1 . We may think we're a culture that gets rid of our worn technology at the first sight of something shiny and new, but a new study shows that we keep using our old devices(装置) well after they go out of style. That’s bad news for the environment — and our wallets — as these outdated devices consume much more energy than the newer ones that do the same things.
To figure out how much power these devices are using, Callie Babbitt and her colleagues at the Rochester Institute of Technology in New York tracked the environmental costs for each product throughout its life — from when its minerals are mined to when we stop using the device. This method provided a readout for how home energy use has evolved since the early 1990s. Devices were grouped by generation — Desktop computers, basic mobile phones, and box-set TVs defined 1992. Digital cameras arrived on the scene in 1997. And MP3 players, smart phones, and LCD TVs entered homes in 2002, before tablets and e-readers showed up in 2007.
As we accumulated more devices, however, we didn't throw out our old ones. "The living-room television is replaced and gets planted in the kids' room, and suddenly one day, you have a TV in every room of the house," said one researcher. The average number of electronic devices rose from four per household in 1992 to 13 in 2007. We're not just keeping these old devices — we continue to use them. According to the analysis of Babbitt's team, old desktop monitors and box TVs with cathode ray tubes are the worst devices with their energy consumption and contribution to greenhouse gas emissions(排放)more than doubling during the 1992 to 2007 window.
So what's the solution(解决方案)? The team's data only went up to 2007, but the researchers also explored what would happen if consumers replaced old products with new electronics that serve more than one function, such as a tablet for word processing and TV viewing. They found that more on-demand entertainment viewing on tablets instead of TVs and desktop computers could cut energy consumption by 44%.
1. What does the author think of new devices?| A.They are environment-friendly. | B.They are no better than the old. |
| C.They cost more to use at home. | D.They go out of style quickly. |
| A.To reduce the cost of minerals. |
| B.To test the life cycle of a product. |
| C.To update consumers on new technology. |
| D.To find out electricity consumption of the devices. |
| A.The box-set TV. | B.The tablet. |
| C.The LCD TV. | D.The desktop computer. |
| A.Stop using them. | B.Take them apart. |
| C.Upgrade them. | D.Recycle them. |
1.小组观点;
2.陈述理由。
注意:
1.词数80左右;
2.请在答题卡的相应位置作答。
Hello, everyone!
_______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Thank you for listening!
Jean’s dream was to be a great chef, so when she was 20, she travelled to France, which has the most famous cuisine in the world, to learn to cook. After twelve years, she was among the best.
Her father, Bob, was getting old, and she wanted to be near him. Jean accepted an offer from one of Washington’s top restaurants. The manager offered her a handsome salary, and 30% ownership of the restaurant. The next day, Jean went to sign the contract. As she got out of the car, she caught sight of a green sunshade. Instead of going to meet the manager, she crossed the street towards the old restaurant, Fargonetti’s. She pushed open the door and the memories came flooding back.
Jean’s mum died when she was just 11, and her father lost his job and was forced to freelance (从事自由职业). Money was very short. When Jean turned thirteen, Bob had made a reservation at Fargonetti’s, the capital’s best restaurant.
“I’m not hungry, baby girl. I had a huge breakfast,” Bob said. “This is all for you!” “Oh,” Jean cried. “Daddy was so silly! He’s been saving to come here for lunch for MONTHS and now he ruined his appetite with breakfast!” The waiter, Carl Bader, immediately realised what was going on and went to Mr Fargonetti, the restaurant owner, and told him about Jean and Bob.
An hour later, surprisingly, the waiter brought wonderful dishes and set them before the father and daughter. “Lunch is on the house with Mr Fargoneti’s compliments (致意),” Carl said. For Bob and Jean, it was a free but magical meal. They were on cloud nine when they walked out. “Jean,“ said Bob happily. “I feel our luck has changed!” And it did! The next day, one of Bob’s old friends called and offered him a job at a new magazine, and Jean believed Fargonetti’s had made it all happen. That was when she decided to become a chef!
Twenty years later, the old restaurant looked run-down and sad, but Jean recognised the waiter immediately. “Carl?” she asked delightedly.
注意:1.续写词数应为150左右;2.请按如下格式在答题卡的相应位置作答。
The man looked surprised.
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________Jean was staring at Carl and a brilliant idea was taking shape in her mind.
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________4 . On a bright sunny day, I stared my day off by volunteering at the L. A. Food Bank. My reason for volunteering at the food bank was to satisfy my need to help others and leave a
By helping pack food items. I was able to make as significant impact on my community by helping people fight
| A.change | B.message | C.blank | D.chance |
| A.established | B.examined | C.entered | D.equipped |
| A.shabby | B.steady | C.tidy | D.noisy |
| A.check in | B.give up | C.show off | D.move out |
| A.aid | B.duties | C.awards | D.test |
| A.appointed | B.begged | C.forced | D.persuaded |
| A.consumed | B.inspected | C.searched | D.replaced |
| A.abandoned | B.delivered | C.packed | D.explored |
| A.represent | B.shelter | C.deserve | D.contain |
| A.studio | B.factory | C.museum | D.theatre |
| A.bank | B.list | C.step | D.row |
| A.quickly | B.secretly | C.casually | D.anxiously |
| A.burden | B.thought | C.regret | D.interest |
| A.recognize | B.welcome | C.help | D.visit |
| A.focus | B.respect | C.wisdom | D.ambition |
| A.understood | B.counted | C.led | D.heard |
| A.leadership | B.technical | C.social | D.business |
| A.prove | B.discover | C.stress | D.guarantee |
| A.fear | B.loneliness | C.hunger | D.doubt |
| A.direction | B.identity | C.belonging | D.satisfaction |
5 . Artificial—intelligence systems like Grammarly, an automated grammar—checker, are trained with data. for instance, translation software is fed sentences translated by humans, Grammarly's training data involve a large number of standard error—free sentences and human—corrected sentences.
But grammar is the real magic of language, joining words into structures, joining those structures into sentences, and doing so in a way that maps onto meaning.
| A.Grammarly can seem to miss more errors than it marks. |
| B.One Grammarly feature that works fairly well is feeing analysis. |
| C.To correct such writing requires knowing what the writer intended. |
| D.Grammarly has some obvious strengths in understanding meaning or intentions. |
| E.Computers outpace humans at problems that can be solved with pure maths. |
| F.Developers also add certain rules to the patterns Grammarty has taught itself. |
| G.In this decisive structure—meaning connection, machines are no match for humans. |
6 . The most important day I remember in all my life is the one on which my teacher, Anne Mansfield Sullivan, came to me. I am filled with wonder when I consider the immeasurable contrasts between the two lives which it connects. It was the third of March, 1887, three months before I was seven years old.
On the afternoon of that eventful day, I stood on the porch, dumb,
Have you ever been at sea in a dense fog, when it seemed as if a tangible white darkness shut you in, and the great ship, tense and anxious, groped her way toward the shore with plummet(铅锤) and sounding-line(测深索), and you waited with beating heart for something to happen? I was like that
I felt approaching footsteps. I stretched out my hand as I would to my mother. Someone
The morning after my teacher came she led me into her room and gave me a doll. The little blind children at the Perkins Institution had sent it and Laura Bridgman had dressed it; but I did not know this until
| A.hesitant | B.reluctant | C.expectant | D.defendant |
| A.consequently | B.unconsciously | C.deliberately | D.simultaneously |
| A.come forth | B.brought about | C.left behind | D.hidden away |
| A.panic | B.result | C.position | D.marvel |
| A.succeeded | B.exposed | C.inherited | D.demonstrated |
| A.fog | B.ship | C.shore | D.plummet |
| A.compassion | B.compromise | C.compass | D.companion |
| A.paradise | B.habitat | C.residence | D.harbor |
| A.took | B.shook | C.clung | D.rescued |
| A.share | B.devote | C.reveal | D.celebrate |
| A.beforehand | B.backward | C.afterward | D.forward |
| A.illustrate | B.exhibit | C.guess | D.imitate |
| A.fluttered | B.flourished | C.flashed | D.flushed |
| A.unrealistic | B.uncomprehending | C.unsurmountable | D.unproductive |
| A.title | B.name | C.credit | D.role |
7 . A new commodity brings about a highly profitable, fast-growing industry, urging antitrust(反垄断) regulators to step in to check those who control its flow. A century ago, the resource in question was oil. Now similar concerns are being raised by the giants(巨头) that deal in data, the oil of the digital age. The most valuable firms are Google, Amazon, Facebook and Microsoft. All look unstoppable.
Such situations have led to calls for the tech giants to be broken up. But size alone is not a crime. The giants’ success has benefited consumers. Few want to live without search engines or a quick delivery. Far from charging consumers high prices, many of these services are free (users pay, in effect, by handing over yet more data). And the appearance of new-born giants suggests that newcomers can make waves, too.
But there is cause for concern. The internet has made data abundant, all-present and far more valuable, changing the nature of data and competition. Google initially used the data collected from users to target advertising better. But recently it has discovered that data can be turned into new services: translation and visual recognition, to be sold to other companies. Internet companies’ control of data gives them enormous power. So they have a "God’s eye view" of activities in their own markets and beyond.
This nature of data makes the antitrust measures of the past less useful. Breaking up firms like Google into five small ones would not stop remaking themselves: in time, one of them would become great again. A rethink is required — and as a new approach starts to become apparent, two ideas stand out.
The first is that antitrust authorities need to move from the industrial age into the 21st century. When considering a merger(兼并), for example, they have traditionally used size to determine when to step in. They now need to take into account the extent of firms’ data assets(资产) when assessing the impact of deals. The purchase price could also be a signal that an established company is buying a new-born threat. When this takes place, especially when a new-born company has no revenue to speak of, the regulators should raise red flags.
The second principle is to loosen the control that providers of on-line services have over data and give more to those who supply them. Companies could be forced to reveal to consumers what information they hold and how much money they make from it. Governments could order the sharing of certain kinds of data, with users’ consent.
Restarting antitrust for the information age will not be easy. But if governments don’t want a data economy controlled by a few giants, they must act soon.
1. Why is there a call to break up giants?| A.They have controlled the data market. |
| B.They collect enormous private data. |
| C.They no longer provide free services. |
| D.They dismissed some new-born giants. |
| A.Data giants’ technology is very expensive. |
| B.Google’s idea is popular among data firms. |
| C.Data can strengthen giants’ controlling position. |
| D.Data can be turned into new services or products. |
| A.kill a new threat |
| B.avoid the size trap |
| C.favour bigger firms |
| D.charge higher prices |
| A.Big companies could relieve data security pressure. |
| B.Governments could relieve their financial pressure. |
| C.Consumers could better protect their privacy. |
| D.Small companies could get more opportunities. |
8 . Tolerance means tolerating or putting up with differences.
There are many different ways to show tolerance. A person might fully disagree with other on any issue,while at the same respecting those with different opinions and treat them with dignity
One problem is the fact this respect is sometimes one-sided.
Some degree of tolerance is necessary in any civilized society.
| A.Therefore, both parties should change their opinions if necessary. |
| B.It is widely accepted that tolerance is a critical step towards a peaceful world. |
| C.It refers to showing respect for the race, religion and opinions of other people. |
| D.Disagreement alone does not equal intolerance. |
| E.However, it is not realistic to believe that all people can achieve it completely on every issue. |
| F.Those who disagree with a particular issue must respect the opinions of those who support it. |
| G.When it comes to controversial issues,tolerance may also represent a let's agree to disagree attitude. |
9 . Up and down the economic ladder, many Americans who work—and especially those raising kids—are pressed for time, wishing they had more of it to devote to leisure activities (or even just sleeping). At the same time, research has indicated that people who are busy tend to be happier than those who are idle, whether their busyness is purposeful or not.
A research paper released late last year investigated this trade-off, attempting to pinpoint (精确指出) how much leisure time is best. Its authors examined the relationship between the amount of “discretionary time” people had—basically, how much time people spend awake and doing what they want—and how pleased they were with their lives.
The paper, which analyzed data covering about 35,000 Americans, found that employed people’s ratings of their satisfaction with life peaked when they had in the neighborhood of two and a half hours of free time a day. For people who didn’t work, the optimal (最佳) amount was four hours and 45 minutes.
The research traced a correlation (关联) between free time and life satisfaction, but didn’t provide any definitive (最后的) insight into what underlies that correlation—“which is exciting, because this is a work in progress,” says Cassie Mogilner Holmes, a professor at UCLA’s Anderson School of Management and a co-author of the paper, which hasn’t yet been peer-reviewed or published in an academic journal.
An experiment that the researchers arranged hinted at (暗示) a possible explanation of the correlation they found. They asked participants to picture and describe what it would be like to have a certain amount of daily free time, and then report how they’d feel about that allotment (分配). “What we find is that having too little time makes people feel stressed, and maybe that’s obvious,” says Holmes. “But interestingly, that effect goes away—the role of stress goes away—once you approach the optimal point.” After that point, Holmes says, the subjects started to say they felt less productive overall, which could explain why having a lot of free time can feel like having too much free time.
It’s not clear what an individual is to do with these findings, since the amount of free time people have usually has something to do with a variety of factors, such as having children or a degree of control over work schedules. Holmes shared her research with the MBA students in her class on happiness, and some of the most time-crunched among them were comforted by the findings: “I think that two and a half hours creates a nice goal that even if you increase a little bit more of your discretionary time use, you can expect that it will translate into greater life satisfaction.”
1. According to the passage, what happens to Americans occupied with their work?| A.They allow themselves more leisure time. |
| B.They keep themselves busy on purpose. |
| C.They know how much leisure time is best. |
| D.They experience higher level of satisfaction. |
| A.Researchers have cast light on the cause of the correlation. |
| B.Unemployed people need more leisure time to feel content. |
| C.The paper on the correlation has achieved peer recognition. |
| D.Employed people enjoy more leisure time in the neighborhood. |
A.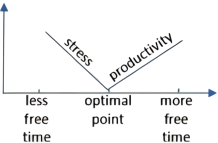 | B.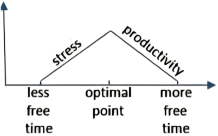 |
C.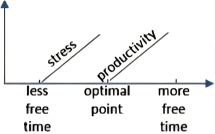 | D.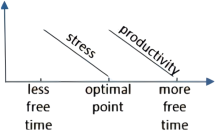 |
| A.Holmes is optimistic about the influence of her findings |
| B.individuals are encouraged to control their work schedules |
| C.people with tight schedules can’t benefit from the findings |
| D.the MBA students find no free time to obtain life satisfaction |
10 . Don't get mad the next time you catch your teenager texting when he promised to be studying. He simply may not be able to resist. A University of lowa(UI) study found teenagers are far more sensitive than adults to the immediate effect or reward of their behaviors. The findings may help explain why the initial rush of texting may be more attractive for adolescents than the long-term pay off of studying.
"For the teenager, 'the rewards are attractive." says Professor Jatin Vaidya,an author of the study. "They draw adolescent. Sometimes, the rewards are a kind of motivation for them. Even when a behavior is no longer in a teenager's best interest to continue, they will, because the effect of the reward is still there and lasts much longer in adolescents than in adults ."
For parents,that means limiting distraction (分心的事情)so teenagers can make better choices. Take the homework and social media dilemma: At 9 p.m., shut off everything except a computer that has no access to Facehook or Twitter, the researchers advise. "I'm not saying they shouldn't be allowed access to technology," Vaidya says. But some help in netting their concentration is necessary for them so they can develop those impulse-control skills.”
In their study,Vaidya and co-author Shaun Vecera note researchers generally believe teenagers are impulsive(冲动的),make bad decisions,and engage in risky behavior because the frontal lobes(额叶)of their trains are not fully developed. But the UI researchers wondered. whether something more fundamental was going on with adolescents to cause behaviors independent of higher-level reasoning.
"We wanted to try to understand the brain's reward system how it change from chillhood to adulthood," Says Vaidya, who adds the reward character in the human brain is easier than decision-making. “We've been trying to understand the reward process in adolescence and whether there is more to adolescence behavior than an under-developed frontal lobe,”he adds.For their study ,the researchers persuaded 40 adolescents, aged 13 and 16,and 40 adults, aged 20 and 35 to participate.
In the future,researchers hope to look into the psychological and neurological(神经学上的)aspects of their results.
1. What does the passage mainly tell us?| A.The initial rush of texting is less attractive for adolescents than the long-term pay off of studying. |
| B.Always, rewards are attractive to teenagers. |
| C.Resistance can be controlled well by adolescents. |
| D.Getting rewards is the greatest motivation for adolescents to study. |
| A.The influence of the reward is weak in adolescents. |
| B.Parents should help children in making decisions. |
| C.Children should have access to the Internet. |
| D.Children need help in refocusing their attention. |
| A.Doing things after some thought. |
| B.Making good decisions. |
| C.Joining in dangerous actions. |
| D.Escaping risky behavior. |
| A.By making a comparison of brain examinations. |
| B.By examining adults’ brain. |
| C.By examining teenage brain. |
| D.By building the train’s reward system. |



