1 . A Fluent Advantage
When schools go through budget cuts, foreign language classes are often placed on the cutting block. School administrators often do not understand how important foreign language study is for their students’ success in the real world. Far from cutting language classes, schools should be demanding them for all students. Studying a foreign language should be required in middle schools.
Language study strengthens students’ minds. Many studies have indicated that multilingual people—people who speak more than one language—are better at certain tasks. Specifically, multilingual people have better executive function than people who speak only one language. Executive function is the way the brain manages all the information it’s given, such as performing different tasks and deciding what to focus on. In brain scans, multilingual people show increased activity in the areas of the brain that control executive function. Researchers have guessed that this advantage exists because multilingual people must constantly decide which words from which language to use. As a result, multilingual people get lots of practice with executive function. Their brains can then apply those skills to other tasks, like paying attention or multitasking. This effect is especially strong for people who grow up speaking more than one language. The earlier students start language classes, the more benefits they may get from language study.
Moreover, language study helps prepare students for their future careers. Today, language skills are in high demand on the job market and more and more businesses work in many countries across the world. As businesses become global, they need people who can communicate easily across national borders. To prepare for their careers, more students should be learning foreign languages. From 2010 to 2015, the demand in the United States for workers who speak a second language doubled. This trend included workers of all skill levels and backgrounds.
Of course, in order to make better use of the advantages of foreign language study, middle school foreign language classes should not just make students memorize new words and sounds.
They must also teach students about new cultures. Foreign language classes should be required to include lessons about history, literature, customs, and government along with the languages themselves. These subjects will help students become better global citizens and support their studies in other subjects.
Requiring middle schoolers to study a foreign language offers them opportunities to sharpen their brains. It also gives them tools that will help them become productive members of today’s global society.
1. How does the author feel about foreign language study in middle schools?| A.More foreign language classes should be offered in middle schools. |
| B.Taking a foreign language class in middle schools should be a choice. |
| C.Foreign language classes should be cut because of the limited funds. |
| D.Studying a foreign language should be a middle school requirement. |
| A.people who speak more than one language have better executive function |
| B.being able to work in another country doubles people’s job opportunities |
| C.people learn languages better as young people than when they are older |
| D.people’s executive function improves after foreign language classes |
| A.To sum up his argument. | B.To put forward a solution. |
| C.To emphasize his point of view. | D.To introduce an additional suggestion. |
I: Introduction P: Point Sp: Sub-point (次要点) C: Conclusion
A.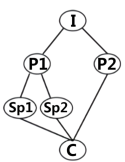 | B.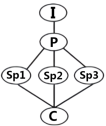 |
C. | D. |
1. 介绍同学们的听说训练情况;
2. 希望提供更有效的学习方法;
3. 询问对方的意向。
注意:1. 词数不少于80;
2. 邮件的开头和结尾已给出,不计入总词数。
Dear Jim,
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Yours,
Li Hua
3 . Some people say global English is no longer just controlled by British or American English,but is running free and developing uniquely local forms.Can you figure out the following terms?
“I like your smile,but unlike you put your shoes on my face.”This is a way of saying“Keep off the grass.”Or“people mountain,people sea”,which means“very crowded”.
These examples are what we call Chinglish.When it comes to Chinglish,if all you know is“good good study,day day up”,you will be considered“out man”.
Nowadays,more Chinglish words have been created,for example,a Chinese idiom is translated as“smilence”,a combination by the English word smile and silence.
Chinglish usually offers a humorous look at misuses of the English language in Chinese street signs,products,and advertising.They are favoured by some English speaking tourists and visitors.Dominic Swire has been living in Beijing for a couple of years.“I think many Chinese people complain about the Chinglish and badly translated English.But you know,sometimes for us foreigners,it’s actually quite charming to see them.I think if the translations of English in China were all perfect,then something would be lost from Chinese culture.”
However,Chinglish will probably become a“cultural relic”in the near future.Beijing has made a comprehensive plan to improve foreign language services and correct Chinglish within five years.“It is very ridiculous to see Chinglish on the signs in some scenic spots.And they are a kind of barrier for communication between Chinese and people from other countries,”a Beijinger said.
Some Chinese university experts side with Chinglish.They argue that English has absorbed elements from other languages such as French and Spanish in its growth,and now it’s Chinese’s turn.
1. What can we call Chinglish?| A.English words which get new Chinese meanings. |
| B.The Chinese words which are difficult to translate. |
| C.The words combining English vocabulary and Chinese grammar. |
| D.The local words preventing foreigners from learning Chinese well. |
| A.Saying nothing but to smile. | B.Smiling without being noticed. |
| C.Laughing at somebody. | D.Knowing little about speech. |
| A.It can show the humour of Chinese. | B.It will attract more foreign tourists. |
| C.It helps him to learn Chinese well. | D.It seems part of Chinese culture. |
| A.Because it has become a unique bridge between Chinese and English. |
| B.Because Chinglish is a chance to enrich Chinese and English. |
| C.Because it improves the understanding between Chinese and foreigners. |
| D.Because Beijing is determined to get rid of Chinglish signs. |
The Chinese language has become increasingly popular in the world. More British students chose to take Chinese tests than German in this year's A levels, showing a great
This is the first time that Mandarin
A total of 3,334 candidates chose Mandarin
French and Spanish still remain the most popular foreign languages. The German language
According to the Office of Chinese Language Council International, as of 2017, some 100 million people, excluding native speakers, use Chinese
South Korea has a
The United Nations in 2010 suggested a Chinese Language Day which falls on April 20th each year to celebrate cultural diversity as well as to promote the equal use of all official languages.
5 . Experts say over half of the world’s 7,000 languages are in danger of disappearing. Every two weeks one language disappears. As the last speakers of a language die off, the valuable information contained within a language also disappears.
What would happen if you were the only person left who spoke your language? Who would you share stories with, sing songs to, or exchange jokes with?
Sometimes a language disappears immediately when the last person speaking it dies.
So, smaller cultures lose their local language as the language of the culture in power becomes the stronger influence.
Languages contain the histories, ideas and knowledge of a culture. Languages also contain valuable information about local medicines, plants and animals. Many endangered languages are spoken by native cultures in close connection with the natural world.
The Internet could be thought of as a new method of language control. The United Nations cultural organization — UNESCO, says that ninety percent of the world’s languages are not shown on the Internet.
| A.Learn a language that will disappear now. |
| B.Or a local language might disappear more slowly. |
| C.That’s why endangered languages must be protected. |
| D.Protecting languages is very important for these reasons. |
| E.The more powerful culture almost never respects that of smaller groups. |
| F.Who would understand your names for local plants, animals and traditions? |
| G.Your interest in language may be changed with more languages disappearing. |
6 . Communicating effectively means more than knowing what to say and when to say it. Communication involves the subtle signals your body language sends to those who are watching. Here are some common body actions and the impressions they create:
● Fiddling (好动) — Playing with your watch or a pen looks like you’re bored or impatient.
● Clock watching — It looks like you’re to move on to something else.
● Tapping — Tapping your feet or fingers suggests you are impatient or nervous.
● Staring — An unblinking (不眨眼的) stare conveys threatening or violent behaviour.
● Legs crossed or body hunched (弓背,耸肩) — Closing up your body profile — becoming smaller — looks like you lack confidence.
● Arms crossed — If you keep your arms folded during communication, you appear to be defending yourself against the others.
● Touching your face — When you have your hand in front of your mouth, you appear very shy.
● Rubbing your nose, looking away — People who are lying often rub their nose or look away when speaking.
● No eye contact — If you won’t look the other speaker in the eye, you seem to have low interest or a lack of confidence. (Don’t forget staring above.)
How you communicate with your body language is just as important as what you say. Watch your body language and control the unconscious messages you might be sending.
1. According to the passage, effective communication includes all of the following EXCEPT _____.| A.knowing what to say |
| B.sending unconscious messages to other people |
| C.saying the right thing at the right time |
| D.getting information from the other speaker’s body language |
A. | B. |
C. | D. |
| A.cross your legs or hunch your body |
| B.avoid direct eye contact |
| C.look the other speaker in the eye |
| D.keep touching your face |
| A.How to make a good impression on others |
| B.Can you read body language? |
| C.Control your body language for effective communication |
| D.How to send effective information through body language |
7 . Ma uka, ma uka ka ua,
Ma kai, ma kai ka ua
So sing the children at Hawaiis Punana Leo Hilo kindergarten on the Big Island of Hawaii. The chant is much like any other “Rain, rain, go away” nursery rhyme, but it has an unusual power: it is one of the tools that has brought about the revival(复兴)of a near-dead language.
The decline of Hawaiian was not, as is the case with most disappearing languages, a natural death caused by migration and mass media. In 1896, after the overthrow of the Hawaiian monarchy (君主政体) by American business interests, schools were banned from using the language, and children were beaten for speaking it. By the late 20th century, aside from a couple of hundred people on one tiny island, English had replaced Hawaiian and only the old spoke the language to each other.
Larry Kimura, a professor there, and his students wanted to bring it back to life. In 1985, when educating children in Hawaiian was still banned, Kauanoe Kamana and her husband Pila Wilson, both students of Kimura's created the first Punana Leo (which means language nest) at Hilo. They gathered together a small group of children and elderly native speakers. The movement grew: there are now 12 kindergartens and 23 schools. The number of children being educated in Hawaiian has risen from 1,877 in 2008 to 3,028 in 2018. Along with Japanese, Hawaiian is the non-English language most commonly spoken among children.
The success has been hard-won. Campaigners had to get the law changed. “People in the community, even in our families, were saying: ‘You'll ruin your children's future. They won't be able to go to college.’ ” Such fears turned out to be unfounded. All the pupils at Nawahi, the main Hawaiian-medium school, complete high school, compared with the state average of 83%; 87% go to college, compared with a state average of 55%.
But academic outcomes are not the primary focus, says Mr. Wilson. “We value our connection with our ancestors more than we value being millionaires,” he says. Mr. Kimura explains that the schools have allowed Hawaiians to pass on their culture.
1. What made the Hawaiian language nearly die out?| A.Migration. | B.The ban on it. |
| C.Mass media. | D.Population decline. |
| A.Going on a strike. | B.Supporting the law. |
| C.Setting up a community college. | D.Educating more local children in it. |
| A.Making a fortune by learning it. | B.Focusing on academic outcomes. |
| C.Passing on the Hawaiian culture. | D.Reducing the influence of English. |
| A.The value of Hawaiian. | B.The revival of Hawaiian. |
| C.The popularity of Hawaiian. | D.The near-death of Hawaiian. |
8 . A crucial period for learning the rules and structure of a language lasts up to around age 17 or 18, say psychologist Joshua Hartshorne of MIT and his colleagues.
Previous research had suggested that grammar-learning ability developed in early childhood before hitting a dead end around age 5. However, Hartshorne’s team reports online in Cognition that people who started learning English as a second language in an English-speaking country by age 10 to 12 ultimately mastered the new tongue as well as folks who had learned English and another language at the same time from birth. Both groups, however, fell somewhat short of the grammatical fluency displayed by English-only speakers. After ages 10 to 12, new-to-English learners reached lower levels of fluency than those who started learning English at younger ages because time ran out when their grammar-absorbing ability fell starting around age 17.
Aiming for a sample of tens of thousands of volunteers, Hartshorne began by contacting friends on Facebook to take an online English grammar quiz, which used a person’s responses to guess his or her native language and dialect (方言) of English. Then volunteers filled out a questionnaire asking where they had lived, languages they had spoken from birth, the age at which they began learning English and the number of years they had lived in an English-speaking country.
In the end, the researchers analyzed responses of 669,498 native and nonnative English speakers. Statistical calculations focused on estimating at what ages people with varying amounts of experience peaking English reached peak grammar ability.
Researchers who study language learning regard the new study as fascinating, but exploratory. According to psycholinguist David Barner of the University of California, San Diego, Hartshorne’s team can’t yet say that language skill develops along a single timeline. Different elements of grammar, such as using correct word order or subjects and verbs that agree with one another, might be learned at different rates, Barner says. It’s also unclear whether the responses of volunteers to an online, 132-item grammar test reflect how well of poorly they actually speak English, he says.
What’s more, language learning involves more than a crucial period for acquiring grammar, cautions linguist David Birdsong of the University of Texas at Austin. For instance, growing up speaking two languages at once puts still poorly understood burdens on the ability to grasp grammar, he says.
In the new study, people who were bilinguals from birth fell short of peak English grammar scores achieved by English-only speakers. That’s consistent with evidence that bilinguals cannot easily turn off one language while speaking another, Birdsong says. Interactions between tongues spoken by one person may slightly depress how much can be learned about both languages, even if bilingual communication still reaches high levels, he suggests.
1. Hartshorne and his colleagues found that____ .| A.one reaches a higher level of fluency at age 10 |
| B.one learns a second language fastest at about age 12 |
| C.one gets a good grasp of English grammar before age 5 |
| D.one’s ability to master grammar declines at around age17 |
| A.social media |
| B.experiments in the lab |
| C.literature review |
| D.face-to-face interviews |
| A.language skill develops along a single timeline |
| B.online volunteers do not cover a wide enough range |
| C.different grammar items may be acquired at different paces |
| D.the quiz in the new study does not include enough questions |
| A.They can achieve a perfect grammar score. |
| B.Grammar learning is the biggest burden for them. |
| C.They are able to make a swift shift between languages. |
| D.Speaking two languages affects their language acquisition. |
9 . Learning a second language is tricky at any age and it only gets tougher the longer you wait to open that dusty French book. Now, in a new study, scientists have pinpointed the exact age at which your chances of reaching fluency in a second language seem to plummet: 10.
The study, published in the journal Cognition, found that it’s “nearly impossible” for language learners to reach native-level fluency if they start learning a second tongue after 10. But that doesn’t seem to be because language skills go downhill. “It turns out you’re still learning fast. It’s just that you run out of time, because your ability to learn starts dropping at around 17 or 18 years old,” says study co-author Joshua Hartshorne, an assistant professor of psychology at Boston College.
Kids may be better than adults at learning new languages for many reasons. Children’s brains are more plastic than those of adults, meaning they’re better able to adapt and respond to new information. “All learning involves the brain changing,” Hartshorne says, “and children’s brains seem to be a lot more skilled at changing.”
Kids may also be more willing to try new things (and to potentially look foolish in the process) than adults are. Their comparatively new grasp on their native tongue may also be advantageous. Unlike adults, who tend to default (默认) to the rules and patterns of their first language, kids may be able to approach a new one with a blank slate (石板).
These findings may seem discouraging, but it was heartening for scientists to learn that the critical period for fluent language acquisition might be longer than they previously thought. Some scientists believed that the brief window closes shortly after birth, while others stretched it only to early adolescence. Compared to those estimates, 17 or 18 — when language learning ability starts to drop off — seems relatively old.
“People fared better when they learned by immersion (沉浸), rather than simply in a classroom. And moving to a place where your desired language is spoken is the best way to learn as an adult. If that’s not an option, you can mimic an immersive environment by finding ways to have conversations with native speakers in their own communities,” Hartshorne says. By doing so, it’s possible to become conversationally proficient — even without the advantage of a child’s brain.
1. The underlined word “plummet” in Paragraph 1 is closest in meaning to “__________”.| A.decrease | B.rise |
| C.end | D.vary |
| A.Children are too young to grasp a second language. |
| B.Age 10-18 is the best time to learn a second language. |
| C.Adults go beyond the critical period for learning a second language. |
| D.Communicating with native speakers enables you to master all the language skills. |
| A.Adults are less influenced by their mother tongues. |
| B.Adults spend more time responding to new information. |
| C.Adults are only too willing to experience something awkward in the process. |
| D.Adults prefer an immersive environment to a classroom in learning a second language. |
| A.the best age to learn a second language |
| B.the approaches to learning a second language |
| C.why kids learn a second language more easily than adults |
| D.whether adults can learn a second language like their younger selves |
假如你是李华,你的英国朋友Peter来信向你咨询如何才能学好中文。请你根据以下提示给他回信。
1. take a Chinese course
2. learn and sing Chinese songs
...
注意:1.词数不少于60。
2.信的开头和结尾已经给出,不计入总词数。
Dear Peter,
I' m glad to receive your letter asking for my advice on how to learn Chinese well.
_________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Looking forward to hearing from you soon!
Yours,
Li Hua



