prevent pollution of recycling is to clean recyclable waste before putting it in the bin. They suggest cutting off the top of old pizza boxes and only recycling that part to avoid pollution from the grease (油脂). Check the on-packaging recycling label to check it can actually be recycled When it comes to plastics, Biffa recommends checking the resin code, the number in the plastic triangle, to know whether it should go in the recycling bin. In general, resin codes 1, 2, 4 and 5 are recyclable, while 3, 6 and 7 are not. Larger items, like electronics, furniture and batteries, can also be recycled but often can not go in household recycling bins as they need specialist separating. These will need to be taken to recycling centers or sustainable waste management companies.
“It’s vital as a nation that we get better at effective ‘pre-cycling’— sorting waste correctly before collection to reduce pollution rates,” added Mr. Heaton.
1. What’s the truth of “wish-cycling” according to the first paragraph?| A.The desire to lead a sustainable life. |
| B.The good intention to help recycling. |
| C.The habit of throwing items that end up in landfills. |
| D.The practice of recycling items that can not be recycled. |
| A.People are becoming more eco-conscious. |
| B.Wish-cycling is on the rise in recent years. |
| C.Pollution happens less frequently in recycling facilities. |
| D.People are used to cleaning recyclable waste before putting it in the bin. |
| A.Dispose of electronics together with household waste. |
| B.Skip the step of checking the on-packaging recycling label. |
| C.Check the resin code of plastics to see whether it is recyclable or not. |
| D.Cutoff the top of old pizza box and throw the rest to the recycling bin. |
| A.Recycling: a Big Project | B.Wish-cycling: a New Trend |
| C.Wish-cycling: a Growing Concern | D.Pre-cycling: an Effective Method |
5 . Of the 8,300 million tons of virgin (原始的) plastic produced up to the end of 2015, 6,300 million tons have been discarded (丢弃). Most of that plastic waste is still with us, buried in landfills or polluting the environment. Microplastics have been found in Antarctic sea ice, in the guts of animals that live in the deepest ocean trenches and in drinking water around the world.
But what if we could wave a magic wand and remove all plastics from our lives? For the sake of the planet, it would be a tempting prospect — but we’d quickly find out just how far plastic has spread to every aspect of our existence.
In hospitals, the loss of plastic would be devastating. “Imagine trying to run a dialysis (透析) unit with no plastic”, says Sharon George, senior lecturer in environmental sustainability and green technology at Keele University in the UK. Plastic is used in gloves, tubing, blood bags, sample tubes and more.
Some everyday plastic items are also vital for protecting health. Face masks, including plastic-based surgical masks and respirators (人工呼吸器), as well as reusable cloth masks, have helped slow the spread of the COVID-19 virus. “A mask that you have for COVID is related to our safety and the safety of others,” says George. “The impact of taking that away could be loss of life if you took it away on a big scale.”
Our food system would also quickly come apart. We use packaging to protect food from damage in transit and preserve it long enough to reach supermarket shelves, as well as for communication and marketing. “I cannot imagine how plastic would be replaced completely in our system,” says Eleni Iacovidou, a lecturer in environmental management at Brunel University London.
Swapping out plastic packaging would have knock-on (产生连锁反应的) environmental effects. While glass has some advantages over plastic, such as being endlessly recyclable, a one-liter glass bottle can weigh as much as 800 g compared to a 40 g plastic one. When those heavier bottles and jars need to be transported over long distances, carbon emissions grow even more.
It’s clear that replacing one material with another won’t solve all our plastic problems.
1. What is the purpose of the first paragraph?| A.To give a definition. | B.To report on a study. |
| C.To introduce a topic. | D.To describe a phenomenon. |
| A.Interesting. | B.Practical. | C.Predictable. | D.Destructive. |
| A.Doubtful. | B.Supportive. | C.Optimistic. | D.Uninterested. |
| A.What if we stopped using plastic? |
| B.Is plastic packaging bad for the environment? |
| C.More recycling won’t solve plastic pollution |
| D.Swapping out plastic for sustainable living |
6 . A cap and trade system is a method for managing pollution, with the end goal of reducing the overall pollution in a nation, region, or industry. Many supporters of pollution control are in favor of the concept of such systems, arguing that well-designed cap and trade systems are extremely effective, and that they make sense economically as well.
Under a cap and trade system, a government authority first sets a cap, deciding how much pollution in total will be allowed. Next, companies are issued credits, essentially licenses to pollute, based on how large they are, what industries they work in, and so forth. If a company comes in below its cap, it has extra credits that it may trade with other companies.
For companies that come in below their caps, this system is great, because they can sell their extra credits, profiting while reducing their pollution. For companies that cannot get their pollution under control, the system punishes them for their excess pollution while still bringing overall pollution rates down. In a sense, the need to purchase credits acts as a fine, encouraging companies to reduce their emissions.
By creating a cap, nations make it clear that they want to reduce overall emissions, rather than just fining companies for excessive emissions or trying to force all companies to reduce their emissions by a set percentage. Cap and trade systems allow for flexibility, which usually benefits the market. Some people view the concept as preferable to a taxation or fining system, because it is easier to administer and it results in a pollution reduction. These systems are most commonly used for carbon emissions, leading people to refer to it as “carbon trading”, and there is a potential for a global carbon trading market, in which more efficient nations could trade credits with other countries.
1. What can be inferred about the cap and trade system?| A.It can greatly promote economy in a nation. |
| B.It will soon be welcomed by all companies. |
| C.It is well-designed and extremely effective. |
| D.It is environmentally and economically friendly. |
| A.Those who always have more extra credits. |
| B.Those whose overall pollution is below their caps. |
| C.Those who have never been fined for overall pollution. |
| D.Those who help other companies reduce their pollution. |
| A.All the pollution will be reduced by the cap and trade system. |
| B.Carbon trading is likely to be conducted among countries. |
| C.Carbon trade is more effective than the cap and trade system. |
| D.The taxation and fining system now is out of use. |
| A.The use of credits in reducing pollution. |
| B.Efficient ways to manage overall pollution. |
| C.An introduction of the cap and trade system. |
| D.Potential application of the cap and trade system. |
7 . Around the world, people are realizing the significant problems caused by plastic waste. In the last 65 years, we have become increasingly dependent on plastic. It’s easy to understand why: it’s cheap to produce, light — therefore easy and cheap to transport — and incredibly strong and durable.
One popular solution to the problem is to prohibit single use plastics. In the British supermarkets, shoppers are encouraged to make more environmentally-friendly choices in packing and transporting their food.
However, such plans may not be beneficial to eliminate (消除) the use of single-use plastic altogether.
Another issue is that alternative materials to plastic are often more environmentally harmful than plastic. Take paper bags, for example.
Clearly there is a need to reduce plastic waste and its impact on the environment.
| A.But it’s these advantages that also make it so harmful. |
| B.They are very fragile and rarely reusable, unlike plastic. |
| C.One of the fields where single-use plastic has a vital role is medicine. |
| D.However, simply banning their single use may not be the best option. |
| E.It also boosts the local economy and save costs in managing littering and waste. |
| F.Bans on single-use plastic items like drinking straws are also coming into place. |
| G.According to a research, they require four times more energy when produced than a plastic bag. |
8 . People often recommend planting trees to make cities greener, cleaner and healthier. But during heat waves, city trees can actually increase air pollution. Indeed, a new study finds that up to 60% of the ozone (臭氧) in a city’s air on hot days may have its origin in chemicals released by trees.
City trees offer a host of benefits. They provide cooling shade, absorb carbon dioxide, and also release oxygen into the air. But oxygen is far from the only gas that trees and certain other green plants release into the air. One of these chemicals is a hydrocarbon(碳氢化合物) that can react with burning pollutants, such as nitrogen oxides (氮氧化合物). The result is the formation of ozone which can cause airway diseases.
Galina Churkina works in Germany at Humboldt University of Berlin. She and her team wanted to explore how much chemicals released by trees could affect city air. To do this, the researchers turned to a computer. They asked it to model the likely reactions between plant chemicals and nitrogen oxides in air throughout the Berlin city area. To do that, the researchers fed in local weather data for two summers. One was 2006, when there was a heat wave. The other was 2014, when temperatures were mild.
An average daily high there in summer tends to be at roughly 25℃. On such a day, chemicals released by area greenery would likely have contributed to making about 6 to 20 percent of the ozone in the city’s air. But during a heat wave, when temperatures are more than 30℃ , tree-chemical emissions (发出物) are also high. As a result, they are now likely to be responsible for up to 60 percent of the ozone in air.
Churkina says her team was not surprised to see the contrary relationship between plants and pollution. The results, Churkina says, suggest city tree-planting programs should not ignore the role this greenery may play in bad summer air pollution. Adding more trees will improve quality of life only if those cities also undertake plans to sharply cut vehicle pollution (汽车污染).
1. What might people think of the new study finding?| A.Reasonable. | B.Intelligent. | C.Surprising. | D.Disappointing. |
| A.It is released by trees and other green plants. |
| B.It directly comes from the burning of oxygen. |
| C.A part of nitrogen oxides results in ozone in the end. |
| D.It is from the chemical reaction between a hydrocarbon and burning pollutants. |
| A.The higher the temperature is, the more ozone forms. |
| B.There’re no emissions of chemicals in spring or autumn. |
| C.Churkina suggests the number of city trees be lessened. |
| D.Churkina was surprised at seeing the contrary finding first. |
9 . Levels of an ozone-destroying chemical are mysteriously rising, despite international efforts to crack down on the problem. The uptick in the airborne chemical HCFC-141b comes even though reported production has declined steadily since 2012, leaving scientists stumped about the source. “All I can really say is these emissions are up,” says Luke Western, an atmospheric scientist at the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) Global Monitoring Laboratory, who helped lead the new research.
The discovery underscores the challenge of getting rid of these once widely used chemicals, which can linger in appliances for decades. It also shows how continent-size gaps in a network of sensors make it hard to pinpoint sources of the problem.The chemical, used chiefly to make foam insulation for appliances such as refrigerators, is part of a family of fluorocarbon molecules blamed for eating away at a layer of stratospheric ozone, roughly 20 kilometers above the ground, that filters out harmful ultraviolet radiation from the Sun. The world began to wean itself off these chemicals under the 1987 Montreal Protocol, widely considered the most successful international environmental treaty. Overall, ozone-damaging chemicals have declined steadily since the early 2000s, and the ozone “holes” above the poles have begun to heal.
In 2018, however, researchers reported that levels of the banned chemical CFC-11 had been rising since 2012. An international panel concluded that surge was likely due to illicit production, much of it in eastern China, perhaps because HCFC-141b, then used as a substitute for CFC-11 because it is less destructive to ozone, was in scarce supply. Releases of CFC-11 started to fall once again in 2019. By now production of HCFC-141b should also be declining. Its phase-out began in 2013, with a complete ban scheduled for 2030. It is already being replaced by a group of chemicals that doesn’t damage the ozone layer.
But scientists say atmospheric levels of HCFC-141b are actually rising. Emissions have climbed each year between 2017 and 2021, an increase totaling 3000 tons from 2017 to 2020, the researchers estimate. The findings, based on a combination of measurements from air sensors and computer models of how the gases move through the atmosphere, were posted online on 27 April by Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, although the paper hasn’t been peer reviewed yet. The rise of the newer chemical doesn’t appear to be a repeat of the CFC-11 incident, says Stephen Montzka, an atmospheric scientist who heads NOAA’s monitoring lab and led the work that uncovered the CFC-11 emissions. “I think in the instance of 141b the situation is much murkier,” he says. Results from air sensors in South Korea suggest the problem isn’t originating from eastern China. It does seem to be coming from somewhere in the Northern Hemisphere, because levels have risen faster there than in the south.
One possibility is that unreported HCFC-141b is being manufactured somewhere in the world, Montzka says. But the blip could also be temporary, triggered as aging appliances are thrown out and the foam breaks down, releasing the gas. “Taking a close look, we realized there are possible explanations that don’t require somebody doing something that they weren’t supposed to do,” Montzka says.The monitoring work in papers like this is “critical,” says Helen Walter-Terrinoni, a member of the Montreal Protocol’s technical panel and a chemical engineer with the Air-Conditioning, Heating, and Refrigeration Institute, which represents major manufacturers. The panel reports every 4 years on the state of ozone-depleting gases and the science surrounding them. Its new report, slated for 2023, “could help shed more light on what’s going on” with the rising emissions, Walter-Terrinoni says.
For now, gaps in the air sensor network have made answers elusive. The sensors are concentrated in North America and Europe, with only a handful in East Asia and at isolated sites elsewhere. Scientists are blind to what’s happening in much of India, Russia, and the Middle East, and most of Africa and South America. “If there were emissions in those regions,” Montzka says, “we wouldn’t be able to tell you very accurately where they are coming from.”
The picture could improve in the coming years. In the wake of the CFC-11 incident, an EU-funded initiative is underway to install more sensors and close some of those gaps. For now, Montzka isn’t alarmed about the added dose of chemicals. It amounts to a “small perturbation” in the ozone layer, he says, just a fraction of 1% of the ozone-damaging power of gases now in the atmosphere.
1. Which type of writing does this passage belong to?| A.Descriptive writing. | B.Expository writing. | C.Persuasive writing. | D.Narrative writing. |
| A.Valid. | B.Licensed. | C.Constitutional. | D.Illegal. |
| A.Ground filters out harmful ultraviolet radiation from the Sun. |
| B.The world began to wean itself off these chemicals. |
| C.Unreported HCFC-141b is being manufactured somewhere in the world. |
| D.Ozone-damaging chemicals haven’t declined steadily. |
| A.Atmospheric Levels of HCFC-141b Are Actually Rising |
| B.Bad Picture Could Improve in The Coming Years |
| C.Ozone-destroying Chemical Is on The Rise Despite Crackdown |
| D.Continent-size Gaps in Sensors Make It Hard to Pinpoint Sources of The Problem |
10 . With roaring ships, hammering oil drill, industrial fishing and coastal construction, humans have strongly influenced the underwater soundscape (声音景观) over the past couple of hundred years — in some cases posting a threat to whales, dolphins and other ocean creatures. Until recently, underwater sound pollution had not attracted the same attention. Now, a new paper published in the journal Science lays out the impacts, demonstrating that noise pollution can be just as harmful to the ocean environment as other kinds of pollution.
Even the cracking of glaciers and any drop of rain falling on the water’s surface can be heard deep under the sea. Sea life uses sound to study their habitat, and to keep in communication with each other. They also use sound by listening to know something about their environment.
“It’s a long-lasting problem that certainly weakens the animals all the way from individuals to populations,” says lead author Carlos M. Duarte, distinguished professor at Saudi Arabia’s King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST), “We are hoping that this report will not only reveal elements of how humans impact the ocean through sound pollution, but that it will also bring the topic to the attention of policymakers who will be able to act based upon the very real solutions.”
Marine (海洋) ecologist Kirsten Thompson of the United Kingdom’s University of Exeter, who was not involved in the study, said the report could not have come at a better time. “It summarizes the fact that we are in this new phase of human-caused noise in our oceans that is having a dramatic impact on different species.” What matters most, she notes, is the fact that the paper “doesn’t just point at the problem, it shows how to solve it.”
Unlike plastic pollution or fertilizer runoff, noise pollution will not take years to fix. The moment we switch our noise off the impact disappears, Duarte says, pointing to marine life surveys conducted around April 5, 2020. Having the world use more renewable energy would lessen the need to drill for oil and gas. The international team of researchers also called for a global regulatory framework for measuring and managing ocean noise.
1. Which of the following threatens ocean creatures?| A.Travel industry. | B.Human activities. |
| C.Construction companies. | D.Sailing off the coast. |
| A.Ocean animals can’t fall asleep. | B.It causes the cracking of glaciers. |
| C.It’s a signal to the lower sea level. | D.It disrupts the behavior of sea life. |
| A.She is one of the paper’s co-authors. |
| B.The report does not come at the right time. |
| C.The solutions are already available. |
| D.The report has raised great attention from seamen. |
| A.Technical advances and regulation. |
| B.A policy to measure the depth of ocean. |
| C.A global ban on drilling for oil and gas. |
| D.Noise standards for cars and trucks. |



