1 . HANDSTITCHED WORLDS: THE CARTOGRAPHY OF QUILTS
Quilts (床罩) are a narrative art; with themes that are political, spiritual, communal, or commemorative, they are infused with history and memory, mapping out intimate stories and legacies through a handcrafted language of design. Handstitched Worlds: The Cartography of Quilts is an invitation to read quilts as maps, tracing the paths of individual histories that illuminate larger historic events and cultural trends.
Spanning the nineteenth to twenty-first centuries, this insightful and engaging exhibition brings together 18 quilts from the collection of the American Folk Art Museum, New York, representing a range of materials, motifs, and techniques from traditional early-American quilts to more contemporary sculptural assemblages. The quilts in Handstitched Worlds show us how this too-often overlooked medium balances creativity with tradition, individuality with collective zeitgeist. Like a road map, these unique works offer a path to a deeper understanding of the American cultural fabric.
Number of Works:18 quilts
Organized by: American Folk Art Museum, New York
Approximate size:175-200 linear feet
Security: Moderate security
Participation Fee: Please inquire
Shipping: IA&A makes all arrangements; exhibitors pay outgoing shipping costs within the contiguous U.S.
Booking Period:12 weeks
Tour: June 2021—August2024
Contact: TravelingExhibitions@ArtsandArtists.org
Leigh Yawkey Woodson Art Museum, Wausau, WI
June 12, 2021—August 29, 2021
Washington State Historical Society, Tacoma, WA
September 17, 2021—January 23, 2022
Utah Museum of Fine Arts, Salt Lake City, UT
February 19, 2022—May 14, 2022
Fort Wayne Muesum of Art, Fort Wayne, IN
June 18, 2022—September 11, 2022
AVAILABLE
October 2022—January 2023
Dane G. Hansen Memorial Museum, Logan, KS
February 17,2023—May 14, 2023
AVAILABLE
June 2023—December 2023
Lauren Rogers Museum of Art, Laurel, MS
January 30, 2024—April 21, 2024
AVAILABLE
May 2024—August 2024
All tour dates can be customized to meet your scheduling needs. Please contact Traveling Exhibitions @ Artsand Artists.org for more information.
1. What is the purpose of the exhibition of Handstitched Worlds: The Cartography of Quilts?| A.To promote creativity and individuality thorough the engaging exhibition. |
| B.To provide an opportunity for visitors to learn to make quilts stitch by stitch. |
| C.To give visitors an insight into the history and culture of America in specific periods. |
| D.To enrich the understanding of the American culture by a tour visit to museums across America. |
| A.The exhibition is free both for the exhibitors and for the visitors. |
| B.Exhibitors that are interested can choose whatever dates they want. |
| C.The artistic and historic value of handstitched quilts used to be neglected. |
| D.Exhibitors that are interested can book the exhibition 12 weeks in advance. |
| A.exhibitors | B.visitors | C.artists | D.historians |
2 . Neuro-technology has long been a favourite of science-fiction writers. In “Neuromancer”, a wildly inventive book by William Gibson written in 1984, people can use neural(神经的) implants to get into the sensory experiences of others. Iain M. Banks came up with the idea of a neural lace, a mesh (网格) that grows into the brain, in his “Culture” series of novels. “The Terminal Man” by Michael Crichton, published in 1972, imagines the effects of a brain implant on someone who is convinced that machines are taking over from humans.
Where the sci-fi led, philosophers are now starting to follow. In Howard Chizeck’s lab at the University of Washington, researchers are working on an implanted device to administer deep-brain stimulation (DBS) in order to treat a common movement disorder called essential tremor. Traditionally, DBS stimulation is always on, wasting energy and robbing the patient of a sense of control. The lab’s ethicist (伦理学家), Tim Brown, a doctoral student of philosophy, says that some DBS patients suffer a sense of isolation and complain of feeling like a robot.
To change that, the team at the University of Washington is using neuronal activity associated with intentional movements to turn the device on. But the researchers also want to enable patients to use a conscious thought process to override these settings. That is more useful than it might sound: stimulation currents for essential tremor can cause side-effects like distorted (失真的) speech, so someone about to give a presentation, say, might wish to shake rather than make his words unclear. Giving humans more options of this sort will be essential if some of the more advanced visions for brain-computer interfaces are to be realized. Hannah Maslen from the University of Oxford is another ethicist who works on a BCI project. One of her jobs is to think through the distinctions between inner speech and public speech: people need a dependable mechanism for separating what they want to say from what they think.
That is only one of many ethical questions that the sci-fi versions of brain-computer interfaces bring up. What protection will BCIs offer against neural hacking? Who owns neural data, including information that is gathered for research purposes now but may be understandable in detail at some point in the future? Where does accountability lie if a user does something wrong? And if brain implants are performed not for treatment but to improve people’s abilities, will that make the world an even more unequal place?
1. What do the three books mentioned in paragraph 1 have in common?| A.They are all among what philosophers like best. |
| B.They all tell the stories well beyond imagination. |
| C.They are all works of the greatest sci-fi writers of the time. |
| D.They all deal with people’s losing control of their brains. |
| A.improve the accuracy of DBS | B.let patients decide when to turn on DBS |
| C.get rid of the side effects of DBS currents | D.separate what we think from what we say |
| A.Neuronal activity fails to work without intentional movements. |
| B.Brain-computer interfaces do more harm than good. |
| C.People suffering from essential tremor will shake. |
| D.DBS settings cannot be changed once fixed. |
| A.How these questions will be handled. |
| B.Why these questions used to be ignored. |
| C.Which questions come from science fiction. |
| D.Who has first raised these questions. |
3 . How to Feel Connected
It's easy to feel disconnected from what is going on around you in today's fast-paced world.
Consider why you feel disconnected. Knowing what is making you feel disconnected can help you choose the best ways to address it.
Interact with people in person. Technology is a great way to stay in touch, but sometimes you need to spend time with other people in person.
Your loved ones could feel shy, so you may never know how to improve your relationship unless you ask the right questions. Asking them to open the doors can give you some insight on what you can do. Learning this information can help to strengthen your bond.
Show your commitment to them. Simply showing up and being there for your loved ones says a lot about how much you value your relationships. Putting in the time shows them that you are committed and want to stay connected.
Show appreciation. A simple “thank you” goes a very long way. Unfortunately, it is something that people who are close often take for granted. Telling someone you appreciate their time, love, and efforts can strengthen your bond and help you to become more connected.
| A.Ask others what they need from you. |
| B.Sometimes you can feel isolated and distant from the ones you love. |
| C.Be brave to express your love. |
| D.Reach out to people to schedule a time to get together. |
| E.Attending family events, or simply visiting someone once a week can help to strengthen your relationship and keep it strong. |
| F.Targeting your efforts toward those issues allows you to close that distance more effectively. |
| G.You can have a gift delivered to friends on special occasions. |
4 . The history of microbiology begins with Dutch cloth maker named Antoni van Leeuwenhoek, a man of no formal scientific education. In the late 1600s. Leeuwenhoek, inspired by the magnifying lenses(放大镜)he used to examine cloth, built some of the first-microscopes. He developed technique to improve the quality of tiny, rounded lenses, some of which could magnify an object up to 270 times. After removing some plaque from between his teeth and examining it under a lens, Leeuwenhoek found tiny twisting creatures, which he called “animalcules”.
His observations, which he reported to the Royal Society of London, are among the first descriptions of microbes(微生物). Leeuwenhoek discovered an entire universe invisible to the human eye. He found different microbes in samples of pond water, rain water, and human blood. He gave the first description of red blood cells, observed plant tissue, examined muscle, and investigated the life cycle of insects.
Nearly two hundred years later, Leeuwenhock’s discovery of microbes helped French chemist and biologist Louis Pasteur to develop his “theory of disease”. This concept suggested that disease originates from tiny organisms attacking and weakening the body. Pasteur’s theory later helped doctors to fight infectious diseases including anthrax, diphtheria, polio, smallpox, tetanus, and typhoid. All these breakthroughs were the result of Leeuwenhoek’s original work. Leeuwenhoek did not foresee this legacy.
In a 1716 letter, he described his contribution to science this way: “My work, which I’ve done for a long time, was not pursued in order to gain the praise I now enjoy, but chiefly from a strong desire for knowledge, which I notice resides in me more than in most other men. And therefore; whenever I found out anything remarkable, I have thought it my duty to put down my discovery on paper, so that the scientific community might be informed thereof.”
1. Which of the following best describes Leeuwenhoek?| A.trained researcher with an interest in microbiology |
| B.A curious amateur who made pioneer studies of microbes |
| C.A talented scientist interested in finding a cure for disease |
| D.A bored cloth maker who accidentally made a major discovery |
| A.the discovery of microbes |
| B.Pasteur’s theory of disease |
| C.Leeuwenhoek’s contribution |
| D.the origin of the tiny organism |
| A.He admitted that many of his discoveries happened by chance. |
| B.He considered his work to be central to later medical breakthroughs. |
| C.He was greatly concerned with improving people’s living conditions. |
| D.He believed the sharing of knowledge was a key to scientific progress |
a. Magnifying lenses were built.
b. The “theory of disease” was put forward
c. Microbes were discovered in samples of waters.
d. Leeuwenhoek’s first microscopes were successfully developed.
e. Leeuwenhoek explained his thoughts upon his own contribution.
| A.a-d-c-e-b | B.d-a-c-e-b | C.a-c-d-b-e | D.d-a-e-b-c |
5 . Pollution
Pollution happens when the environment is dirtied, by waste, chemicals, and other harmful substances(物质).Pollution is a problem all over the world. But it is especially bad in large cities with a lot of industries and cars.
Wildfires, volcanoes, and industrial chemicals cause some air pollution. But most air pollution comes from burning fossil fuels (矿物燃料)These include coal, oil and natural gas. The burning of fossil fuels may release harmful gases. Air pollution may cause such diseases cancer and asthma. It also leads to polluted rain that can harm living things
Causes of water pollution are easy to see. People dump(倾倒) garbage and dirty water into river, lakes and oceans. Factories or cities sometimes release poisonous chemicals, and other wastes into water. These chemicals may make the groundwater unfit to drink.
Littering, or throwing garbage on the ground, is a form of land pollution. Litter can destroy the habitats of plants and animals. The buildup of dangerous chemicals in the ground is another form of land pollution. The chemicals may come from farms or factories.
Many governments, environmental groups, and ordinary people are working to control pollution. Governments have passed laws to keep people from releasing dangerous chemicals into the environment
| A.Farmers use chemical to help crops grow. |
| B.This type of pollution may be seen in big cities. |
| C.They also can harm fish and other forms of life. |
| D.These chemicals can spread to plants and animals. |
| E.In addition, air pollution may be a cause of global warming. |
| F.There are three main forms of pollution: air, water, and land. |
| G.Some companies and people are trying to use fewer fossil fuels. |
6 . Modern medicine’s ability to keep us alive makes it tempting to think human evolution may have stopped. But if we look at the rate of our DNA’s evolution, we can see that human evolution hasn’t stopped – it may even be happening faster than before.
Evolution is a gradual change to the DNA of a species over many generations. It can occur by natural selection, when certain traits created by genetic changes help an organism survive or reproduce. Such genes are thus more likely to be passed on to the next generation, so they increase in frequency in a population. Gradually, these changes and their associated traits become more common among the whole group.
By looking at global studies of our DNA, we can see evidence that natural selection has recently made changes and continues to do so. Though modern healthcare disrupts a key driving force of evolution by keeping some people alive longer, in countries without access to good healthcare, populations are continuing to evolve. Survivors of infectious disease outbreaks drive natural selection by giving their genetic resistance to offspring. Our DNA shows evidence for recent selection for resistance of killer diseases like Lassa fever and malaria. Selection in response to malaria remains in regions where the disease remains common.
Humans are also adapting to their environment. Gene change allowing humans to live at high altitudes have become more common in populations in Tibet, Ethiopia, and the Andes. The spread of genetic changes in Tibet is possibly the fastest evolutionary change in humans, occurring over the past 3,000 years. This rapid increase in frequency of a mutated gene that increases blood oxygen content gives locals a survival advantage in higher altitudes, resulting in more surviving children.
Diet is another source for adaptations. Studies show that natural selection favoring a change allowing adults to produce lactase – the enzyme (酶) that breaks down milk sugars – is why some groups of people can digest milk. Over 80 per cent of northwest Europeans can, but in parts of East Asia, where milk is much less commonly drunk, an inability to digest lactose is the norm. Like high altitude adaptation, selection to digest milk has evolved more than once in humans and may be the strongest kind of recent selection.
Yet, despite these changes, natural selection only affects about 8 per cent of our genome. But scientists can’t explain why some genes are evolving much faster than others. We measure the speed of gene evolution by comparing human DNA with that of other species. One fast-evolving gene is human accelerated region 1 (HAR1), which is needed during brain development. A random section of human DNA is on average more than 98 per cent identical to the chimp comparator, but HAR1 is so fast evolving that it’s only around 85 per cent similar. Though scientists can see these changes are happening – and how quickly – we still don’t fully understand why fast evolution happens to some genes but not others.
1. Which of the following statements may the author agree with?| A.Evolution occurs among several people overnight. |
| B.Genes may change and some are beneficial to people’s lives. |
| C.Evolution is done when the whole population possesses a certain gene. |
| D.The changed genes leading to higher survival rates are chosen deliberately. |
| A.explains | B.causes | C.upsets | D.heals |
| A.some people can resist infectious diseases like malaria |
| B.children in Tibet tolerate living environments with thin air |
| C.northwestern Europeans digest lactose better than East Asians |
| D.the human gene HAR1 resembles that of a chimp to a lesser extent |
| A.What Is Natural Selection? |
| B.Are Humans Still Evolving? |
| C.Why Will Certain Genes Evolve? |
| D.How Do Mutated Genes Function? |
7 . It’s late in the evening, time to close the book and turn off the computer. You’re done for the day. What you may not realize, however, is that the learning process actually continues in your dreams.
It might sound like science fiction, but researchers are increasingly focusing on the relationship between the knowledge and skills our brains absorb during the day and the often strange imaginings they generate at night. Scientists have found that dreaming about a task we’ve learned improves performance in that activity (suggesting that there’s some truth to the popular idea that we’re “getting” a foreign language once we begin dreaming in it). What’s more, dreaming may be an essential part of understanding, organizing and retaining what we learn.
While we sleep, research indicates, the brain replays the patterns of activity it experienced during waking hours, allowing us to enter what one psychologist calls a neural (神经的) virtual reality. A vivid example of such replay can be seen in a video researchers made recently about sleep disorders. They taught a series of dance moves to patients suffering from sleepwalking and related conditions. They then videotaped the subjects as they slept. Lying in bed, eyes closed, one female patient on the tape performs the dance moves she learned earlier.
This shows that while our bodies are at rest, our brains are drawing what’s important from the information and events we’ve recently encountered, then integrating that material into the vast store of what we already know. In a 2010 study, researchers reported that college students who dreamed about a computer maze (迷宫) task they had learned showed a 10-fold improvement in their ability to find their way through the maze compared with participants who did not dream about the task.
That study’s chief researcher Herbert Smith suggested that studying right before bedtime or taking a nap following a study session in the afternoon might increase the probability of dreaming about the material. Think about that as you go to sleep tonight.
1. What happens when one enters a dream state?| A.The body continues to act as if the sleeper were awake. |
| B.The neural activity of the brain will become intensified. |
| C.The brain once again experiences the learning activities of the day. |
| D.The brain behaves as if it were playing a virtual reality video game. |
| A.It replaces old information with new material. |
| B.It processes and absorbs newly acquired information. |
| C.It regroups information and places it in different files. |
| D.It systematizes all the information collected during the day. |
| A.Staying up late before finally going to bed. |
| B.Having a period of sleep right after studying. |
| C.Having a dream about anything you are interested in. |
| D.Thinking about the chances of dreaming about the material. |
| A.How study affects people’s dreams. |
| B.Why people learn more after sleeping. |
| C.What time students should study and sleep. |
| D.How dreaming may lead to improved learning outcomes. |
8 . Imagine looking at a view of mountaintops and wondering about the name of each peak. Suddenly, above each mountaintop, a name appears on the sky. The words are not written in smoke by skywriting planes. The words are actually not in the sky at all. They come from tiny computers in contact lenses (隐形眼镜).
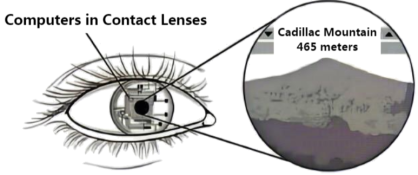
Computers have become smaller and smaller over the decades. The first computers filled houses. Transistors (晶体管) and then chips allowed computers to become small enough to fit on a desktop, then a laptop, and finally a phone. When experimenting with further contraction in size, developers often have to deal with the limits of human eyesight, which control how small the computers can be and still present visible information.
One new solution employs microprojectors (微型投影机) to create a readable display (显示) for tiny computers. These machines project computer information onto any surface. Though an impressive breakthrough, there are potential problems. Such public displays can lead to privacy concerns; most people do not want their information displayed on a wall for everyone to see. Besides, these projectors are extremely expensive, and their screens give users headaches.
Babak Parviz, a researcher at the University of Washington, created another solution: inventing a screen visible only to a person wearing a contact lens. Parviz created a computer in a contact lens that uses the wearer’s field of vision as the display. To create the display, Parviz took ordinary soft contact lenses with a wirelessly controlled system. At some point, Parviz says, it will be possible to connect the lens to a remote personal computer device such as a cellphone or a laptop. By looking in a certain direction, the wearer sends the computer visual information about what he or she sees. The device then uses this information to point out the names of peaks.
These contact lenses are inserted and removed in much the same way as ordinary contact lenses. In addition, the computers in the lenses won’t block the wearer’s sight at all. Although now the computers are not on lenses treating eyesight problems, Parviz hopes that someday the technology will progress to that level.
1. The contact lenses in the text can ________.| A.treat eyesight problems | B.offer beautiful views of nature |
| C.project information on wall surface | D.show information about what wearers see |
| A.expansion | B.spread |
| C.reduction | D.revolution |
| A.put people’s privacy at risk | B.save computer information |
| C.cause serious illnesses | D.support users’ needs |
| A.saving users’ expenses | B.reducing computers’ size |
| C.limiting the field of vision | D.guarding remote computers |
| A.Tiny Computers, Amazing Sights | B.Smaller Lenses, Closer Views |
| C.Progress towards Clearness | D.Road to the Small World |
9 . A block chain is a data structure that stores time-ordered data in an ever-growing list, like an accounting ledger (分类账簿). The block chain data structure is maintained using a distributed, peer-to-peer network of computers with no central “master”. As with many new concepts, block chain technology generates much optimism and also a huge amount of interest and excitement. Just what is it good for?
In short, block chains may improve any process where people need to access, confirm, send or store information securely. This information could be a person’s identity, a product’s shipment history or digital property like money.
Typical databases, spreadsheets (电子数据表), and ledgers store information about objects, people, and the interactions between them. Much of the world’s information, from credit card transactions to medical and financial records, is stored in these types of systems.
These types of systems have considerable, well-documented weaknesses that arise from their being centralized. A centralized record is hard to understand and is exposed to unauthorized access or distribution. It is also, because it is a ‘master’ copy, exposed to permanent changing or deletion.
Block chains are also used to store information. Crucially, however, they differ in two ways.
First, information is parceled up into blocks and sealed. Bitcoin, for example, which is the most famous practical example of a production block chain, stores all transactions across the network every ten minutes or so in a single, newly formed block. Each block is then added to the previous one to form a chain.
Second, this “chain of blocks” is not stored centrally. Instead, each block is copied and distributed around an entire network of peers - be they individuals, public institutions, or businesses - using distributed ledger technology. (The terms “block chain” and “distributed ledger” are often used interchangeably; for the sake of clarity, block chain technologies tend to employ distributed ledger technology.)
Each time someone adds a new block to the chain, meanwhile it is added to everyone’s copy.
1. What is the biggest strength of a block chain?| A.It promotes people’s enthusiasm about new technology. |
| B.It strengthens the security of processing information. |
| C.It enables people to store more data in time order. |
| D.It stores a large part of world’s information. |
| A.they are difficult to operate | B.they can be accessed easily |
| C.they have a central “master” | D.they store considerable documents |
| A.making comparisons | B.giving examples |
| C.making a list | D.showing the effect and causes |
| A.To analyze the weaknesses of typical systems. |
| B.To encourage the popularity of the block chain. |
| C.To introduce the new concept of the block chain. |
| D.To compare the two different data structures. |
10 . A robot created by Washington State University (WSU) scientists could help elderly people with dementia (痴呆) and other limitations live independently in their own homes.
The Robot Activity Support System, or RAS, uses sensors installed in a WSU smart home to determine where its residents are, what they are doing and when they need assistance with daily activities. It navigates (定位) through rooms and around obstacles to find people on its own, provides video instructions on how to do simple tasks and can even lead its owner to objects like their medication or a snack in the kitchen.
“RAS combines the convenience of a mobile robot with the activity detection technology of a WSU smart home to provide assistance in the moment, as the need for help is detected,” said Bryan Minor, a postdoctoral researcher in the WSU School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science.
Currently, an estimated 50 percent of adults over the age of 85 need assistance with every day activities such as preparing meals and taking medication and the annual cost for this assistance in the US is nearly $2 trillion. With the number of adults over 85 expected to triple by 2050, researchers hope that technologies like RAS and the WSU smart home will relieve some of the financial strain on the healthcare system by making it easier for older adults to live alone.
RAS is the first robot researchers have tried to incorporate into their smart home environment. They recently published a study in the journal Cognitive Systems Research that demonstrates how RAS could make life easier for older adults struggling to live independently.
“While we are still in an early stage of development, our initial results with RAS have been promising,” Minor said. “The next step in the research will be to test RAS’ performance with a group of older adults to get a better idea of what prompts, video reminders and other preferences they have regarding the robot.”
1. How does RAS serve elderly people?| A.Through sensors. | B.Through objects. |
| C.Through a mobile robot. | D.Through their daily activities. |
| A.It is the first robot used in daily life. | B.Its function remains to be tested. |
| C.It can locate people and do any task. | D.It can cook for owners on its own. |
| A.Doubtful. | B.Negative. |
| C.Optimistic. | D.Uncertain. |
| A.Elderly people leave the nursing home. |
| B.Smart Home Tests first elder-Care robot. |
| C.RAS, the first robot to make home smart. |
| D.Older adults have benefited from RAS. |



